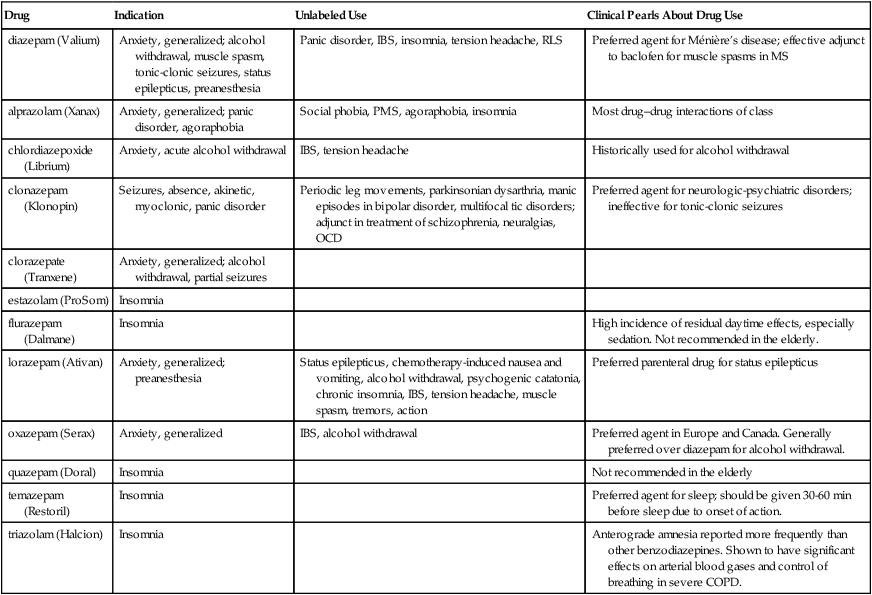
Chapter 48 See Chapter 15 for discussion of diphenhydramine (Benadryl), which commonly is used off-label for sleep, particularly in geriatric patients. ∗GABA-BZ receptor agonists: nonbenzodiazepine benzodiazepine-receptor agonists. In the primary care setting, anxiety often is a symptom of an underlying disorder, such as a medical or a psychologic problem (Box 48-1). The practitioner must obtain a comprehensive history and perform a complete physical examination of the patient to assess the possible causes and effects of the anxiety. Symptoms of anxiety vary with the subtype of anxiety experienced. The physical symptoms of anxiety are listed in Box 48-2. Elements of the history that are particularly important in evaluating anxiety include the following: • Somatic complaints that defy remedy (e.g., stomach pains, dyspnea) • Complaints of a lump in the throat • Inability to fall asleep at night—racing thoughts or worries • These symptoms may be somewhat different in children and may vary, depending on their age and other experiences with anxiety. • Five major subtypes of anxiety have been identified: generalized anxiety disorder, panic disorder, phobias, obsessive-compulsive disorder, and posttraumatic stress disorder. 1. Agoraphobia is the fear of being in a place or situation that would elicit symptoms of a panic attack and that would cause the patient to have difficulty leaving or that would cause him to be embarrassed. This often occurs in concert with a panic attack. 2. Social phobia is a fear of social situations such as public speaking. 3. Specific phobia is a fear of specific objects or situations, which may include animals, insects, heights, water, needles, and so forth.
Antianxiety and Antiinsomnia Agents
Class
Subclass
Generic Name
Trade Name
Antianxiety and antiinsomnia agents
Benzodiazepines
diazepam ![]()
Valium
alprazolam
Xanax
chlordiazepoxide
Librium
clonazepam
Klonopin
clorazepate
Tranxene
estazolam
ProSom
flurazepam
Dalmane
lorazepam
Ativan
oxazepam
Serax
quazepam
Doral
temazepam
Restoril
triazolam
Halcion
Antianxiety agents
buspirone
BuSpar
Antiinsomnia agents or hypnotics
GABA-BZ receptor agonists∗
zolpidem ![]()
Ambien
Edluar
Zolpimist
eszopiclone
Lunesta ![]()
chloral hydrate
Chloral hydrate
zaleplon
Sonata
Tricyclic antidepressants
doxepin
Silenor
Melatonin receptor agonists
Melatonin
ramelteon
Rozerem
Therapeutic Overview
Anatomy and Physiology
Disease Process
Anxiety
Phobic Disorders
Mechanism of Action
Benzodiazepines
< div class='tao-gold-member'>
![]()
Stay updated, free articles. Join our Telegram channel

Full access? Get Clinical Tree