Angiolymphoid Hyperplasia with Eosinophilia
Lester D. R. Thompson, MD
Key Facts
Terminology
Benign vascular tumor with well-formed, immature blood vessels associated with prominent inflammatory component, rich in eosinophils
Clinical Issues
Head most commonly affected; nodule in dermal/subcutaneous tissues
Nodules may be multiple, ultimately coalescing
Microscopic Pathology
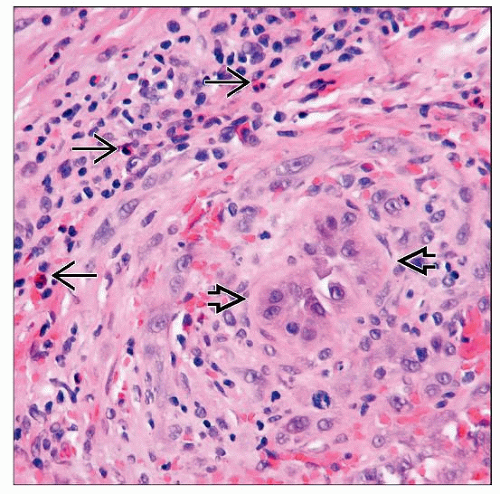
Multiple lobules composed of inflammatory cells within rich vascularity
Proliferation of small immature capillary-type vessels, lined by enlarged endothelial cells
Endothelial cells are epithelioid or histiocytic with cytoplasmic vacuolization
Top Differential Diagnoses
Kimura disease, papillary endothelial hyperplasia
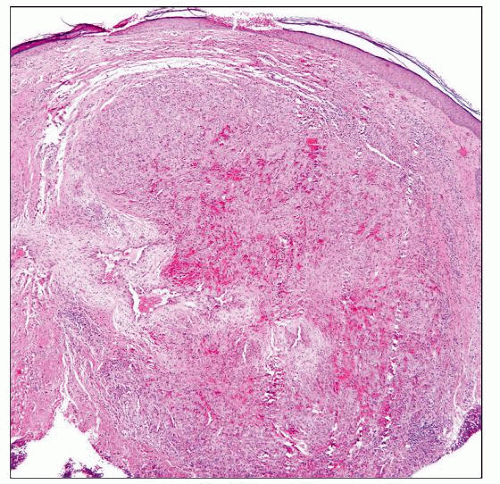 Histology at scanning magnification shows an intact surface epithelium with a richly vascularized stroma containing inflammatory cells. |
TERMINOLOGY
Abbreviations
Angiolymphoid hyperplasia with eosinophilia (ALHE)
Synonyms
Epithelioid hemangioma
Nodular, angioblastic hyperplasia with eosinophilia and lymphofolliculosis
Definitions
Benign vascular tumor with well-formed, immature blood vessels, most of which are lined by plump, epithelioid (histiocytoid) endothelial cells
Most cases have prominent inflammatory component in which eosinophils are conspicuous feature
ETIOLOGY/PATHOGENESIS
Stay updated, free articles. Join our Telegram channel

Full access? Get Clinical Tree