QUESTION 42.5
A. Carbonic anhydrase IX
B. CD10
C. CK7
D. EMA
E. Pax2
6. A 50-year-old man undergoes resection of a renal neoplasm, which grossly appears as a well-circumscribed, multilocular cystic mass. Microscopically, the tumor is composed of thin-walled cysts lined by one or several layers of clear cells, as shown in this picture. In which of the following features does this variant differ from the clear cell (conventional) RCC?
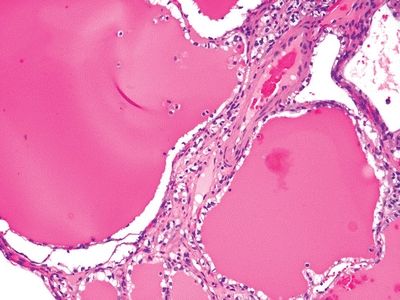
QUESTION 42.6
A. Cytologic characteristics
B. Immunoreactivity for CAIX
C. Indolent growth and lack of invasion
D. Underlying genetic alterations
E. None of the above
7. A partially cystic, encapsulated renal neoplasm displays the histologic appearance shown in this picture. Neoplastic cells are immunoreactive for CAIX in a “cup-like” fashion, where the luminal border is not stained. The tumor is also positive for CK7 and PAX2, but negative for CD10. Cytogenetic and molecular studies show no 3p losses, VHL gene mutations, or promoter hypermethylations, nor trisomy of chromosomes 7/17. Which of the following is this type of renal tumor?
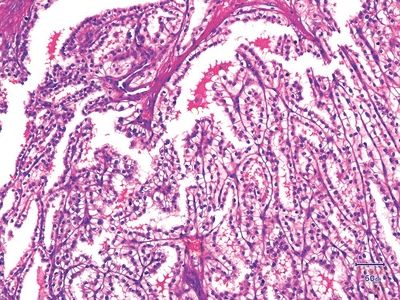
QUESTION 42.7
A. Clear cell (conventional) RCC
B. Clear cell papillary RCC
C. Cystic nephroma/mixed epithelial stromal tumor
D. Multilocular cystic RCC
E. Papillary RCC
8. The microscopic features of a 5-cm cortical renal tumor are shown in the picture. Tumor cells express Pax2, CD10, CK7, and AMACR, but not CAIX or CD117. Cytogenetic studies reveal various chromosomal abnormalities, including trisomies 7 and 17, and loss of chromosome Y. Which of the following histologic features can be found in this tumor?
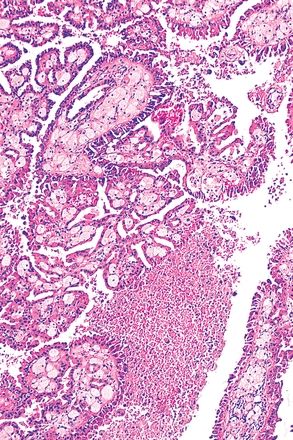
QUESTION 42.8
A. Foamy macrophages in fibrovascular stalks
B. Geographic necrosis
C. Hemosiderin within tumor cells
D. Psammoma bodies in fibrovascular stalks
E. All of the above
9. A 51-year-old woman undergoes resection of a well-circumscribed 8-cm renal tumor. On gross examination, the tumor has tan brown cut surfaces, and microscopically, it has the features shown in this picture. This type of renal cell tumor arises from:
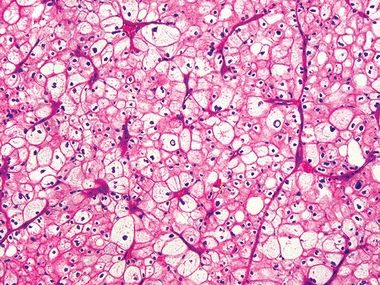
QUESTION 42.9
A. Cells from the distal convoluted tubule
B. Cells of the proximal convoluted tubule
C. Collecting ducts of the renal medulla
D. Intercalated cells of the renal cortex
E. Urothelial cells of the pelvis
10. On gross examination, a renal tumor displays the features shown in this picture. Which of the following microscopic features will be most likely associated with such gross appearance?
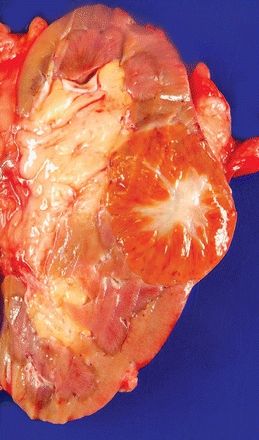
QUESTION 42.10
A. Neoplastic ducts and tubules in a desmoplastic stroma
B. Nests and tubules of malignant cells with prominent nucleoli
C. Oncocytic cells with eosinophilic cytoplasm and round nuclei
D. Papillary architecture lined by hemosiderin-laden epithelial cells
E. Solid sheets of cells with sharp borders and perinuclear clearing
11. This photomicrograph shows the morphology of a type of RCC typically located in the renal medulla. This tumor may have light microscopic features and immunohistochemical profile indistinguishable from:
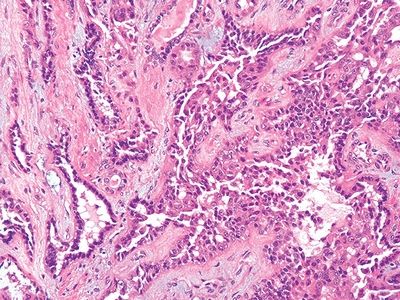
QUESTION 42.11
A. Clear cell RCC
B. Mixed epithelial and stromal tumor
C. Papillary RCC
D. Renal medullary carcinoma
E. Urothelial carcinoma
12. A 20-year-old African American male with sickle cell trait undergoes removal of a renal tumor, whose histologic appearance is shown here. This tumor is most likely to be:
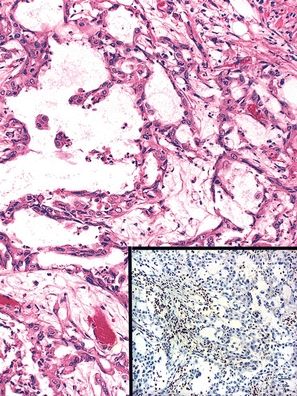
QUESTION 42.12
A. Chromophobe cell carcinoma
B. Clear cell (classic) renal cell carcinoma
C. Collecting duct carcinoma
D. Medullary carcinoma
E. Oncocytoma
13. This photomicrograph taken under partially polarized light shows scattered deposits of oxalate crystals in this type of RCC. Which type is it?
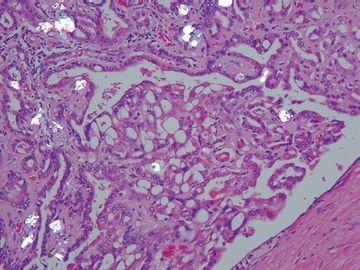
QUESTION 42.13
A. Acquired cystic disease of kidney-associated RCC
B. Clear cell (conventional) RCC
C. Clear cell papillary RCC
D. Mucinous tubular and spindle cell carcinoma
E. Papillary RCC
14. The renal neoplasms known as mixed epithelial and stromal tumors affect preferentially:
A. African American men with sickle cell disease
B. Patients with end-stage renal disease
Stay updated, free articles. Join our Telegram channel

Full access? Get Clinical Tree


