QUESTION 14.1
A. Adrenoleukodystrophy
B. Beckwith-Wiedemann syndrome
C. Carney complex
D. MEN2
E. von Hippel-Lindau disease
2. The most frequent form of congenital adrenal hyperplasia is due to deficient activity of:
A. 21-Hydroxylase
B. 11-Beta-hydroxylase
C. 3-Beta-hydroxysteroid dehydrogenase
D. 17-Alpha-hydroxylase
E. Steroid acute regulatory (STAR) gene product
3. Which of the following is the most common cause of adrenal hypofunction in the United States?
A. Amyloidosis
B. Autoimmune adrenalitis
C. Bilateral metastases
D. Hemorrhage
E. Tuberculosis
4. Primary pigmented nodular adrenocortical disease (PPNAD) is a form of adrenocortical hyperplasia that is often associated with:
A. Adrenoleukodystrophy
B. Beckwith-Wiedemann syndrome
C. Carney complex
D. MEN2
E. von Hippel-Lindau disease
5. Surgical excision of an adrenal gland is performed because of a 2-cm well-demarcated tumor. This tumor has a homogeneous, tan-yellow cut surface without hemorrhage or necrosis. Histologically, it is composed of cells with vacuolated cytoplasm in a trabecular arrangement. Large bizarre nuclei are scattered throughout the tumor, but mitotic figures are not appreciated. There is neither vascular nor capsular invasion. The cells are immunoreactive for low molecular weight keratin and vimentin, but not epithelial membrane antigen (EMA). Which of the following is the most likely diagnosis?
A. Adrenal cytomegaly
B. Adrenocortical adenoma
C. Adrenocortical carcinoma
D. Metastatic renal cell carcinoma
E. Pheochromocytoma
6. A patient suffering from hypertension undergoes surgical excision of an adrenal tumor. Histologic examination reveals intracytoplasmic eosinophilic inclusions such as the ones seen in this picture. On closer examination, these bodies consist of concentric laminations. The presence of such inclusions indicates:
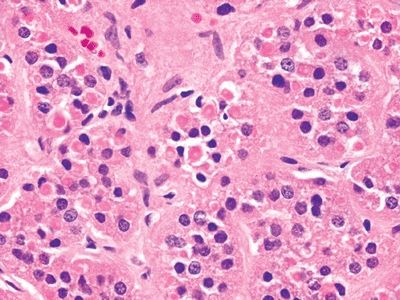
QUESTION 14.6
A. Aggressive behavior of tumor
B. Hyperproduction of androgens
C. Hyperproduction of cortisol
D. Nonfunctioning adenoma
E. Prior treatment with spironolactone
7. Which of the following features is characteristic of adrenocortical carcinoma?
A. Approximately 80% of tumors produce hormones.
B. Homogeneous cut surface without necrosis or hemorrhage.
C. Paucity of mitotic figures or atypical mitoses.
D. Presence of glandular formations.
E. Small size (<100 g) at clinical presentation.
8. A large suprarenal mass is removed from a 56-year-old woman. Its histologic appearance is shown in this picture. The tumor displays diffuse immunoreactivity for vimentin, inhibin, calretinin, melan-A, and D2-40. It is negative for S100, EMA, AFP, synaptophysin, chromogranin, and pankeratin. Which of the following is the most likely diagnosis?
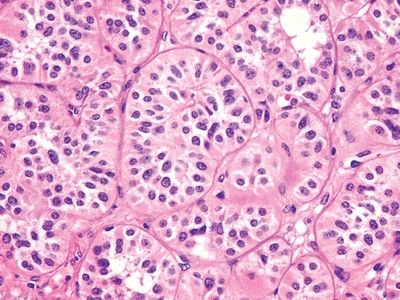
QUESTION 14.8
A. Adrenocortical carcinoma
B. Hepatocellular carcinoma
C. Liposarcoma
D. Metastatic adenocarcinoma
E. Pheochromocytoma
F. Renal cell carcinoma
9. A surgically resected adrenal gland has a circumscribed, but nonencapsulated, tumor measuring 5 cm in greatest dimension. The cut surface is yellow with areas of brown color. The tumor has the microscopic features shown in this picture. Which of the following is the most likely diagnosis?
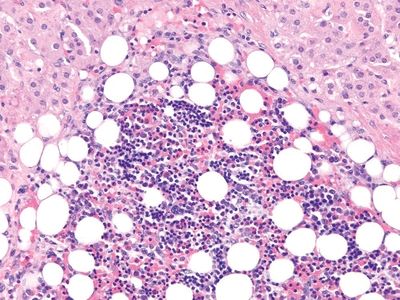
QUESTION 14.9
A. Adrenoleukodystrophy
Stay updated, free articles. Join our Telegram channel

Full access? Get Clinical Tree


