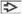Yolk Sac Tumor, Vagina
C. Blake Gilks, MD, FRCPC
Esther Oliva, MD
Key Facts
Clinical Issues
Children < 3 years
Painless vaginal mass, may prolapse through introitus
Combination chemotherapy associated with > 95% cure rate
Microscopic Pathology
Admixture of patterns (reticular, solid, papillary, and polyvesicular-vitelline most common)
Schiller-Duval bodies rare, pathognomonic if present
Primitive nuclei, prominent amphophilic nucleoli
Intracytoplasmic hyaline bodies may be present
Ancillary Tests
Serum α-fetoprotein levels markedly elevated
α-fetoprotein, Glypican-3, and SALL4 positive
Top Differential Diagnoses
Clear cell carcinoma
Embryonal rhabdomyosarcoma, botryoides type
 Yolk sac tumor of the vagina shows internastomosing spaces with reticular and microcystic patterns lined by flattened to cuboidal cells and containing only minimal amount of loose stroma. |
TERMINOLOGY
Abbreviations
Yolk sac tumor (YST)
Synonyms
Endodermal sinus tumor (EST)
Definitions
Primitive germ cell tumor showing differentiation along lines of endodermal sinus or yolk sac