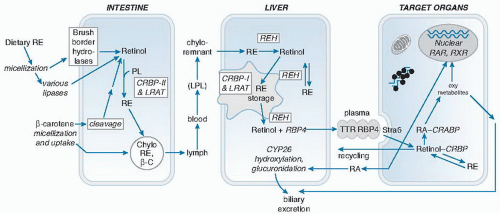
or provitamin A, namely, β-carotene and certain other carotenoids. The vitamin A molecule contains a β-ionone ring, a conjugated polyene side chain, and a terminal functional group. The parent molecule, all-trans-retinol (Fig. 17.1A), can be esterified with long-chain fatty acids to form retinyl esters (RE). Much of the world’s vitamin A is now produced commercially and is used in the production of animal feeds, nutritional supplements, and food fortification. The major synthetic forms of vitamin A are retinyl palmitate, which is identical to the major RE in most animal tissues, and retinyl acetate used in supplements.
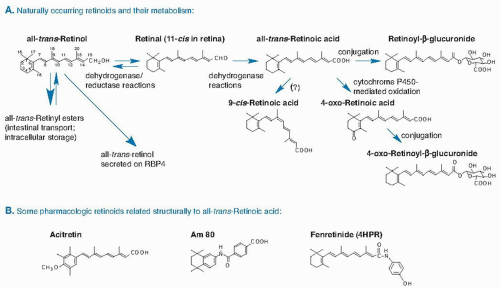 Fig. 17.1. A. Structures and metabolism of major naturally occurring retinoids. B. Pharmacologic retinoids structurally related to all-trans-retinoic acid. RBP, retinol-binding protein. |
carotenoids that are produced exclusively by plants, fungi, and bacteria. The highest concentrations of preformed vitamin A are found in liver and fish liver oils and other organ meats; lower levels are present in milk and eggs. Foods fortified with RE or β-carotene such as milk, margarine, and breakfast cereals are also significant sources (16). In the United States, approximately two thirds of vitamin A intake is preformed, partly from nutritional supplements. In the developing world, vitamin A is consumed mainly as provitamin A carotenoids (see the chapter on carotenoids for food sources, metabolism, and formation of vitamin A from β-carotene).
TABLE 17.1 DIETARY REFERENCE INTAKE VALUES FOR VITAMIN A BY LIFE STAGE GROUP | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
increased risk (16, 18). The critical indicators used to specify the UL were birth defects in women of reproductive age and liver abnormalities for all other age-sex groups. The UL is specified as 3000 µg of retinol/day for both women and men, and 600, 900, 1700, and 2800 µg retinol/day for the age ranges 0 to 3, 4 to 8, 9 to 13, and 14 to 18 years, respectively (18).
RBP protein. Adipose-derived RBP may function as an adipokine and play a role in glucose homeostasis (29), and numerous studies have correlated its levels with various metabolic parameters. Whether it is a causative factor or a correlative biomarker is still unclear, however.
the rationale for the relative dose response (RDR) test, described later, which is used clinically.
Stay updated, free articles. Join our Telegram channel

Full access? Get Clinical Tree