Palmoplantar warts show especially prominent keratohyaline inclusions
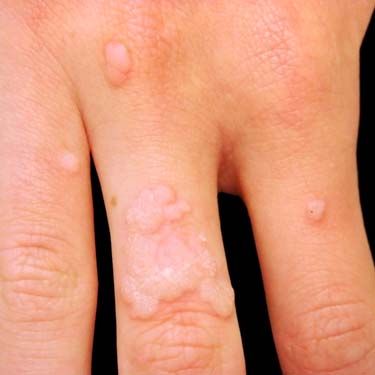
Clinical photograph shows multiple verrucae on the dorsal hand and fingers. (Courtesy J. Wu, MD.)
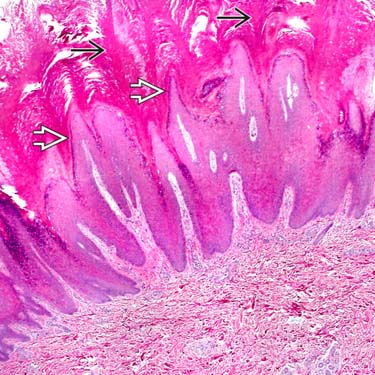
This verruca vulgaris (VV) shows dense hyperkeratosis
 , parakeratosis, acanthosis, and marked papillomatosis
, parakeratosis, acanthosis, and marked papillomatosis  . Most lesions show few or no dermal changes.
. Most lesions show few or no dermal changes.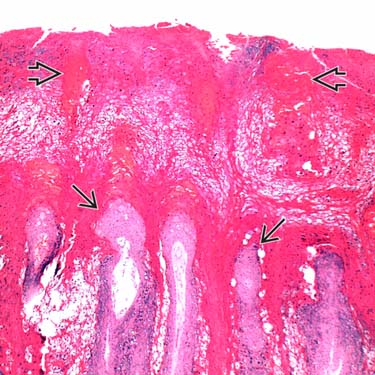
Scanning magnification of a palmoplantar wart (myrmecia) shows prominent papillomatosis
 with thick overlying hyperkeratosis and parakeratosis with areas of hemorrhage
with thick overlying hyperkeratosis and parakeratosis with areas of hemorrhage  .
.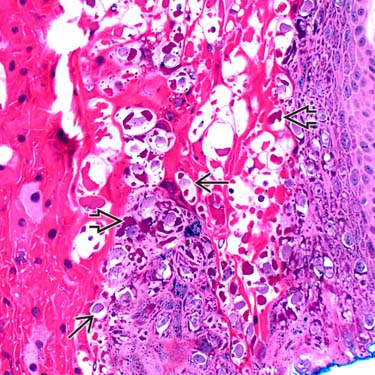
Palmoplantar warts (myrmecia) often show especially prominent koilocytes with perinuclear halos
 and large, dense keratohyaline inclusions
and large, dense keratohyaline inclusions  .
.MICROSCOPIC
Histologic Features
• Exophytic and endophytic papillomatous epidermal proliferation
 Epidermal acanthosis with hypergranulosis, dense overlying hyperkeratosis, and tiers of parakeratosis (church spires)
Epidermal acanthosis with hypergranulosis, dense overlying hyperkeratosis, and tiers of parakeratosis (church spires)




 Epidermal acanthosis with hypergranulosis, dense overlying hyperkeratosis, and tiers of parakeratosis (church spires)
Epidermal acanthosis with hypergranulosis, dense overlying hyperkeratosis, and tiers of parakeratosis (church spires)Stay updated, free articles. Join our Telegram channel

Full access? Get Clinical Tree










