Venoocclusive Disease
Sanjay Kakar, MD
Key Facts
Etiology/Pathogenesis
Stem cell transplantation and high-dose chemotherapy
Sinusoidal endothelial cell injury is important initial event
Clinical Issues
Hyperbilirubinemia, weight gain, and painful hepatomegaly
Attenuated or reverse flow in portal vein on Doppler ultrasound
Microscopic Pathology
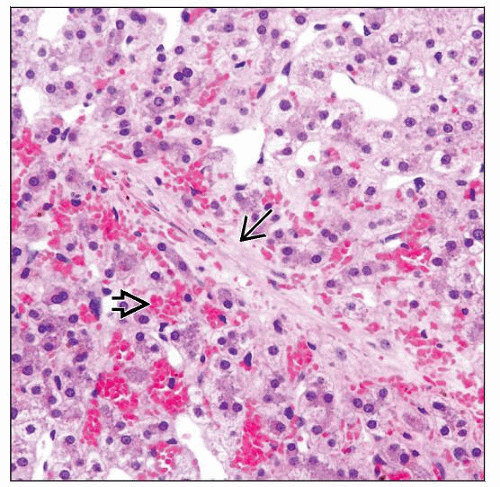
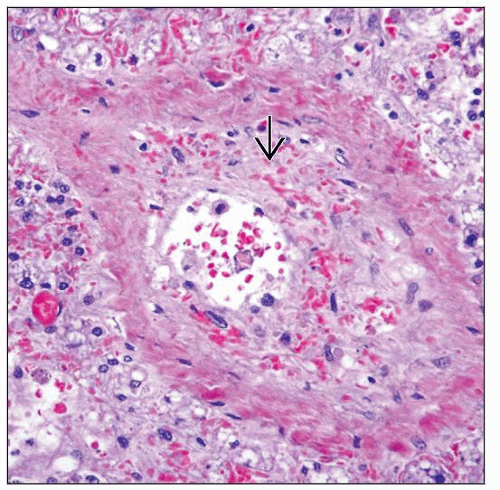
Subendothelial edema, red cell extravasation, fibrin deposition in sinusoids and central vein
Zone 3 sinusoidal dilatation and hepatocellular necrosis
Venular obliteration and widespread fibrosis
TERMINOLOGY
Abbreviations
Venoocclusive disease (VOD)
Synonyms
Sinusoidal obstruction syndrome (SOS)
ETIOLOGY/PATHOGENESIS
Etiology
Stem cell transplantation and high-dose chemotherapy are most common causes
Risk Factors
Age < 6 years and poor performance status
Human leukocyte antigen (HLA) disparity in allogeneic stem cell transplant
Preexisting liver dysfunction
Prior abdominal radiation
Pretransplant use of acyclovir or vancomycin
High-dose busulphan and cyclophosphamide therapy
Stay updated, free articles. Join our Telegram channel

Full access? Get Clinical Tree