Vaginal Intraepithelial Neoplasia
C. Blake Gilks, MD, FRCPC
Key Facts
Clinical Issues
More common > 40 years (peak: 60-70)
Frequent history of HPV-associated CIN, VIN, or cervical or vulvar squamous cell carcinoma
Microscopic Pathology
Low-grade VaIN: Koilocytic atypia in upper epithelial layers, expanded basal layer with scattered mitoses
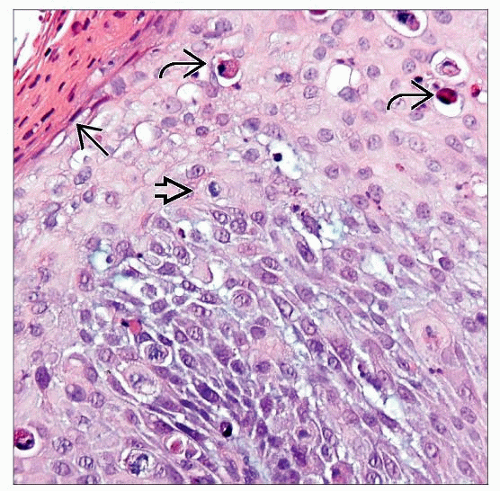
High-grade VaIN: Full-thickness epithelial involvement
Ancillary Tests
p16 weak and focal, Ki-67 basal labeling (low grade)
p16 strong and diffuse nuclear, Ki-67 at all levels (high grade)
Top Differential Diagnoses
Reactive squamous atypia
Atrophy
Transitional cell metaplasia
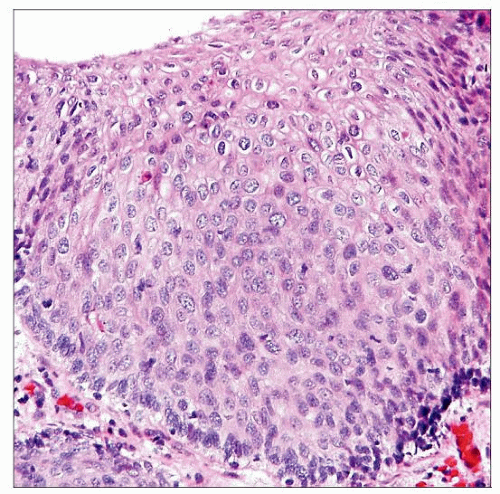 High-grade VaIN shows increased cellularity, loss of maturation, and atypia throughout all epithelial layers. |
TERMINOLOGY
Abbreviations
Vaginal intraepithelial neoplasia (VaIN)
Synonyms
Squamous dysplasia; carcinoma in situ; high-grade squamous intraepithelial lesion (HSIL)/low-grade squamous intraepithelial lesion (LSIL)
Definitions
Low-grade VaIN
No reproducible definition
Koilocytic change/condyloma = low-grade VaIN
High-grade VaIN: Replacement of preexisting squamous epithelium by dysplastic squamous cells in all levels
Stay updated, free articles. Join our Telegram channel

Full access? Get Clinical Tree