19 Uterus and Adnexal Diseases
Anatomy of the Uterus, Adnexa, and Vagina
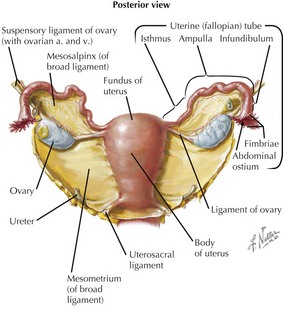
Uterus
• Derived from fusion of paired embryonic paramesonephric (müllerian) ducts: basis for divided, asymmetrical, or bifid (didelphic) uteruses
• Endometrium: highly vascular and glandular uterine lining; thickness or state varies with menstrual cycle
• Myometrium: dense, fibrous connective tissue and smooth muscle, derived from embryonic splanchnic mesoderm
• Mesometrium: peritoneal covering of the uterus, continuous with peritoneum of broad, transverse (cardinal), uterosacral, and suspensory (infundibulopelvic) ligaments
Ovaries
• Lie laterally and posterior to the broad ligament, attached near its upper borders via a peritoneal mesovarium