Urachal Adenocarcinoma
Jesse K. McKenney, MD
Key Facts
Terminology
Primary carcinoma of any morphologic subtype originating from urachus
Clinical Issues
Very rare
Hematuria is most common symptom
Mucusuria rarely seen
Partial or radical cystectomy, usually with umbilectomy, is treatment of choice
Prognosis is variable
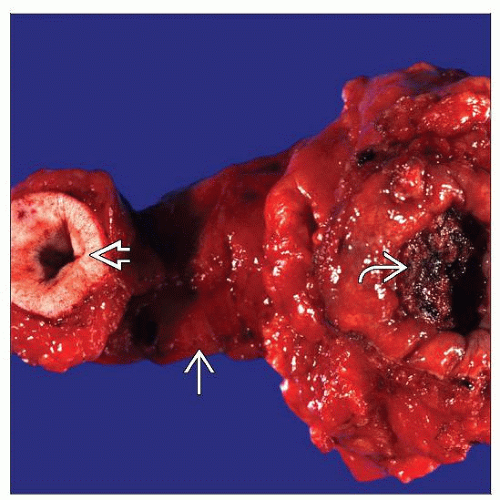
Macroscopic Features
Mucosa is intact in early stages
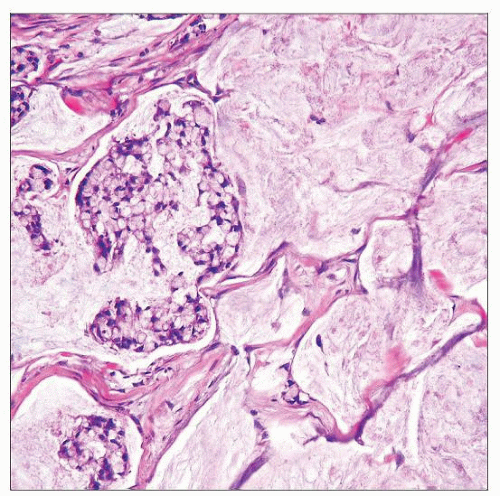
Microscopic Pathology
Malignant epithelial neoplasm of diverse morphology
Enteric
Mucinous
Signet ring cell
Low-grade mucinous neoplasm
Presence of urachal remnants offer important clue of urachal origin
Top Differential Diagnoses
Primary adenocarcinoma of urinary bladder
Colonic adenocarcinoma (or other secondary adenocarcinoma)
Invasive urothelial carcinoma with glandular differentiation
Diagnostic Checklist
Urachal carcinoma is clinicopathologic diagnosis
Recognition of urachal carcinoma is important
Different surgical approach than bladder primary
TERMINOLOGY
Definitions
Primary carcinoma of any morphologic subtype originating from urachus and fulfilling following criteria
Tumor primarily located in dome of bladder
Epicenter of mass is in wall (muscularis propria) of bladder
Absence of surface intestinal metaplasia or precursor lesions
Absence of adenocarcinoma elsewhere
ETIOLOGY/PATHOGENESIS
Developmental Anomaly
Urachal remnants
May undergo malignant transformation
CLINICAL ISSUES
Epidemiology
Incidence
Rare
Age
5th and 6th decades
Gender
More common in men (M:F = 2:1)
Site
Dome of bladder
Anatomic location of urachus
Refining feature of urachal origin
Intramural bladder
Presentation
Hematuria is most common symptom
Irritative bladder symptoms, such as voiding difficulties
Mass lesion
Mucusuria seen rarely
Treatment
Partial or radical cystectomy, usually with umbilectomy, is treatment of choice
Adjuvant therapy depends on stage
Chemotherapy
Radiotherapy
Prognosis
Poor prognosis
Usually diagnosed at advanced stage
5-year survival rate reported from 25-61%
IMAGE FINDINGS
CT Findings
Thickened bladder dome
May extend along urachus to umbilicus
MACROSCOPIC FEATURES
General Features
Mucosa is intact in early stages
Becomes ulcerated as tumor grows endophytically
Mass localized to dome of bladder
MICROSCOPIC PATHOLOGY
Histologic Features
Malignant epithelial neoplasm of diverse morphology
Stay updated, free articles. Join our Telegram channel

Full access? Get Clinical Tree