5
Understanding Insurance Policies
After completing this section, readers should be able to:
 Describe carrier reimbursement systems.
Describe carrier reimbursement systems.
 Describe insurance carrier policy.
Describe insurance carrier policy.
 Understand how to use a relative value study.
Understand how to use a relative value study.
Section 1
Insurance Carriers and Policies
| Term | Definition |
| Actual Charge | The amount charged by the practice when providing services. |
| Adjudicate | A term for processing payment of a claim. |
| Adjudicator | Person who reviews the claim to determine payments. |
| Allowed Charge | The amount set by the carrier for reimbursement of services. |
| Assignment of Benefits | Request that money be paid directly to the physician for services rendered on a given claim. In some instances, accepting assignment may result in adjustments or write-offs. |
| BR | By Report. Based on the codes submitted, the claim may need to have a report sent explaining the charges. |
| Capitation | A form of prepayment in which a provider agrees to furnish services to members of a particular insurance program for a fixed fee. Capitations mostly affect monthly payments to primary care physicians in HMO groups. |
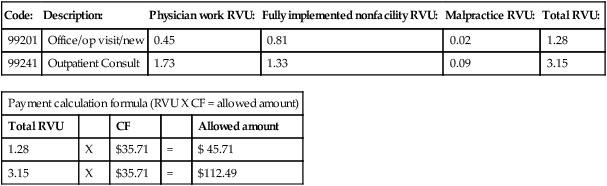
| CF | Conversation Factor. Dollar value multiplier for fee calculation. |
| COB | Coordination of Benefits. A clause that has been written into a health insurance policy stating the primary insurance will take into account benefits payable by a secondary insurance. Prevents overpayment of the charges billed to the patient. |
| Co-payment | The amount the insured has to pay toward the amount allowed by the insurance company for services. |
| CPT | Current Procedural Terminology. Nomenclature published by the American Medical Association as a means to describe services rendered to a patient using numerical codes. |
| Customary Charge | The amount representing the charge most frequently used by a physician in a given period of time. |
| Deductible | The dollar amount that must be paid by the patient before insurance will pay a claim based on coverage plans and benefits. |
| DOS | Date of Service. |
| DRG | Diagnosis-Related Group. Patient classification system to categorize patients who are medically related with respect to diagnosis, treatment, or statistically similar with regard to length of hospital stay. |
| EOB | Explanation of Benefits. Form accompanying an insurance remittance with a breakdown and explanation of payments for a claim; also referred to as a Remittance Advisory (RA). |
| HCPCS | Healthcare Common Procedure Coding System. More commonly referred to as “HCPCS” (sometimes pronounced hick pix). A coding system designed by the CMS to report patient services utilizing codes from CPT and other alphanumeric codes. |
| ICD-9-CM | International Classification of Diseases, 9th edition, Clinical Modification. The source of diagnosis coding required by insurance carriers and government agencies. |
| Indemnity Insurance | Traditional insurance programs referred to as “Fee for Service” programs. |
| PC | Professional Component. Defines services provided by a physician or other health care professional. |
| Percentile | The ranking of fees from all providers in a given area to develop a reimbursement base. |
| POS | Place Service Codes. Codes used on insurance claim forms to specify the location where services were provided. A complete list is found in the introduction section of the Professional Version of the CPT manual. |
| Precertification | A method for preapproving all elective admissions, surgeries, and other services as required by insurance carriers. Approval is essential before receiving payment for services. |
| Prevailing Charge | The charge most frequently used, in a specific area by physicians, based on specialty. The highest charge in the prevailing range establishes the absolute maximum limitation, or the highest amount a carrier will pay for a service. |
| PRO | Professional Review Organization. An organization of physicians that reviews services to determine medical necessity. |
| RBRVS | Resource-Based Relative Value Scale. A system of assigning values to CPT codes developed for Medicare to determine reimbursement amounts for services. |
| Relative Value Unit (RVU) | A method to calculate fees for services. A unit is translated into a dollar value using a conversion factor or dollar multiplier. The assigned value is generally based on three factors: physician work component, overhead practice expense, and malpractice insurance. |
| Remittance Advisory | Statement sent by an insurance company detailing how submitted claims were processed for payment along with payment amounts. |
| RVS | Relative Value Scale. The unit value attached to a code used to determine payment for services. |
| TC | Technical Component. The portion of a test or study that pertains to the use of equipment or technicians. |
| Third-Party Payer | A carrier that has an agreement with an individual or organization to provide heath care benefits. |
| Timely Filing Clause | The amount of time allowed by an insurance company for a claim to be submitted for payment from the date of the service. |
| UCR | Usual, Customary, and Reasonable. The reimbursement method that establishes a maximum fee an insurance company will pay for services. |
| Utilization Review | The process of assessing medical care services to ensure quality, medical necessity, and appropriateness of treatment. |
| Withhold Incentive | The percentage of payment held back for a risk account in the HMO program. Withhold arrangements are used to share potential losses or profits with providers of service. |
Introduction
There are three ways a person may obtain insurance coverage:
 Group Health Plan: A plan arranged by an employer or special interest group for the benefit of members and their eligible dependents. This plan provides maximum benefit packages based on desired coverage and cost factors.
Group Health Plan: A plan arranged by an employer or special interest group for the benefit of members and their eligible dependents. This plan provides maximum benefit packages based on desired coverage and cost factors.
 Individual or Personal Plan: A plan issued to an individual. This type of coverage has a high premium with benefits based on the needs and financial factors of the individual policy holder.
Individual or Personal Plan: A plan issued to an individual. This type of coverage has a high premium with benefits based on the needs and financial factors of the individual policy holder.
 Prepaid Health Care Program: A plan whereby services are rendered by physicians or facilities that elect to participate in a set program for services.
Prepaid Health Care Program: A plan whereby services are rendered by physicians or facilities that elect to participate in a set program for services.
Test Your Knowledge
1. Define the following abbreviations.
UCR: ___________________________ COB: ___________________________
PRO: ___________________________ POS: ___________________________
2. Define the term deductible.
_______________________________________________________________________________________________
3. What is a timely filing clause?
_______________________________________________________________________________________________
4. What are the three factors used to determine a relative unit value of a code?
_______________________________________________________________________________________________
_______________________________________________________________________________________________
Usual, Customary, and Reasonable Payment Plans
Usual Fee: The fee most often charged by a physician for a service or procedure.
Customary Fee: The fee most often charged by other physicians of similar training and experience within a geographic region for the same service or procedure.
Reasonable Fee: The fee the insurance company considers appropriate reimbursement based on the criteria of usual or customary fees.
Test Your Knowledge
Payment Factors
1. What are the three factors that determine a relative value unit for a code?
___________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________
Stay updated, free articles. Join our Telegram channel

Full access? Get Clinical Tree