May also represent later stage/regressing variant of trichofolliculoma, but is typically dermal-based tumor with prominent sebaceous glands
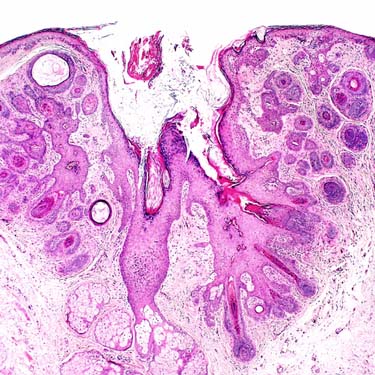
Trichofolliculoma is an invaginated cystic tumor lined by keratinizing squamous epithelium that communicates with the overlying epidermis. The central cystic space is usually filled with keratinous debris.
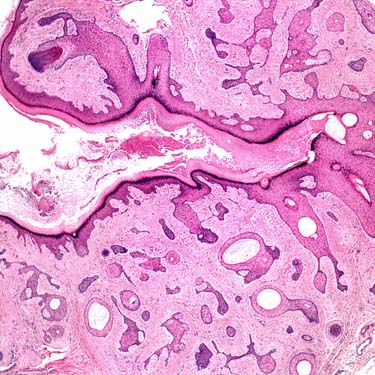
Trichofolliculoma is characterized by an invaginated cystic lesion lined by mature, keratinizing squamous epithelium that communicates with the overlying epidermis.
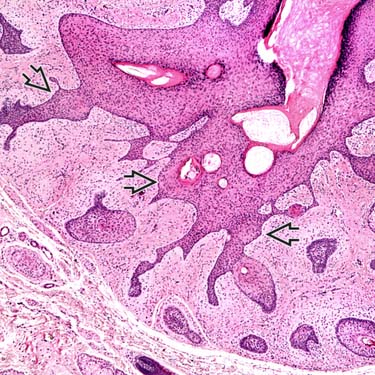
Small, branching follicular structures
 radiate out from, and communicate with, the central cystic space.
radiate out from, and communicate with, the central cystic space.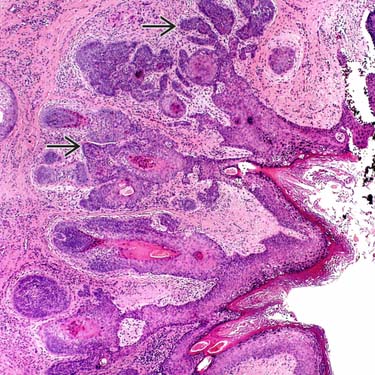
Radiating around the central cystic space are numerous primitive follicles that connect with the central cystic space. The follicles often show secondary branching
 .
.CLINICAL ISSUES
Epidemiology
Treatment
• Surgical approaches




Stay updated, free articles. Join our Telegram channel

Full access? Get Clinical Tree











