Chapter 30 Toxicology and Drugs of Abuse
1. Toxicology is the study of the hazardous effects of chemicals, including drugs, on biologic systems.
2. Toxicity is a reflection of how much, how fast, and how long an individual is exposed to a poison.
• Individuals are fast or slow acetylators of isoniazid (slow acetylator have increased neurotoxicity).
• Increased risk of drug-induced torsades de pointes with mutations in ion channels leading to prolonged QT interval
• Interactions between drugs and between drugs and environmental chemicals may occur by both toxicokinetic and toxicodynamic mechanisms
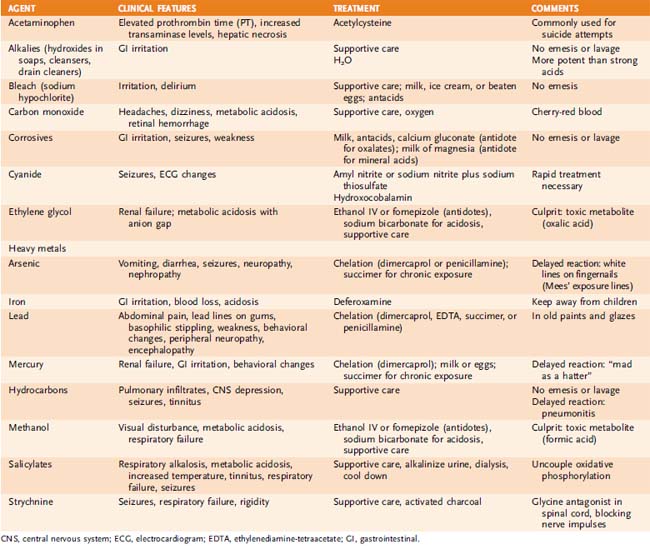
TABLE 30-2 Specific Antidotes for Selected Drugs and Toxins
| Antidote | Poison |
|---|---|
| Drugs That Chelate Metals | |
| Calcium disodium edetate (CA2+,2Na+EDTA) | Lead |
| Deferoxamine | Iron |
| Dimercaprol | Arsenic, gold, mercury, lead |
| Penicillamine | Lead, copper, arsenic, gold |
| Succimer | Lead; also used for chronic exposure to arsenic and mercury |
| Substances That Act Against Specific Drugs or Toxins | |
| Acetylcysteine | Acetaminophen |
| Amyl nitrite/sodium nitrate | Cyanide |
| Atropine | Cholinesterase inhibitor |
| Digoxin-specific FAB antibodies | Cardiac glycosides (e.g., digoxin) |
| Esmolol | Theophylline, caffeine, metaproterenol |
| Ethanol | Methanol or ethylene glycol |
| Flumazenil | Benzodiazepine |
| Fomepizole | Ethylene glycol, methanol |
| Glucagon | Beta blockers |
| Naloxone | Opioids |
| Oxygen | Carbon monoxide |
| Physostigmine | Anticholinergics |
| Pralidoxime (2-PAM) | Organophosphates; contraindicated for carbamates |
| Pyridoxine | Isoniazid |
| Sodium bicarbonate | Cardiac depressants (tricyclic antidepressants, quinidine) |
| Sodium thiosulfate | Cyanide |
FAB, fragment antigen binding.
Stay updated, free articles. Join our Telegram channel

Full access? Get Clinical Tree