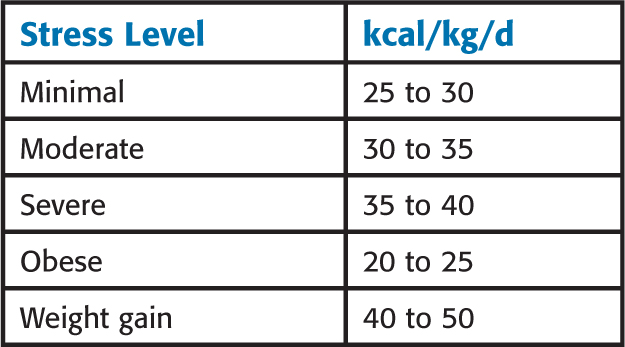
Instead of using the Harris-Benedict equation, the following weight based requirements can be used:
Practice Problems
1. What are the caloric requirements of a 37-year-old male patient who is 6’2”, weighs 205 lb, and is in moderate stress?
Answer
Male, moderate stress
BEE = [66 + 13.8(205 lb/2.2 lb/kg) + 5(74 in)(2.54 cm/in) – 6.8(34)] × 1.4 to 1.6
BEE = 2885 to 3297 kcal/d
2. What are the caloric requirements of a 64-year-old female patient who is 5’3”, weighs 137 lb, and is in severe stress?
Answer
Female, severe stress
BEE = [665 + 9.6(137 lb/2.2 lb/kg) + 1.8(63 in)(2.54 cm/in) – 4.7(64)] × 1.6 to 1.8
BEE = 2000 to 2250 kcal
3. What are the caloric requirements of a 22-year-old male patient who is 5’9”, weighs 80 kg, and is in minimal stress?
Answer
Male, minimal stress
BEE = [66 + 13.8(80 kg) + 5(69 in)(2.54 cm/in) – 6.8(22)] × 1.2 to 1.4
BEE = 2276 to 2655 kcal
4. A patient is admitted after suffering severe burns to the body. What are the caloric requirements of this 16-year-old female patient who is 4’ 10” and weighs 110 lb?
Answer
Female, severe stress
BEE = [665 + 9.6(110 lb/2.2 lb/kg) + 1.8(58 in × 2.54 cm/in) – 4.7(16)] × 1.6 to 1.8
BEE = 2136 to 2403 kcal/d
5. A 76-year-old male patient is admitted for Crohn’s disease and cannot tolerate oral feedings. How many calories must he receive if he is in moderate stress? Ht: 6’0”; wt: 165 lb
Answer
Male, moderate stress
BEE = [66 + 13.8(165 lb/2.2 lb/kg) + 5(72 in × 2.54 cm/in) – 6.8(76)] × 1.4 to 1.6
BEE: 2098 to 2398 kcal/d
6. The stress factor for a burn patient is 1.8. He weighs 180 lb, is 5’10”, and is 33 years old. How many kcal per day should he be receiving?
Answer
Male, severe stress
BEE = [66 + 13.8(180 lb/2.2 lb/kg) + 5(70 in × 2.54 cm/in) – 6.8(33)] × 1.8
BEE = 3347
7. A 55-year-old female patient weighing 144 lb needs TPN. Using the alternative method to determine energy requirements of the moderately stressed patient, what is her daily caloric requirement?
Answer
144 lb moderate stress—from the table is 30 to 35 kcal/kg/d, then
144 lb/2.2 lb/kg × 30 kcal/kg/d = 1964 kcal/d to
144 lb/2.2 lb/kg × 35 kcal/kg/d = 2291 kcal/d
8. E.V. is a 75yo, 5’7”, 73 kg, male patient. He was hospitalized for severe diverticulitis and is being discharged on TPN until his GI tract has more completely recuperated. Using the alternate method, determine his energy requirements for his minimal stress level.
Answer
73 kg minimal stress—from the table: 25 to 30 kcal/kg/d, then
73 kg × 25 kcal/kg/d = 1825 kcal/d to
73 kg × 30 kcal/kg/d = 2190 kcal/d
9. During GI surgery, L.E. suffered a perforated bowel. She is now on IV antibiotics and TPN. She is 82yo and weighs 98 lb. Using the alternate method, determine her energy requirements for her severe stress level.
Answer
98 lb severe stress—from the table: 35 to 40 kcal/kg/d, then
98 lb/2.2 lb/kg × 35 kcal/kg/d = 1558 kcal/d to
98 lb/2.2 lb/kg × 40 kcal/kg/d = 1782 kcal/d
10. Using the alternate method, determine the daily calorie requirements of a 53yo, 315 lb male patient.
Answer
315 lb obese—from the table: 20 to 25 kcal/kg/d, then
315 lb/2.2 lb/kg × 20 kcal/kg/d = 2864 kcal/d
315 lb/2.2 lb/kg × 25 kcal/kg/d = 3580 kcal/d
11. Calculate the caloric content of a TPN solution running at 60 mL/h and containing 750 mL of amino acid 5% and 750 mL of dextrose 25%. The patient will also be receiving 250 mL of 20% fat solution in a 24-hour period. What is the patient’s daily calorie intake from the IV solutions?
< div class='tao-gold-member'>



