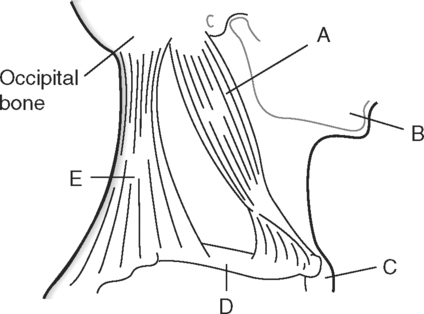
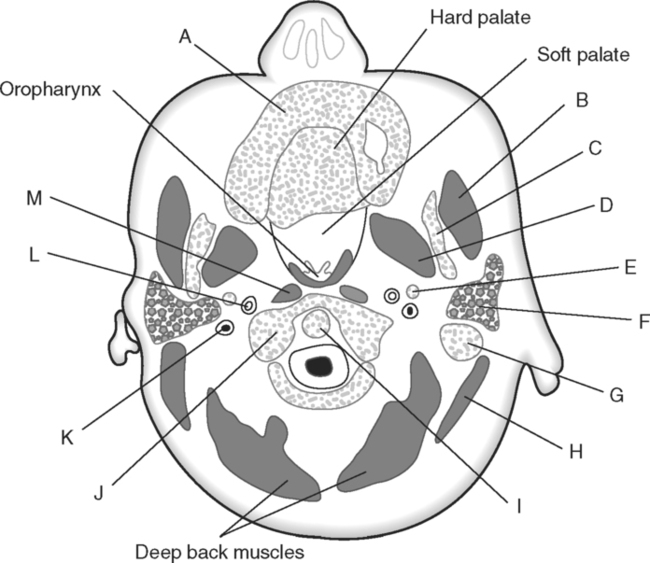
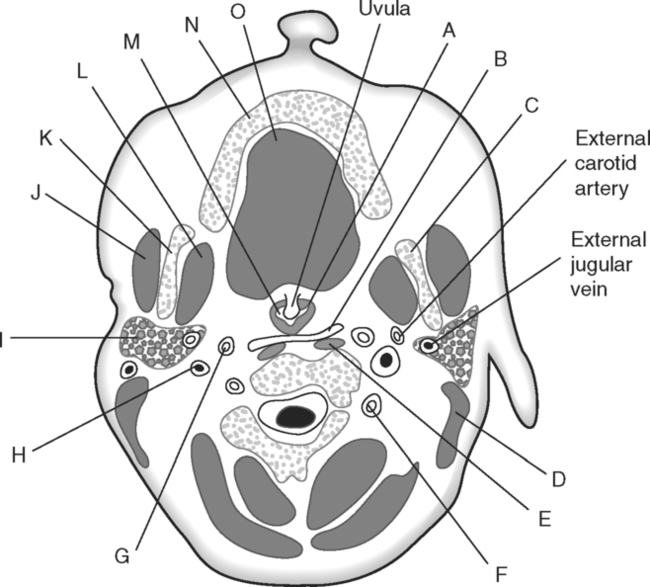
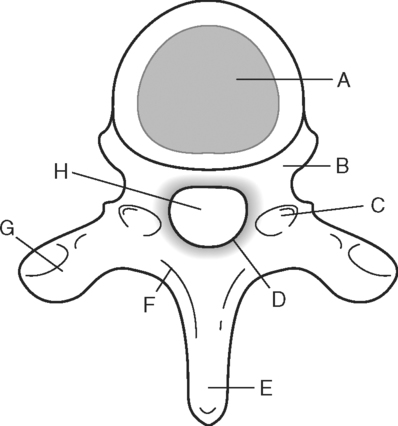
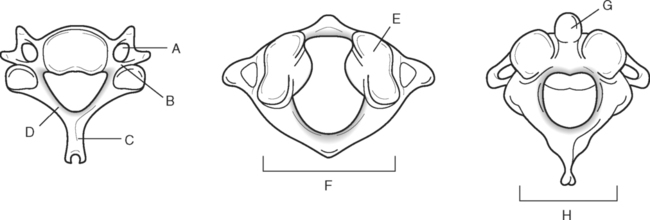
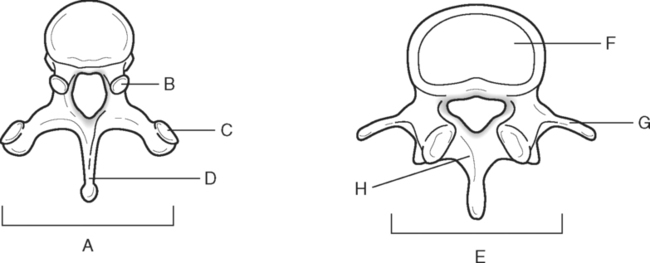
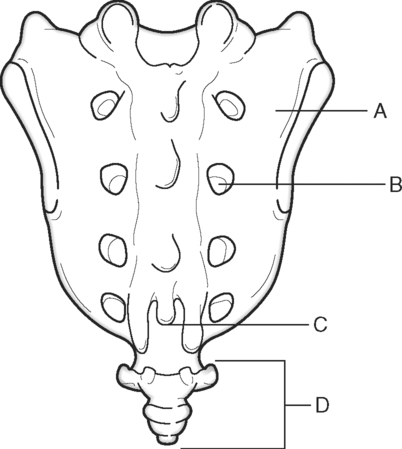
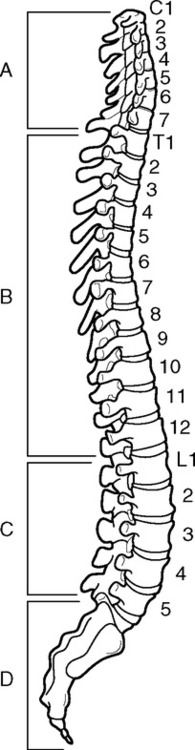
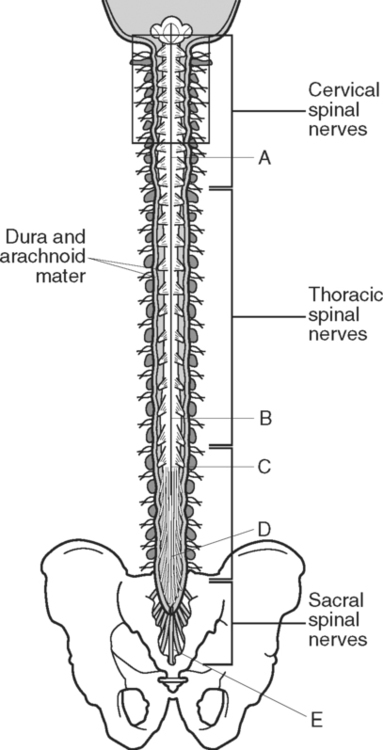
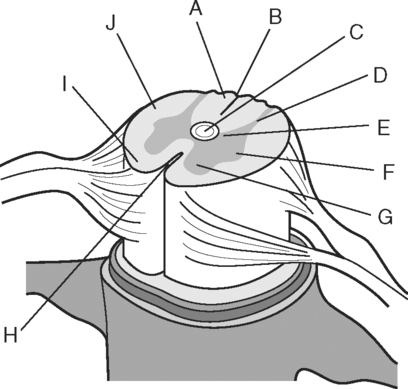
Identify the Features Indicated in Fig. 6-1: 1. What is the concave surface on the upper and lower margins of the pedicles called? 2. Where are the intervertebral foramina located? 3. What articulates with the superior articular process of a vertebra? 4. What three features of a vertebra enclose or surround the vertebral foramen? Identify the Items Indicated in Fig. 6-2: 1. What is unique about the transverse processes of cervical vertebrae? 2. What distinguishes the spinous processes of cervical vertebrae from the spinous processes of other vertebrae? 3. What specific name is given to C1? 4. What specific name is given to C2? Identify the Items Indicated in Fig. 6-3: 1. What distinguishes thoracic vertebrae from other types of vertebrae? 2. Where does the head of a rib articulate on the thoracic vertebrae? 3. Where does the tubercle of a rib articulate on the thoracic vertebrae? Identify the Items Indicated in Fig. 6-4: 1. What passes through the sacral foramina? 2. What fuses to form the lateral mass? 3. What is the most inferior region of the vertebral column? What marking on the sacrum denotes the beginning of the true pelvic cavity? 4. How many sacral vertebrae are there before they fuse together? Identify the Items Indicated in Fig. 6-5: 1. What direction is the curvature that is formed by the cervical vertebrae? 2. What two curvatures are concave anteriorly? 3. What term is used to denote an exaggerated thoracic curvature? 4. What is the purpose of curvatures in the vertebral column? Identify the Items Indicated in Fig. 6-6: 1. At what vertebral level does the spinal cord usually end? 2. What are the two regions of enlargement in the spinal cord? What nerves arise from these two enlarged areas? 3. What term is used for the terminal triangular region of the spinal cord? 4. What is found in the epidural space around the spinal cord? Identify the Items Indicated in Fig. 6-7: 1. What makes up the white matter of the spinal cord? 2. What makes up the gray matter of the spinal cord? 3. What type of fiber is found in the dorsal root of a spinal nerve? 4. What type of fiber is found in the ventral root of a spinal nerve? Identify the Structures Indicated in Fig. 6-8: 1. What muscle separates the anterior triangle from the posterior triangle of the neck? 2. In which triangle is the carotid sheath located? 3. What are the contents of the carotid sheath? 4. What three structures form the boundaries of the posterior triangle of the neck? 5. Name one vein and two nerves that are located in the posterior triangle of the neck. Identify the Structures Indicated in Fig. 6-9: 1. What tiny piece of bone is anterior to the internal jugular vein and lateral to the internal carotid artery? 2. What bone forms the anterior portion of the hard palate? 3. What is the space or opening at the posterior margin of the soft palate? 4. What is the round piece of bone immediately anterior to the spinal cord? 5. What muscles form the wall of the pharynx? 6. Which is normally most lateral or superficial, the internal jugular vein, the internal carotid artery, or the parotid gland? In Fig. 6-10 Color or Outline: Identify the Structures Indicated in Fig. 6-10: 1. Which is usually more lateral or superficial, the external jugular vein or the external carotid artery? 2. What is the extension of the soft palate that projects into the oropharynx? 3. Which is usually most posterior, the vertebral artery, the internal carotid artery, or the internal jugular vein?
The Vertebral Column, Spinal Cord, and Neck
![]()
Stay updated, free articles. Join our Telegram channel

Full access? Get Clinical Tree


Basicmedical Key
Fastest Basicmedical Insight Engine