Chapter 19 The Skin
1 What are the three main layers of the skin?
 Dermis, composed of connective tissue (Its upper part extending between the rete ridges of the epidermis is called papillary dermis, whereas the lower part is called reticular dermis. In some portions of the body, the dermis also contains hair follicles and sweat and sebaceous glands. Dermis contains blood vessels and nerves.)
Dermis, composed of connective tissue (Its upper part extending between the rete ridges of the epidermis is called papillary dermis, whereas the lower part is called reticular dermis. In some portions of the body, the dermis also contains hair follicles and sweat and sebaceous glands. Dermis contains blood vessels and nerves.)3 How are skin lesions classified?
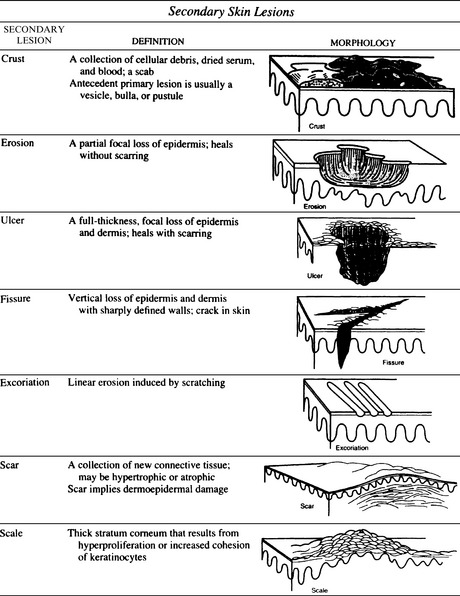
In clinical practice, it is customary to classify skin lesions as primary or secondary. Primary skin lesions include macules, papules, patches, plaques, nodules, cysts, wheals, vesicles, bullae, and pustules. Secondary skin lesions are related to the progression of the disease but may also be caused by scratching, trauma, or treatment. This group of lesions includes crusts, erosions, ulcers, fissures, excoriations, scars, and scales (Figs. 19-1 and 19-2).
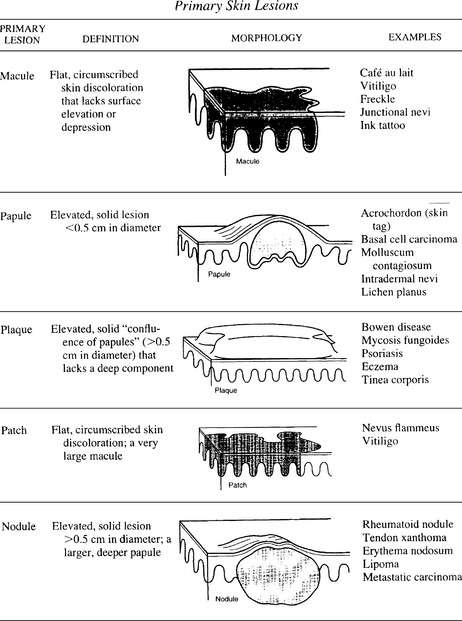
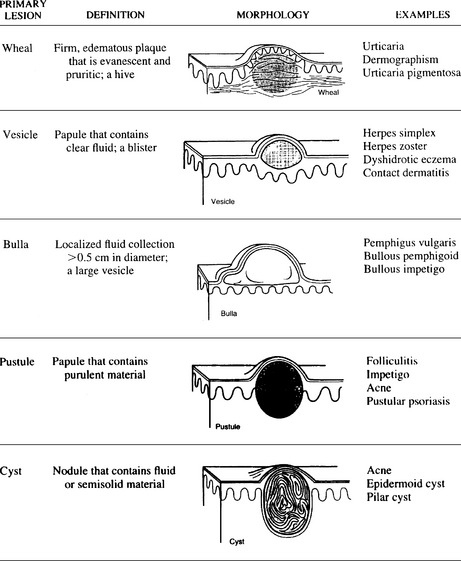
Figure 19-1 Primary skin lesions.
(From Fitzpatrick JE, Aeling JL: Dermatology Secrets. Philadelphia, Hanley & Belfus, 1996, pp. 9–10.)
5 What is the difference between a papule and a nodule?
Papules are small, slightly elevated solid skin lesions measuring less than 0.5 cm. In practice, this means they can be covered with the flat end of a pencil. Nodules are deeper seated and larger, measuring more than 0.5 cm in diameter. Most skin tumors present as nodules, but obviously some can be diagnosed early in their development while they are still smaller than 0.5 cm. (Continued on p. 390)
CLASSIFICATION OF SKIN DISEASES
13 How are skin diseases classified etiologically?
Skin diseases can be classified according to their causation into several categories:
 Diseases caused by chemical or physical irritants (e.g., burns, frostbite, ulcers caused by exposure to caustic materials, and dust-induced eczema)
Diseases caused by chemical or physical irritants (e.g., burns, frostbite, ulcers caused by exposure to caustic materials, and dust-induced eczema) Infectious diseases (e.g., viral exanthemas of childhood, such as rubella or varicella, and impetigo caused by pus-forming cocci)
Infectious diseases (e.g., viral exanthemas of childhood, such as rubella or varicella, and impetigo caused by pus-forming cocci) Idiopathic diseases (e.g., psoriasis and epidermolysis bullosa; many chronic skin diseases are poorly understood and fall into this category. Some of these diseases have a hereditary component and have a tendency to occur in families.)
Idiopathic diseases (e.g., psoriasis and epidermolysis bullosa; many chronic skin diseases are poorly understood and fall into this category. Some of these diseases have a hereditary component and have a tendency to occur in families.)15 How are skin diseases classified according to their distribution?
16 How are skin diseases classified microscopically?
 Diseases of the dermal–epidermal interface (e.g., epidermolysis bullosa, bullous pemphigoid, erythema multiforme, and lupus erythematosus)
Diseases of the dermal–epidermal interface (e.g., epidermolysis bullosa, bullous pemphigoid, erythema multiforme, and lupus erythematosus) Diseases of the superficial and deep vascular bed (e.g., urticaria, cutaneous vasculitis, and contact dermatitis)
Diseases of the superficial and deep vascular bed (e.g., urticaria, cutaneous vasculitis, and contact dermatitis) Inflammatory disorders of the panniculus adiposus (e.g., erythema nodosum, erythema induratum, and arthropod infestations)
Inflammatory disorders of the panniculus adiposus (e.g., erythema nodosum, erythema induratum, and arthropod infestations)INFECTIOUS DISEASES
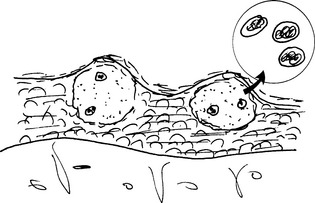
19 Which skin diseases are caused by herpes viruses?
Herpes viruses (HSVs; Fig. 19-3) cause several skin diseases:
 HSV-1 is the cause of herpetic vesicles on the lips (herpes labialis), also known as cold sores. Histologically, the vesicles contain fluid and detached epithelial cells containing intranuclear viral inclusions.
HSV-1 is the cause of herpetic vesicles on the lips (herpes labialis), also known as cold sores. Histologically, the vesicles contain fluid and detached epithelial cells containing intranuclear viral inclusions. Varicella-zoster virus is the cause of chickenpox in children. Reactivation of the same virus causes shingles (herpes zoster) in adults.
Varicella-zoster virus is the cause of chickenpox in children. Reactivation of the same virus causes shingles (herpes zoster) in adults.20 Which skin diseases are caused by human papillomaviruses?
Human papillomaviruses are DNA viruses that are classified into more than 70 subgroups. Some of these viruses have a predilection for certain anatomic sites, causing clinically identifiable skin lesions known as verrucae or warts (Fig. 19-4).
 Verruca vulgaris (common wart): These rough-surfaced, hyperkeratotic papules usually appear on hands. May be solitary or multiple. Histologically, the warts show papillomatosis (formation of papillae that have a central vascular connective tissue core and are covered with thick epithelium), acanthosis (i.e., thickening of the epithelium), granular layer thickening, and hyperkeratosis.
Verruca vulgaris (common wart): These rough-surfaced, hyperkeratotic papules usually appear on hands. May be solitary or multiple. Histologically, the warts show papillomatosis (formation of papillae that have a central vascular connective tissue core and are covered with thick epithelium), acanthosis (i.e., thickening of the epithelium), granular layer thickening, and hyperkeratosis. Verruca plana (flat wart): These small (2–5 mm), flat-topped, multiple hyperpigmented multiple papules appear on the face and hands of children.
Verruca plana (flat wart): These small (2–5 mm), flat-topped, multiple hyperpigmented multiple papules appear on the face and hands of children. Condyloma acuminatum (anogenital wart): These moist, cauliflower-like exuberant growths appear on the penis or vulva.
Condyloma acuminatum (anogenital wart): These moist, cauliflower-like exuberant growths appear on the penis or vulva.23 What is folliculitis?
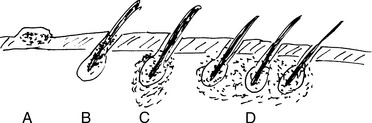
Folliculitis is a bacterial infection of the hair follicles characterized by an accumulation of pus around the hair shaft. Infection is most often caused by S. aureus and involves hairy areas of the skin, such as the buttocks and thighs, bearded part of the face, and the scalp. Suppuration extending into the perifollicular soft tissue may lead to formation of abscesses, which are known as furuncles or boils. Confluent boils form indurated masses that are dark bluish black and are thus known as carbuncles (name derived from a cognate for carbon). See Fig. 19-5.
24 What is acne?
 Overproduction of sebum by the sebaceous glands attached to the hair follicle (Androgenic hormones stimulate the production of sebum, and accordingly the disease is more prominent in men than in women.)
Overproduction of sebum by the sebaceous glands attached to the hair follicle (Androgenic hormones stimulate the production of sebum, and accordingly the disease is more prominent in men than in women.)< div class='tao-gold-member'>
Stay updated, free articles. Join our Telegram channel

Full access? Get Clinical Tree