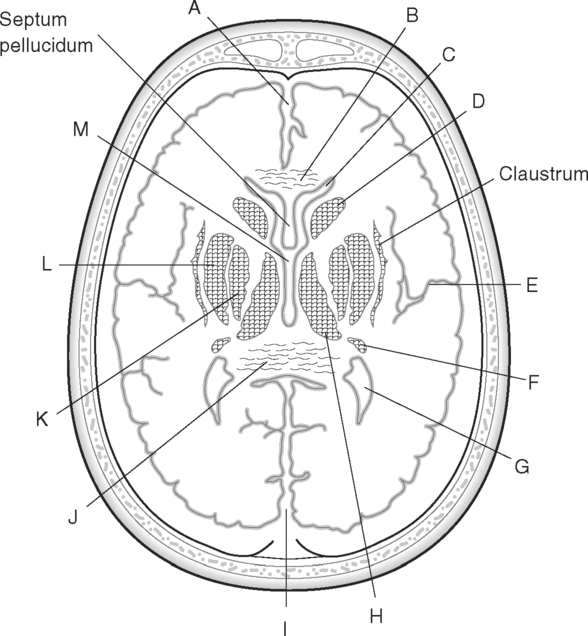
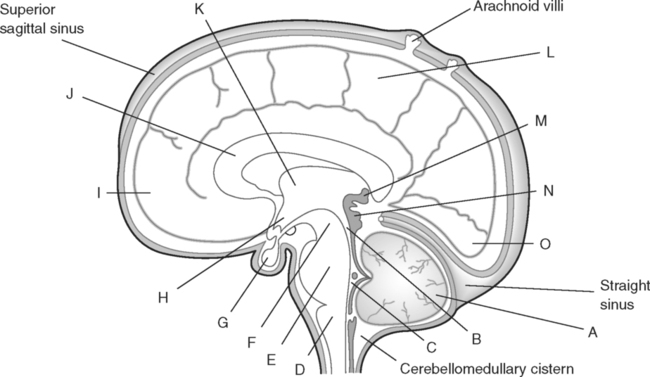
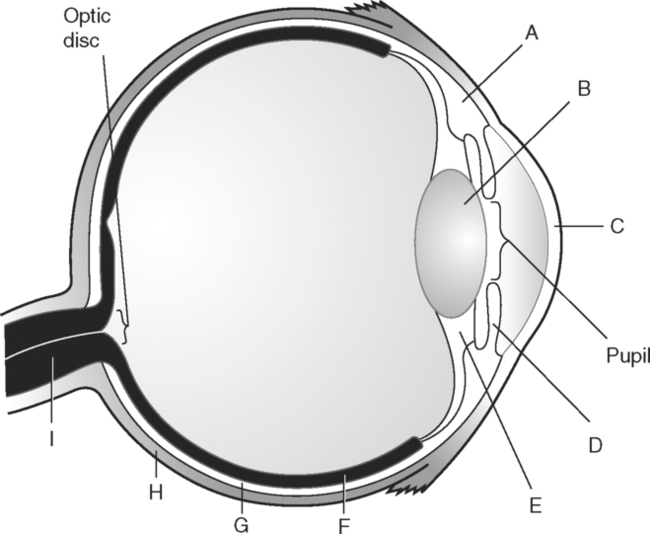
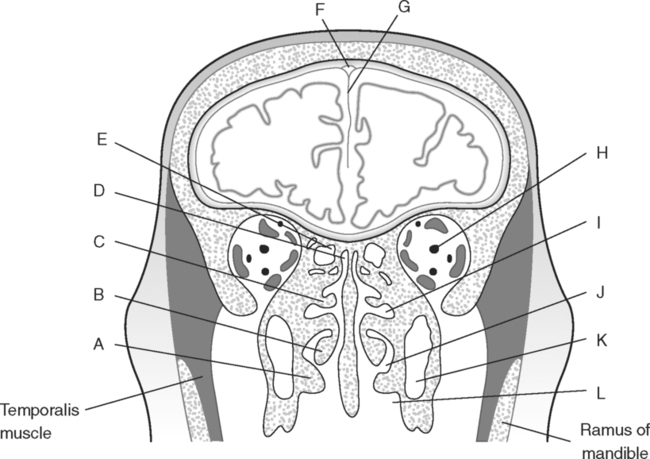
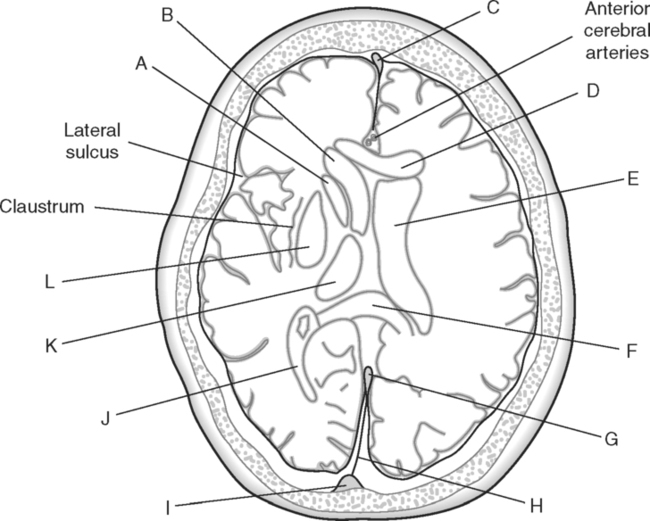
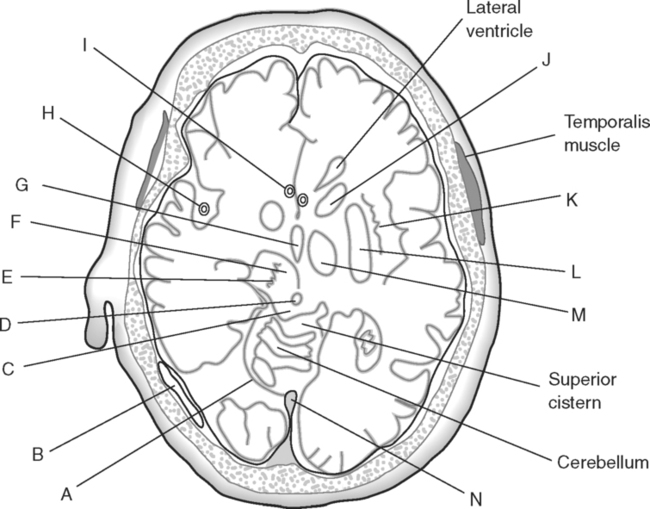
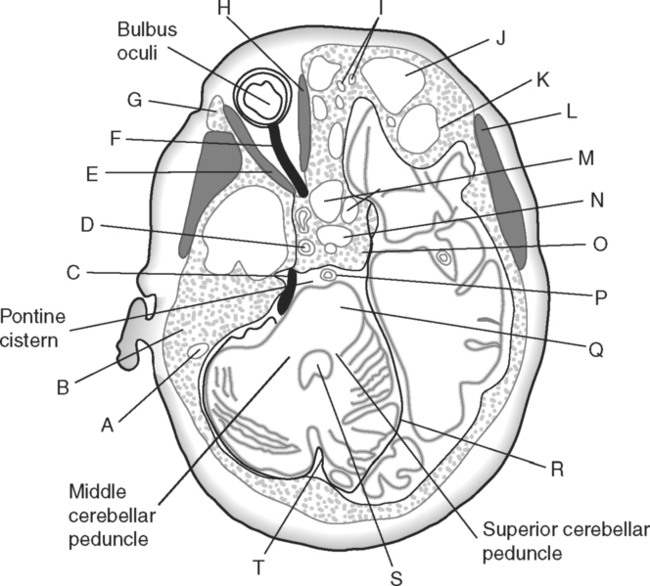
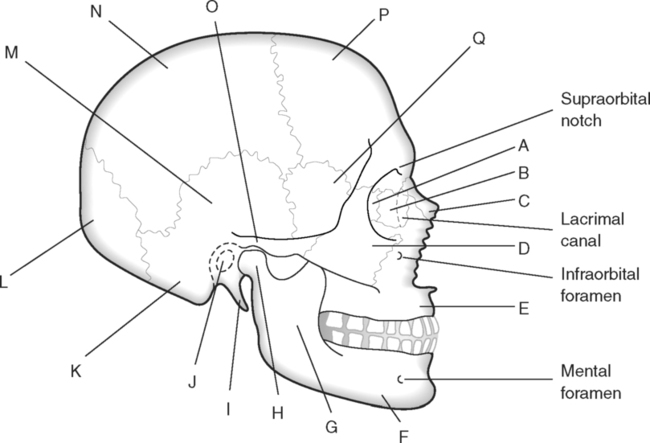
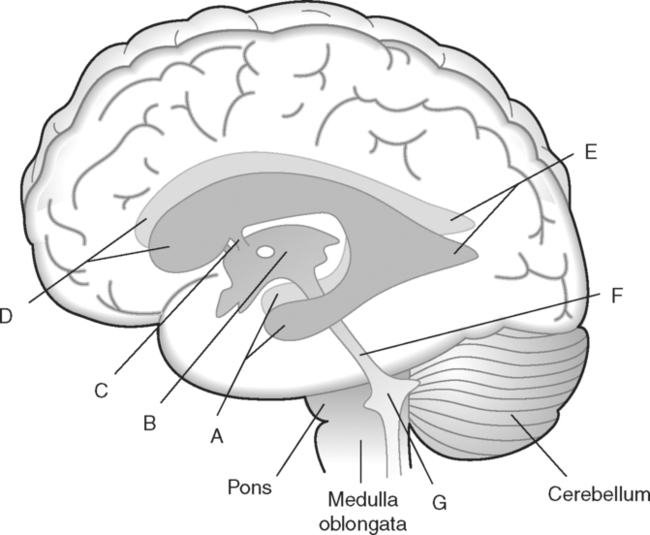
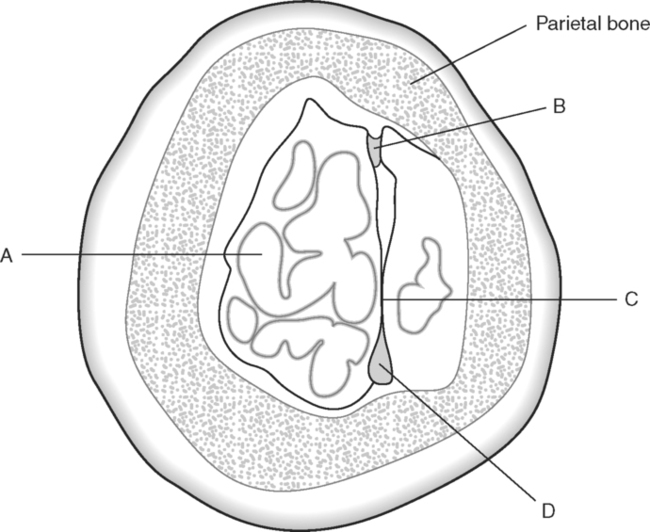
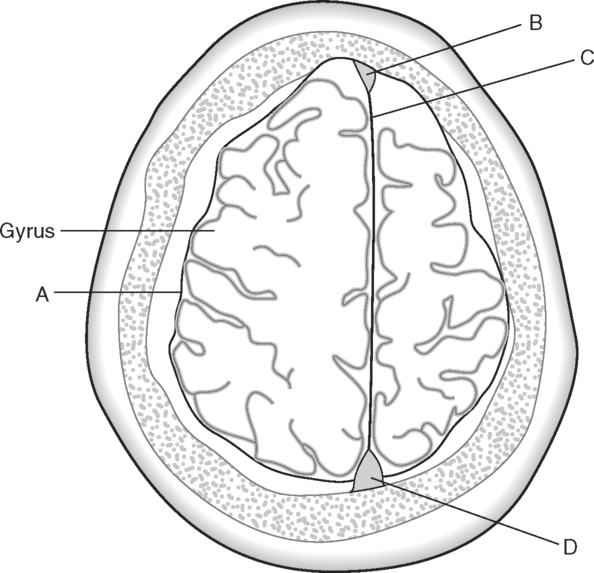
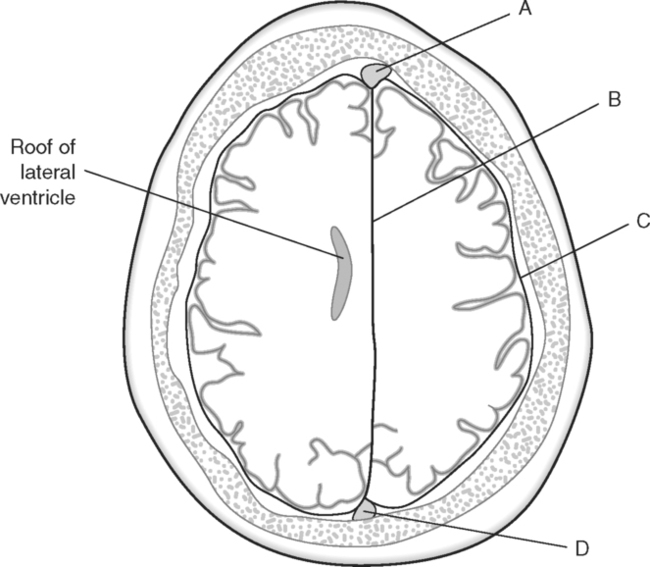
Identify the Structures Indicated in Fig. 5-1: 1. The bone that forms the forehead is the ______________________ bone. 2. The styloid process and external auditory meatus are parts of the ______________________ bone. 3. The bone that forms the prominence of the cheek is the ______________________ bone. 4. The bone that has a mental foramen, ramus, and condyle is the ______________________. 5. Name four bones that contribute to the framework of the orbit. Identify the Structures Indicated in Fig. 5-2: 1. What is the name of the band of white fibers that forms the communication pathway between the two cerebral hemispheres? 2. What region of gray matter forms the lateral walls of the third ventricle? 3. What specific region of the basal ganglia is bordered by the extreme capsule laterally and the external capsule medially? 4. Which portion of the lentiform nucleus is closer to the internal capsule? 5. Name two regions of gray matter that are medial to the internal capsule. Identify the Structures Indicated in Fig. 5-3: 1. What forms the anterior portion of the midbrain? 2. What structure extends posteriorly from the third ventricle and projects into the superior cistern? 3. What glandular structure extends inferiorly from the hypothalamus? 4. What venous sinus extends from the superior cistern to the confluence of the sinuses? Identify the Structures Indicated in Fig. 5-4: 1. What ventricle is at the level of the cerebellum? 2. What ventricle is a midline structure in the region of the diencephalon? 3. What is the name of the communicating channel between the third and fourth ventricles? 4. Which of the ventricles are paired? 5. What ventricles are connected by the interventricular foramen? Identify the Structures Indicated in Fig. 5-5: 1. The region where the optic nerve penetrates the bulbus oculi is called the _____________________. 2. The anterior portion of the outermost tunic of the eye is called the ______________________. 3. The innermost tunic of the eye is called the nervous tunic or the ______________________. 4. The structures that attach the lens of the eye to the ciliary body are called ______________________. 5. The posterior portion of the middle or vascular tunic is the ______________________. Identify the Structures Indicated in Fig. 5-6: 1. The space between the middle and inferior nasal conchae is the ______________________. 2. The large sinus at the same level as, but lateral to, the nasal cavity is the ______________________. 3. What forms the central structure in a coronal section through the posterior portion of the bulbus oculi? 4. What muscle extends from the lateral surface of the squamosal region of the temporal bone to the medial surface of the mandibular ramus? 5. What region of the nasal cavity is superior to the superior nasal concha? Identify the Structures Indicated in Fig. 5-7: 1. The outer layer of the cerebral hemispheres is gray matter and is called the ______________________. 2. The space between the cerebral hemispheres is called the _______________________. 3. Name the three layers of meninges. 4. The membranous partition between the cerebral hemispheres is called the _____________________. 5. The layer of meninges that is in closest contact with the surface of the cerebrum is the _______________________. Identify the Structures Indicated in Fig. 5-8: 1. What is the name of the meningeal layer that forms a tough outer covering for the brain? 2. In transverse sections, what are the triangular spaces at the anterior and posterior ends of the falx cerebri? 3. What is the name of the space between two adjacent cerebral gyri? 4. What is the name of the meningeal layer that extends from the top of one gyrus to another, forming a “bridge” over the sulci? 5. Between which two layers of meninges is the cerebrospinal fluid located? Identify the Structures Indicated in Fig. 5-9: 1. Which ventricle of the brain is the most superior? 2. Name in sequence the five regions of space and meninges between the outer layer of meninges and the cerebral cortex. 3. What is the most anterior lobe of the cerebrum? 4. What blood-filled space is located in the superior margin of the falx cerebri? In Fig. 5-10 Color or Outline: Identify the Structures Indicated in Fig. 5-10: 1. What blood vessels are located in the anterior portion of the longitudinal fissure? 2. What is the blood-filled space at the internal margin of the posterior part of the falx cerebri? 3. What region of white matter is between the caudate nucleus and lentiform nucleus? 4. Which of the basal ganglia is closest to the insula? 5. What specialized capillary structure is found in the ventricles of the brain? In Fig. 5-11 Color or Outline: Identify the Structures Indicated in Fig. 5-11: 1. What are the four hemispherically shaped structures that project into the superior cistern? 2. What is the name of the venous sinus located at the junction of the falx cerebri and the tentorium cerebelli? 3. How can you distinguish between the inferior sagittal sinus and the straight sinus? 4. In transverse sections, what is the small hole in the midbrain? 5. In transverse sections, what ventricle appears as a narrow, midline slit? In Fig. 5-12 Color or Outline: Identify the Structures Indicated in Fig. 5-12:
The Head
Basicmedical Key
Fastest Basicmedical Insight Engine