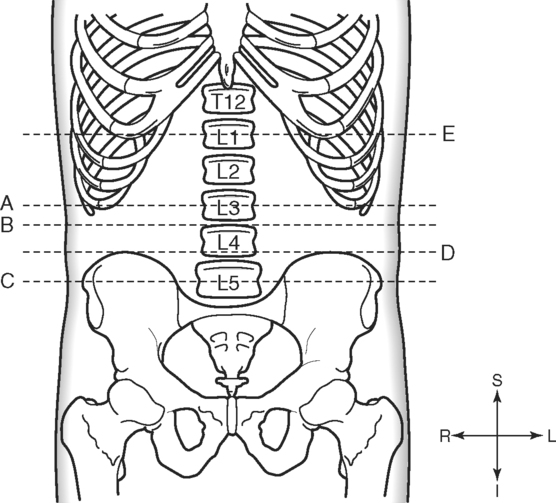
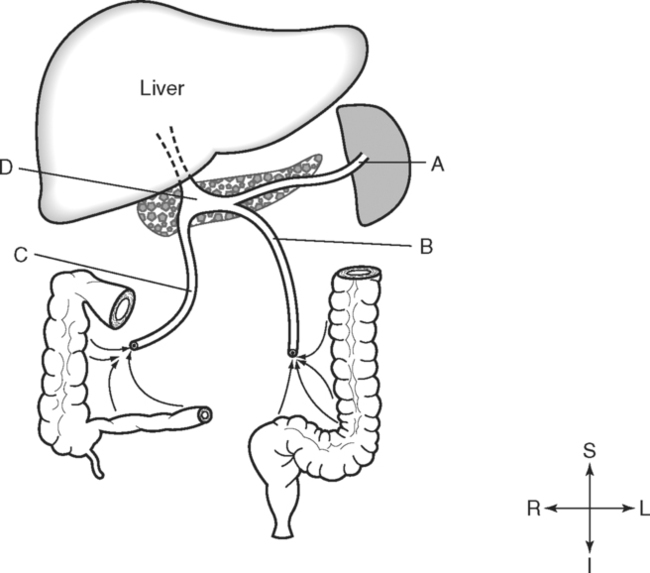
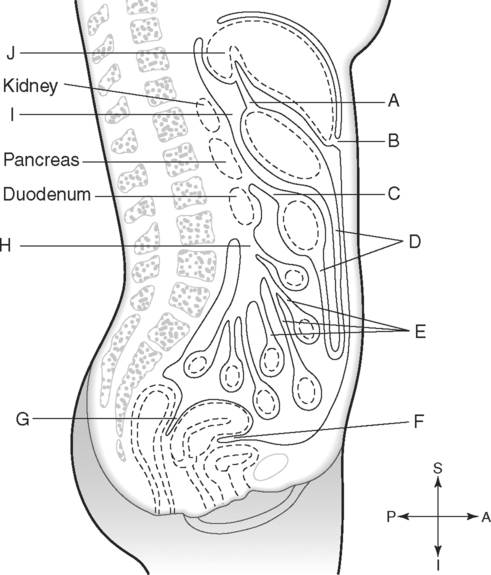
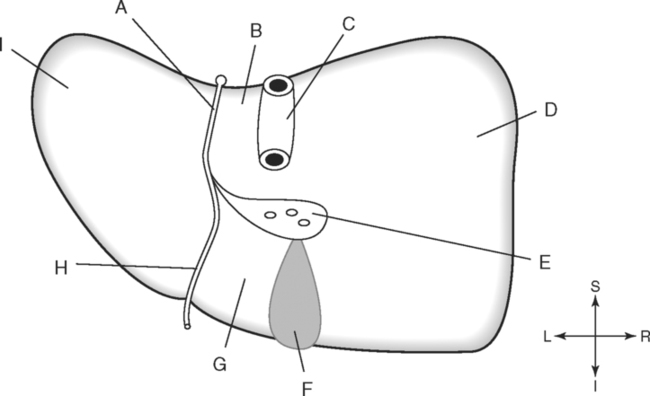
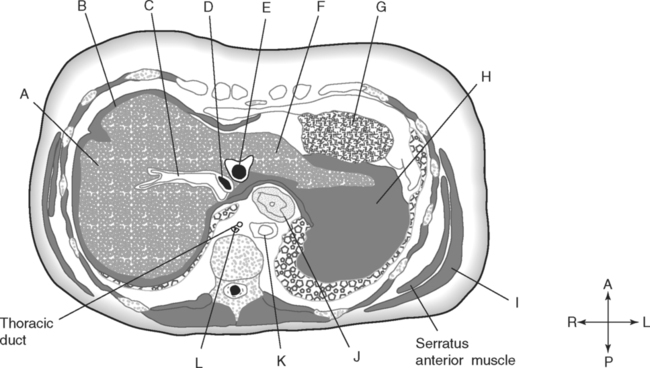
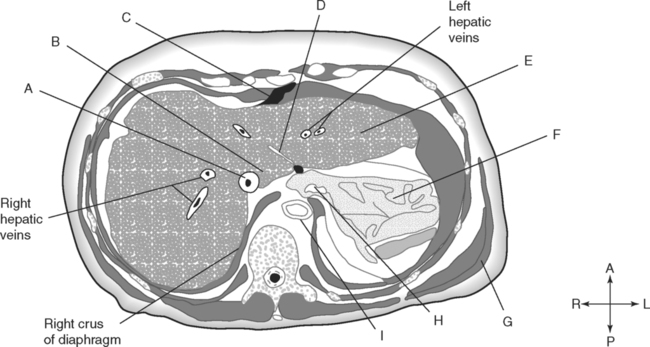
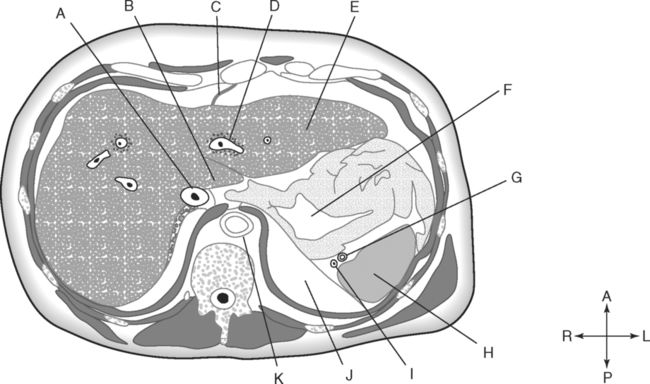
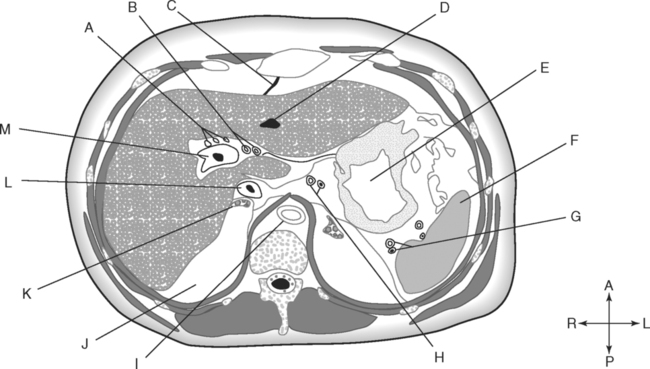
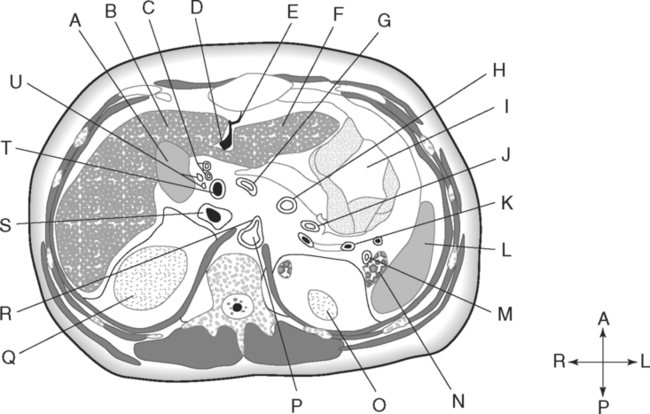
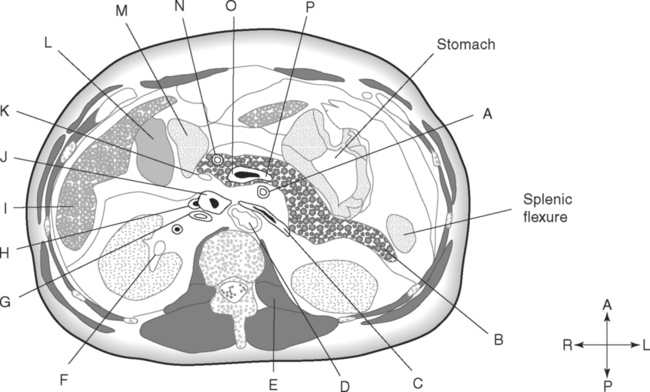
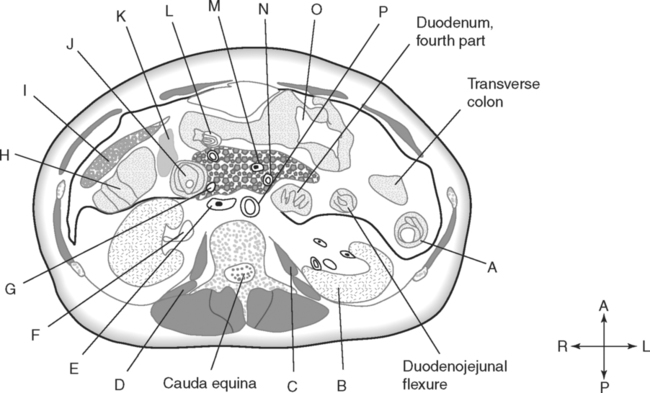
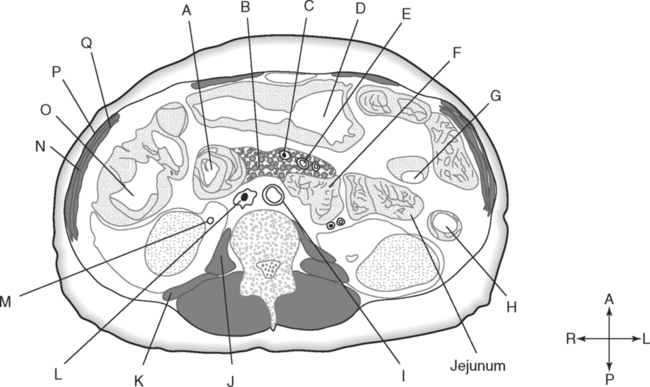
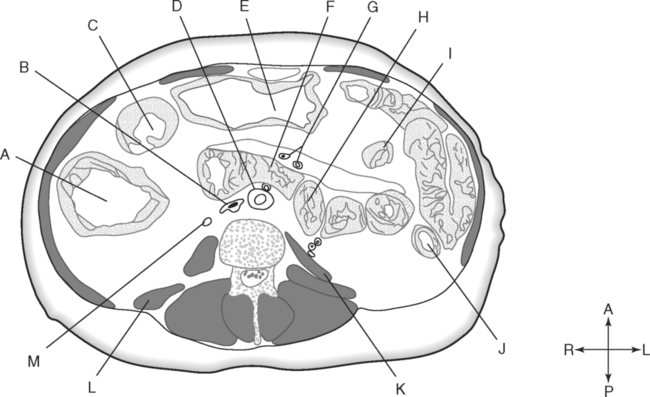
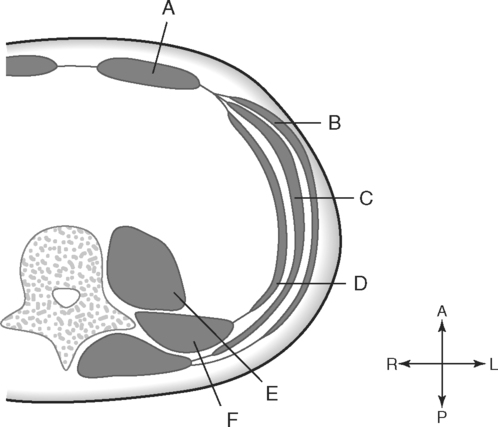
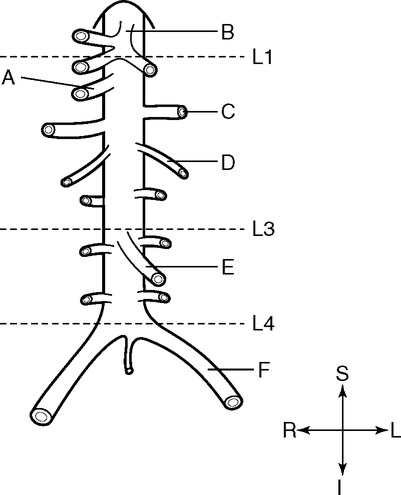
Identify the Planes Indicated in Fig. 3-1: Identify the Muscles Indicated in Fig. 3-2: 1. What muscle is posterior and lateral to the psoas major muscle? 2. What muscle is the deepest of the three lateral muscles? 3. What is the name of the vertical line in the middle of the anterior abdominal wall, between the rectus abdominis muscles? Identify the Vessels Indicated in Fig. 3-3: 1. What are the three main branches of the celiac trunk? 2. What horizontal abdominal plane indicates the origin of the superior mesenteric artery? 3. Which is more superior, the origin of the gonadal arteries or the origin of the renal arteries? 4. What vessels result from the bifurcation of the abdominal aorta? Identify the Vessels Indicated in Fig. 3-4: 1. What vessel drains blood from the descending colon? 2. With what vessel does the splenic vein merge to form the hepatic portal vein? 3. What vessel carrying blood from the intestines enters the liver? 4. The splenic vein drains blood from the spleen and the ______________________. Identify the Structures Indicated in Fig. 3-5: 1. Serous membranes associated with the stomach are called ______________________. 2. Serous membranes associated with the small intestine are called ______________________. 3. Three organs that are retroperitoneal are the ______________________, ______________________, and ______________________. 4. The peritoneal cul-de-sac between the rectum and the uterus is the ______________________. Identify the Structures and Regions Indicated in Fig. 3-6: 1. What structure separates the caudate lobe from the quadrate lobe? 2. What lobe is designated by the ligamentum venosum, inferior vena cava, and porta hepatis? 3. What lobe is between the gallbladder and ligamentum teres? Identify the Structures Indicated in Fig. 3-7: 1. Which one of the liver lobes is most posterior? 2. Which is more anterior, the right hepatic vein or the left hepatic vein? 3. In the thorax the esophagus is typically to the right of the aorta, but in the upper abdomen it appears anterior or to the left of the aorta. What accounts for this apparent shift in position? 4. What vein is located anterior to the vertebral body and slightly to the right of the aorta? Identify the Structures Indicated in Fig. 3-8: 1. At what vertebral level is the esophageal hiatus usually located? 2. In addition to the hepatic veins and portal veins, what vein is frequently located within the substance of the liver? 3. What ligament attaches the liver to the anterior abdominal wall? 4. What ligament is at the right margin of the left lobe of the liver? 5. What pair of muscles forms a vertical strip down the anterior abdominal wall? 6. What portion of the liver is related to the lesser curvature of the stomach? Identify the Structures Indicated in Fig. 3-9: 1. What veins within the liver are surrounded by echogenic connective tissue? 2. What limits the caudate lobe of the liver on the right? 3. What vessels are apparent posterior to the stomach? 4. Anteriorly, the right suprarenal gland is related to what vessel? 5. In addition to a branch of the portal vein and the hepatic duct, what is in a portal triad? In Fig. 3-10 Color or Outline: Identify the Structures Indicated in Fig. 3-10: 1. Within the porta hepatis, what is the relationship between the hepatic duct and the hepatic artery? 2. What blood vessels are in the hilum of the spleen? 3. What is the arrangement, from anterior to posterior, of the three principal organs in the left lateral portion of the upper abdomen? 4. Which is more anterior, the inferior vena cava or the portal vein? 5. What is the medial limitation of the right suprarenal gland? In Fig. 3-11 Color or Outline: Identify the Structures Indicated in Fig. 3-11: 1. Which branch of the celiac trunk courses to the right? 2. What structure is in the inferior margin of the falciform ligament? 3. What lobe of the liver is bordered on the right by the gallbladder? 4. Which portion of the pancreas is related to the spleen? 5. What vessel courses to the right from the spleen to drain into the hepatic portal vein? 6. What is the second major unpaired vessel to branch from the abdominal aorta? In Fig. 3-12 Color or Outline: Identify the Structures Indicated in Fig. 3-12: 1. What vessel descends along the anterior margin of the head of the pancreas? 2. What vessel is anterior to the aorta but posterior to the superior mesenteric artery? 3. What is the most superior portion of the colon? 4. What portion of the colon is related to the tail of the pancreas? 5. What specific portion of the small intestine is related to the gallbladder laterally and to the head of the pancreas medially? In Fig. 3-13 Color or Outline: Identify the Structures Indicated in Fig. 3-13: 1. What fills the vertebral foramen at the lower L2 level? 2. What specific portion of the colon is related to the gallbladder? 3. What structure enters the second part of the duodenum after descending along the posterior margin of the head of the pancreas? 4. What muscle is lateral and posterior to the psoas muscle? 5. What two major blood vessels are posterior to the head of the pancreas but anterior to the vertebral column? 6. What is the name given to the junction of the ascending portion of the duodenum and the second region of the small intestine? In Fig. 3-14 Color or Outline: Identify the Structures Indicated in Fig. 3-14: 1. What is the middle layer of muscle along the lateral abdominal wall? 2. Which is more anterior, the descending colon or the transverse colon? 3. What structure is wedged between the descending and ascending portions of the duodenum? 4. Which is more anterior, the stomach or the ascending colon? 5. Which is more posterior, the transverse colon or the descending colon? In Fig. 3-15 Color or Outline: Identify the Structures Indicated in Fig. 3-15:
The Abdomen
Basicmedical Key
Fastest Basicmedical Insight Engine