Splenic Diffuse Red Pulp Small B-cell Lymphoma
Roberto N. Miranda, MD
Key Facts
Terminology
Abbreviation: SDRP SBCL
Provisional entity in 2008 WHO classification
Clinical Issues
Low level of lymphocytosis
Splenomegaly; usually massive
Bone marrow involvement very common
Clinically indolent B-cell lymphoma presenting at clinical stage IV
Patients have good response after splenectomy
Microscopic Pathology
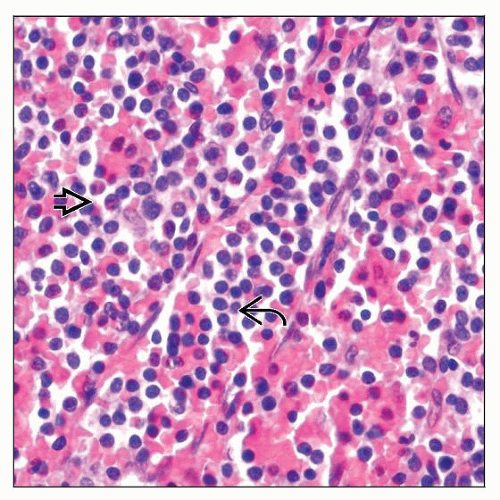
Diffuse infiltration of red pulp cords and sinuses with effacement of white pulp
Monomorphic round, small to intermediate-sized lymphocytes
Vesicular nuclei; subset has small, distinct nucleolus
Bone marrow: Intrasinusoidal pattern with or without interstitial or nodular pattern
Blood and bone marrow smears
Lymphocytes show small cytoplasmic projections (villi) that are broad based
Villi are unevenly distributed around cell
Ancillary Tests
IgM(+), IgD(−/+), pan-B cell(+), CD11c(+), CD25(−), CD103(+/−), CD123(−)
Complex cytogenetic abnormalities in ˜ 33%
Top Differential Diagnoses
Hairy cell leukemia (HCL)
Hairy cell leukemia-variant (HCL-v)
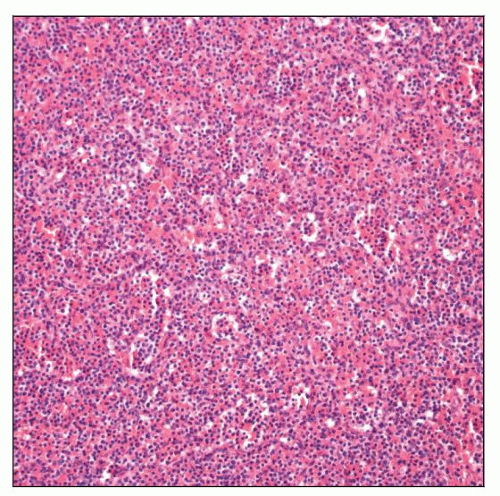 Hematoxylin and eosin stain of small diffuse red pulp small B-cell lymphoma (SDRP SBCL) shows a diffuse effacement of the splenic architecture. No residual white pulp nodularity is noted. |
TERMINOLOGY
Abbreviations
Splenic diffuse red pulp small B-cell lymphoma (SDRP SBCL)
Synonyms
Splenic marginal zone lymphoma, diffuse variant
Splenic B-cell lymphoma with villous lymphocytes
Splenic red pulp lymphoma with numerous basophilic villous lymphocytes
Lymphocytic lymphoma simulating hairy cell leukemia (obsolete term)
Definitions
Mature B-cell neoplasm that involves peripheral blood, bone marrow, and spleen
Overlap with hairy cell leukemia variant
Provisional entity in 2008 WHO classification
ETIOLOGY/PATHOGENESIS
Etiology
Unknown
Cell of origin is a peripheral blood B cell of unknown stage and function
CLINICAL ISSUES
Epidemiology
Incidence
Rare type of lymphoma; < 1% of all non-Hodgkin lymphomas
˜ 10% of B-cell lymphomas diagnosed by splenectomy
˜ 1% of chronic lymphoid leukemias
Age
Most patients are > 40 years
Median: 77 years
Gender
No obvious gender bias; may be slight male predominance
Presentation
Clinically indolent
B symptoms rare
Splenomegaly; usually massive
Usually presents as stage IV with bone marrow involvement
Erythematous and pruritic skin papules in subset
Lymphadenopathy rare
Laboratory Tests
Low-level lymphocytosis in 76% of patients
Median lymphocyte count: 15.8 × 109/L
Thrombocytopenia (< 100 × 109/L) in 22%
Anemia (Hgb < 10 g/L) in 8%
Serum paraproteinemia is rare
Treatment
Surgical approaches
Good clinical response following splenectomy
Prognosis
Clinically indolent but incurable disease
63% of patients alive with median follow-up of 48 months in 1 study
Rare transformation to diffuse large B-cell lymphoma occurs
MACROSCOPIC FEATURES
General Features
Marked splenomegaly with diffuse congested pattern
Median weight: 1,820 g
MICROSCOPIC PATHOLOGY
Histologic Features
Spleen
Diffuse infiltration of red pulp cords and sinuses with effacement of white pulp
Bone marrow
Intrasinusoidal pattern with or without interstitial or nodular pattern
Cytologic Features
Monomorphic population of round, small to intermediate-sized lymphocytes
Vesicular nuclei and occasional distinct nucleoli
Scant to moderate pale or eosinophilic cytoplasm; occasionally cells show plasmacytoid features
Peripheral blood and bone marrow smears
Lymphocytes show small, broad-based cytoplasmic projections (villi)
Villi are unevenly distributed around cell circumference
ANCILLARY TESTS
Immunohistochemistry
Pan-B-cell antigens(+), DBA.44/CD76(+)
p53(+) in subset
CD5(−), CD10(−), CD25(−), annexin-A1(−)
TRAP(−) by enzyme cytochemistry
Flow Cytometry
Characteristic immunophenotype
IgG(+), CD20(+), DBA.44/CD76(+), CD5(−), CD10(−), CD11c(−), CD25(−)
Subset of cases can be IgM(+), IgD(+), CD103(+)
Rare cases CD5(+) or CD123(+)
Cytogenetics
Complex cytogenetic abnormalities in ˜ 33% of cases
Del(7q), trisomy 3q, &/or trisomy 18 reported
Cytogenetic abnormalities are less frequent than in SMZL
t(9;14)(p13;q32)/PAX5-IgH reported in subset of cases
Molecular Genetics
Low frequency of somatic mutations in IgH variable region genes
IgH variable region use similar to classical HCL
Overrepresentation of VH3-23 and VH4-34
No bias of VH1.2 usage of genes (similar to SMZL)
P53 gene mutations in subset
DIFFERENTIAL DIAGNOSIS
Hairy Cell Leukemia
Diffuse splenic red pulp involvement
Diffuse replacement of bone marrow
“Fried egg” cytologic appearance
Blood and bone marrow smears
Lymphocytes evenly surrounded by “hairy” cytoplasmic projections
Blood: Pancytopenia with monocytopenia
Immunophenotype: CD11c(+), CD25(+), CD103(+), CD123(+)
Hairy Cell Leukemia Variant
Many similarities and overlap with SDRP SBCL
Polar cytoplasmic projections and central nuclei, each with distinct nucleolus
Anemia and thrombocytopenia more common than in SDRP SBCL
Higher degree of lymphocytosis than in SDRP SBCL
Splenic Marginal Zone Lymphoma (SMZL), Diffuse Variant
Synonymous with SDRP SBCL
Considered a morphologic variant of SMZL/SLVL
Stay updated, free articles. Join our Telegram channel

Full access? Get Clinical Tree