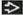Sinonasal Hemangiopericytoma
Jonathan B. McHugh, MD
Key Facts
Clinical Issues
Accounts for < 0.5% of sinonasal neoplasms
Peak incidence in 6th-7th decades
Most frequently involve nasal cavity
Excellent overall 5-year survival (> 90%)
Approximately 1/3 will recur/persist (range: 18-44%)
Often have concomitant paranasal sinus involvement
Macroscopic Features
Mean size is 3.5 cm (range: 1.5-8 cm)
Microscopic Pathology
Composed of uniform, cytologically bland, closely packed, round to spindle-shaped cells intimately associated with vascular component
Prominent perivascular hyalinization is characteristic and is seen in up to 90% of cases
Most tumors have solid or fascicular growth, but mixed growth patterns are common
Vast majority demonstrate myoid phenotype with actin immunohistochemical positivity
Top Differential Diagnoses
Solitary fibrous tumor
Angiofibroma
Lobular capillary hemangioma
Sinonasal smooth muscle neoplasms
Glomus tumor
Various sarcomas with HPC-like vascular pattern
TERMINOLOGY
Abbreviations
Sinonasal hemangiopericytoma (HPC)
Synonyms
Glomangiopericytoma
Hemangiopericytoma-like tumor of sinonasal cavity
Sinonasal glomus tumor
Hemangiopericytoma
Definitions
Unique sinonasal mesenchymal neoplasm demonstrating perivascular myoid phenotype
ETIOLOGY/PATHOGENESIS
Histogenesis
Proposed cell of origin is unidentified modified perivascular glomus-like myoid cell
CLINICAL ISSUES
Epidemiology
Incidence
Accounts for < 0.5% of sinonasal neoplasms
Age
All age groups affected (range: 5-86 years)
75% of cases occur in 6th-8th decades
Peak incidence in 6th-7th decades
Gender
Slight female predilection
Site
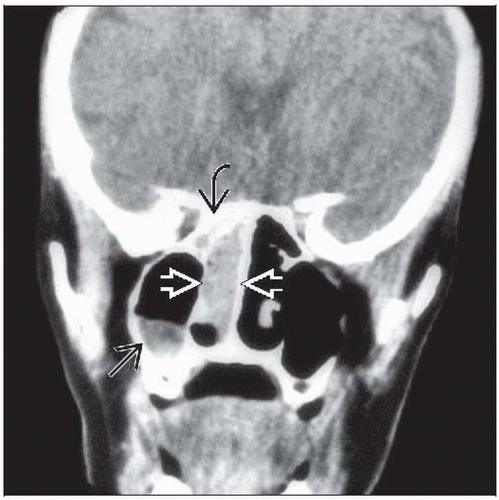
Most frequently involve nasal cavity
Often have concomitant paranasal sinus involvement
Right and left side equally effected
Rarely arise primarily in paranasal sinuses
Presentation
Unilateral polypoid intranasal mass
Nasal obstruction
Epistaxis
Congestion &/or difficulty breathing
Sinusitis
Treatment
Surgical approaches
Complete surgical excision is treatment of choice
Adjuvant therapy
Radiation therapy of unproven value
Prognosis
Excellent overall 5-year survival (> 90%)
Approximately 1/3 will recur/persist (range: 18-44%)
Recurrences can occur after many years
Mean interval to 1st recurrence is around 6.5 years (range: 1-17.5 years)
Long-term follow-up warranted
Malignant degeneration uncommon
Histologic features of malignant sinonasal hemangiopericytoma similar to soft tissue “hemangiopericytoma”
Large size (> 5 cm)
Marked pleomorphism
Necrosis
Bone invasion
> 4 mitoses/10 high-power fields
Ki-67 proliferation index > 10%
IMAGE FINDINGS
Radiographic Findings
Opacification filling nasal cavity ± adjacent sinuses
Bone erosion or sclerosis can be seen
Concomitant sinusitis not uncommon
MACROSCOPIC FEATURES
General Features
Often removed piecemeal
If resected intact, appears as polypoid solid mass with tan hemorrhagic cut surface
Surface mucosa typically intact
Size
Mean size is 3.5 cm (range: 1.5-8 cm)
MICROSCOPIC PATHOLOGY
Histologic Features
Subepithelial, well-demarcated but unencapsulated, cellular mesenchymal proliferation
Surface (Schneiderian) mucosa usually intact but may be eroded or show squamous metaplasia
Usually efface but may surround submucosal minor salivary glands
Composed of uniform, closely packed, round to spindle-shaped cells intimately associated with vascular component
Vascular channels are variable in size ranging from capillaries to patulous “staghorn” vessels
Prominent perivascular hyalinization is characteristic and seen in up to 90% of cases
Stroma is typically scant but may be myxoid in areas
Stromal edema may result in hypocellular zones with residual smaller cellular lobules
Most tumors have solid or fascicular growth, but mixed growth patterns are common
Whorled growth patterns can be seen in up to 10% of cases
Extravasated red blood cells are usually present
Inflammatory cells, including eosinophils, mast cells, lymphocytes, and plasma cells, are invariably present
Stay updated, free articles. Join our Telegram channel

Full access? Get Clinical Tree