Sclerosing Pseudovascular Rhabdomyosarcoma
David R. Lucas, MD
Key Facts
Terminology
Variant of RMS characterized by extensive stromal fibrosis and pseudovascular, microalveolar, or cordlike architecture
Clinical Issues
Rare; only 34 reports
Adults and children
Median age: 30 years; range: 0.3-79 years
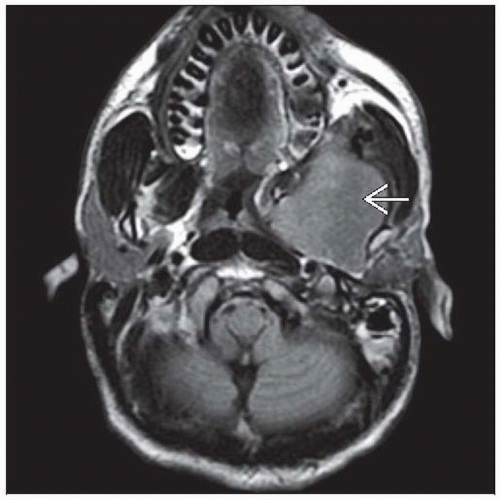
Extremities and head and neck most common
Poor prognosis
Microscopic Pathology
Hyalinizing stromal fibrosis
Can mimic osteoid or chondroid matrix
Small round blue cells or spindle cells
Pseudovascular, microalveolar, cord-like, single cell strand patterns
Solid cellular areas in some
Spindle cell fascicular areas in some
Rare rhabdomyoblasts
Only focal myogenin staining
Top Differential Diagnoses
Alveolar RMS
Sclerosing epithelioid fibrosarcoma
Angiosarcoma
Osteosarcoma
Infiltrating carcinoma
Mesenchymal chondrosarcoma
Extraskeletal myxoid chondrosarcoma
TERMINOLOGY
Abbreviations
Rhabdomyosarcoma (RMS)
Synonyms
Sclerosing RMS, carcinoma-like RMS, microalveolar RMS, desmoplastic RMS
Definitions
Variant of RMS characterized by extensive stromal fibrosis and pseudovascular, microalveolar, or cord-like architecture
CLINICAL ISSUES
Epidemiology
Incidence
Rare; only 34 reports
Age
Adults and children
Median age: 30 years; range: 0.3-79 years
Site
Extremities and head and neck most common
Presentation
Painless mass in extremity
Obstructive symptoms in head and neck
Treatment
Surgical approaches
Wide excision
Adjuvant therapy
Chemotherapy &/or radiotherapy
Prognosis
Poor
Often unresectable
Local recurrence: 25%
Metastasis: 20%
MACROSCOPIC FEATURES
General Features
White to tan, firm to fleshy, hemorrhagic areas
Size
Median: 6 cm; range: 0.3-12 cm
MICROSCOPIC PATHOLOGY
Histologic Features
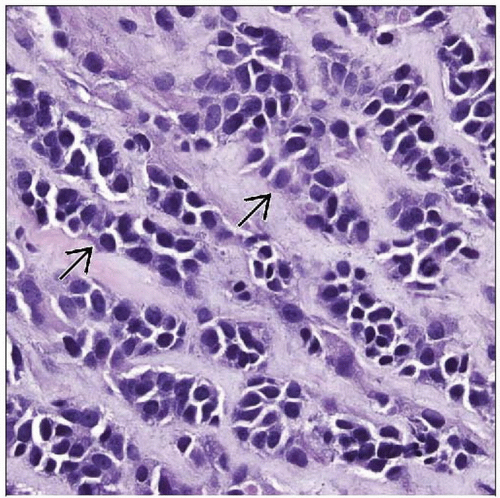
Hyalinizing stromal fibrosis
Can mimic osteoid or chondroid matrix
Pseudovascular, microalveolar, cord-like, single cell strand patterns
Solid cellular areas in some
Spindle cell fascicular areas in some
Cytologic Features
Small round blue cells and spindle cells
Scant eosinophilic or clear cytoplasm
Rare rhabdomyoblasts
DIFFERENTIAL DIAGNOSIS
Alveolar Rhabdomyosarcoma
Larger alveolar spaces
More cohesive growth pattern
Wreath-like giant cells in most
Lacks spindle cells
Very diffuse myogenin staining
t(2:13) or t(1:13) rearrangement in majority
Sclerosing Epithelioid Fibrosarcoma
Cords and single cell strands
Epithelioid cytology
Desmin(-)
MYOD1(-), myogenin(-)
Some have t(7;16) with FUS-CREB3L2 fusion
Angiosarcoma
More complex branching architecture
Often with epithelioid cytology
CD31(-) and CD34(+)
Stay updated, free articles. Join our Telegram channel

Full access? Get Clinical Tree