Sclerosing Epithelioid Fibrosarcoma
Cyril Fisher, MD, DSc, FRCPath
Key Facts
Terminology
Fibrosarcoma variant characterized by at least focal epithelioid cytomorphology and areas of dense fibrosis
Clinical Issues
Around periosteum or fascia
Histologically of variable grade but clinically aggressive, especially in long term
Macroscopic Features
Multinodular
Microscopic Pathology
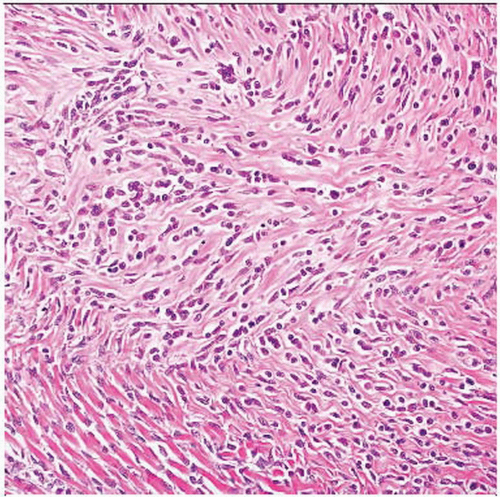
Dense fibrosis divides tumor into cellular islands
Nests and cords of polygonal cells
Ovoid, sometimes angulated nuclei, occasional pleomorphism
Can form files of epithelial-like cells
Other patterns of fibrosarcoma can coexist
Adult-type fibrosarcoma
Low-grade fibromyxoid sarcoma
Stroma can show myxohyaline change, calcification, or osteochondroid metaplasia
Focal hemangiopericytic pattern in some cases
Ancillary Tests
Epithelioid and spindle cells show features of fibroblasts
Diagnostic Checklist
Can resemble carcinoma
Epithelial markers usually absent
Can resemble lymphoma
Lymphoid markers absent
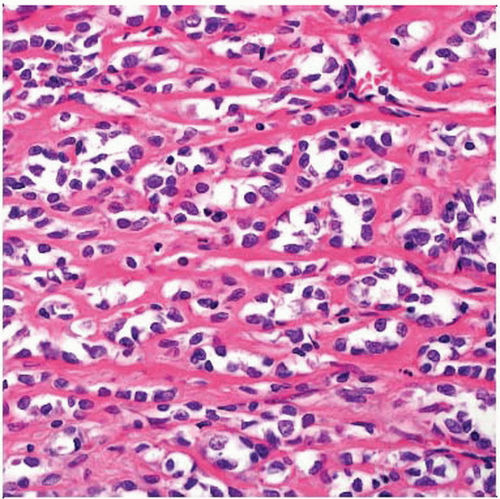 Hematoxylin & eosin shows nests of cells with clear cytoplasm and ovoid, occasionally folded nuclei in a fibrous stroma. Ultrastructurally, these cells show features of fibroblasts. |
TERMINOLOGY
Definitions
Fibrosarcoma variant characterized by at least focal epithelioid cytomorphology and areas of dense fibrosis
ETIOLOGY/PATHOGENESIS
Environmental Exposure
Occasional example attributed to therapeutic irradiation
CLINICAL ISSUES
Epidemiology
Incidence
Rare: ˜ 60 examples reported
Age
Adults, peak in 5th decade
Gender
Slightly more common in females
Site
Limbs and limb girdles, trunk, shoulder, neck
Rarely in visceral sites, e.g., large intestine, ovary, base of penis, pituitary
Deep muscle
Around periosteum or fascia
Can involve or arise in bone including skull, rib, sacrum
Presentation
Deep mass
Painful or painless mass
Treatment
Surgical approaches
Adequate local excision
Can require amputation especially when bone involved
Adjuvant therapy
Chemotherapy or radiation therapy can be tried to control recurrence and metastasis
Prognosis
Histologically of variable grade but clinically aggressive, especially in long term
Local recurrence in > 50%
Metastasis in 43-86%
5-year survival is 43-75%
MACROSCOPIC FEATURES
General Features
In deep soft tissue
Multinodular
Circumscribed or infiltrative
Very hard, can show calcification or ossification
Occasionally cystic
Sections to Be Submitted
Lesion should be extensively sampled to detect cellular areas
Size
Variable
2 to > 20 cm in maximum dimension
MICROSCOPIC PATHOLOGY
Histologic Features
Dense fibrosis divides tumor into cellular islands
Nests and cords of polygonal cells
Cells can lose cohesion, imparting alveolar appearance
Ovoid, sometimes angulated nuclei, occasional pleomorphism
Low mitotic index
Clear or eosinophilic cytoplasm
Cells can form files that simulate scirrhous breast carcinoma or sclerosing lymphoma
Stroma has range of features
Myxohyaline change
Pericellular collagen strands can resemble osteoid
Calcification
Osteochondroid metaplasia
Focal hemangiopericytic pattern in some cases
Occasional focal necrosis
Other patterns of fibrosarcoma can coexist
Spindle cell fascicular areas often present, resembling adult-type fibrosarcoma
Foci resembling low-grade fibromyxoid sarcoma occasionally seen
Stay updated, free articles. Join our Telegram channel

Full access? Get Clinical Tree