Richter Syndrome
Sergej Konoplev, MD, PhD
Key Facts
Terminology
Aggressive lymphoma arising in patient with chronic lymphocytic leukemia/small lymphocytic lymphoma (CLL/SLL)
Subtypes
Common: Diffuse large B-cell lymphoma
Uncommon: Classical Hodgkin lymphoma
Rare: Peripheral T-cell lymphoma, B-lymphoblastic lymphoma
Etiology/Pathogenesis
Aggressive lymphoma is clonally related to CLL/SLL in ˜ 80% of cases
Both DLBCL and classical Hodgkin lymphoma can be clonally related to CLL/SLL
Clinical Issues
2-8% of patients with CLL/SLL develop RS
˜ 0.5% of patients with CLL/SLL develop CHL
Sudden fever, night sweats, &/or weight loss
Rapidly progressive lymphadenopathy
Generalized more common than single site
Anemia, neutropenia, and thrombocytopenia
Rapid rise of serum LDH
Generally dismal prognosis
Median survival: ˜ 20-30 months
Top Differential Diagnoses
Lymphadenopathy secondary to infectious causes
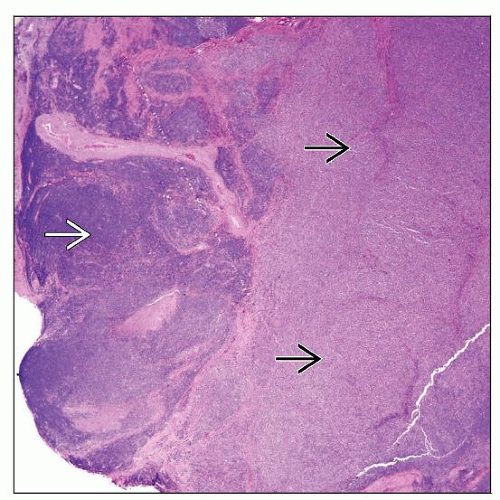
CLL/SLL with prominent proliferation centers
CLL/SLL in prolymphocytoid transformation
CD5(+) de novo DLBCL
TERMINOLOGY
Abbreviations
Richter syndrome (RS)
Synonyms
Richter transformation
Definitions
Aggressive lymphoma arising in patients with chronic lymphocytic leukemia/small lymphocytic lymphoma (CLL/SLL)
Histologic types of aggressive lymphoma
Diffuse large B-cell lymphoma (DLBCL), most common
Classical Hodgkin lymphoma (CHL)
Peripheral T-cell lymphoma (PTCL)
B-lymphoblastic lymphoma/leukemia (very rare)
ETIOLOGY/PATHOGENESIS
Clonal Relationship
Aggressive lymphoma is clonally related to CLL/SLL in ˜ 80% of cases
Both DLBCL and CHL can be clonally related to CLL/SLL
Other Possible Causes
CLL/SLL may contribute to genetic instability, allowing development of additional genetic abnormalities
ATM or P53 abnormalities in CLL/SLL may impair cell response to DNA damage
CLL/SLL is associated with immunosuppression and loss of immunosurveillance
Chemotherapy for CLL/SLL may contribute to immunocompromise
Nucleoside analogues impair host immunity
CLINICAL ISSUES
Epidemiology
Incidence
2-8% of patients with CLL/SLL develop RS
˜ 0.5% of patients with CLL/SLL develop CHL
Peripheral T-cell lymphoma in CLL/SLL patients is extremely rare
Age
Median age: 7th decade
Gender
Male to female ratio: ˜ 2.5 to 1
Site
Most common: Lymph nodes, bone marrow, peripheral blood, spleen
Extranodal sites are not commonly involved
Skin, testes, gastrointestinal tract, liver
Tonsils, bones, lungs, central nervous system
Presentation
Median time from diagnosis of CLL/SLL to RS: ˜ 2-3 years
RS can be diagnosed 1st, before presence of CLL/SLL is known
Sudden onset of symptoms
B symptoms: Fever, night sweats, &/or weight loss
Rapidly progressive lymphadenopathy
Generalized more common than single site
Laboratory Tests
Anemia, neutropenia, and thrombocytopenia
Rapid increase in serum lactate dehydrogenase
Serum paraprotein in subset of patients
Treatment
Prognosis
Generally dismal; median survival: ˜ 20-30 months
Often, survival is < 1 year
Prognosis relatively better for patients with CHL
Risk Factors for RS
Lymph node size > 3 cm
CD38 expression
Absence of del(13q14)
IgVH4-39 gene usage
IMAGE FINDINGS
Radiographic Findings
Generalized or localized lymphadenopathy
Increased 18F-FDG uptake on PET/CT
Increased gallium-67 uptake on single photon emission computed tomography scans (controversial)
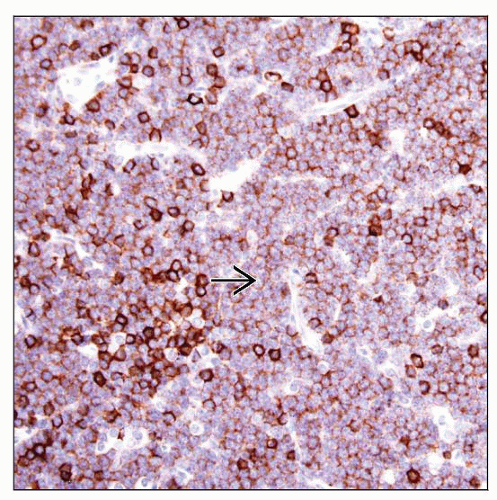
MICROSCOPIC PATHOLOGY
Histologic Features
DLBCL
Centroblastic (most common) or immunoblastic variant
Immunoblastic variant more common relative to de novo DLBCL
Rare cases resemble T-cell/histiocyte-rich large B-cell lymphoma
High mitotic rate; ± necrosis
CHL
Hodgkin and Reed-Sternberg (HRS) cells
Inflammatory background of T cells, histiocytes, ± eosinophils
Necrosis is common
Stay updated, free articles. Join our Telegram channel

Full access? Get Clinical Tree