Prescription review
A foolproof plan
 . Learn a practical and reliable routine for all prescribing situations.
. Learn a practical and reliable routine for all prescribing situations.
 . Learn to identify the common traps in the Prescribing Safety Assessment (PSA, see ‘Common trap’ boxes).
. Learn to identify the common traps in the Prescribing Safety Assessment (PSA, see ‘Common trap’ boxes).
 . Reinforce your learning by using 10 scenarios with worked answers.
. Reinforce your learning by using 10 scenarios with worked answers.
Structure of this Section within the PSA
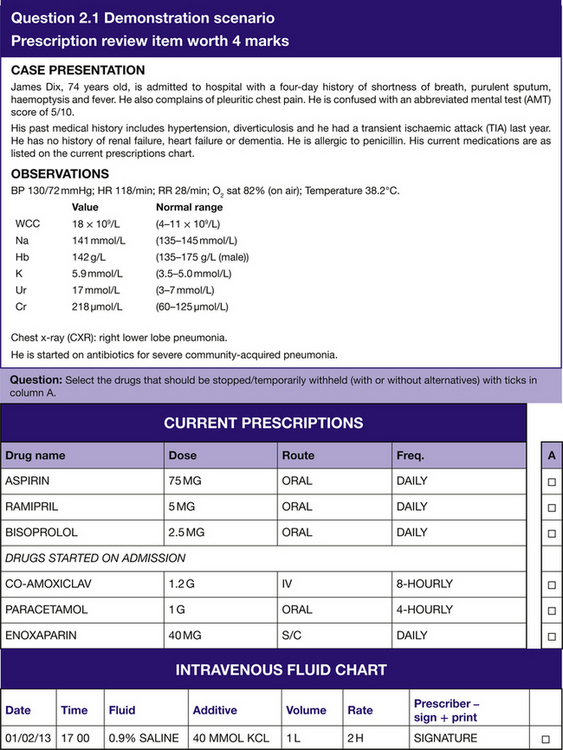
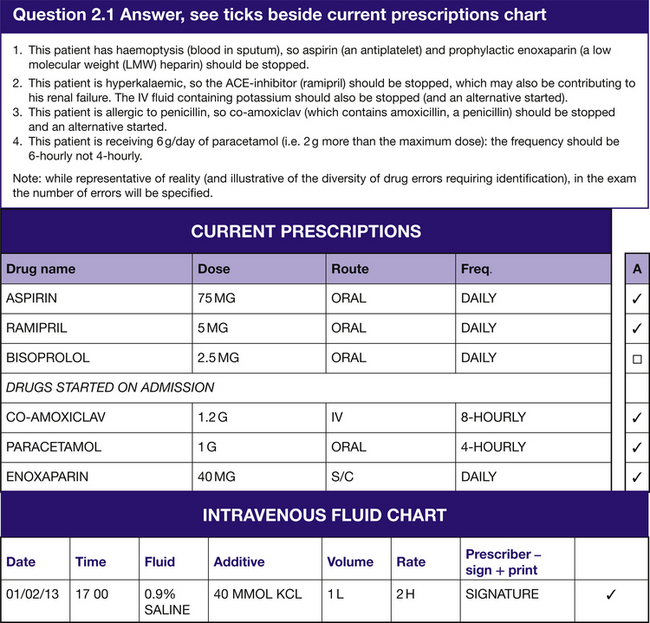
The ‘Prescription review’ section will have 8 questions with 4 marks available per question and a possible total of 32 marks. You will be asked to identify which drug(s) from a list are causing a current problem, which may reflect a side effect, a contraindication, an interaction or ineffectiveness. (See Question 2.1 for a demonstration scenario.)
A Safe Routine for Prescribing
Using the demonstration scenario (Question 2.1), we can identify and address the common pitfalls by:
 ensuring we have the correct patient’s prescription/drug chart
ensuring we have the correct patient’s prescription/drug chart
 noticing and recording allergies
noticing and recording allergies
 signing the front of the chart
signing the front of the chart
 considering the contraindications for each drug we prescribe
considering the contraindications for each drug we prescribe
 considering the route for each drug we prescribe
considering the route for each drug we prescribe
 considering the need for IV fluids
considering the need for IV fluids
 considering the need for thromboprophylaxis
considering the need for thromboprophylaxis
 considering the need for antiemetics
considering the need for antiemetics
PReSCRIBER
This mnemonic will help you to remember the following essentials:
PReSCRIBER explained
Reactions
 If working with a new chart then complete the allergy box including any drug reaction mentioned by the patient.
If working with a new chart then complete the allergy box including any drug reaction mentioned by the patient.
 If amending a chart then check the allergy box before prescribing.
If amending a chart then check the allergy box before prescribing.
Contraindications
For every drug prescribed, consider whether it is contraindicated. Realistically, at undergraduate level there are four groups of drugs for which you must know the contraindications (and less common examples are outlined in Chapter 8):
1. Drugs that increase bleeding (aspirin, heparin and warfarin) should not be given to patients who are bleeding, suspected of bleeding, or at risk of bleeding (e.g. those with a prolonged prothrombin time due to liver disease). Do not forget that prophylactic heparin is contraindicated in acute ischaemic stroke due to the risk of bleeding into the stroke. It is also important to remember that an enzyme inhibitor (such as erythromycin) can increase warfarin’s effect (and thus the prothrombin time (PT) and international normalized ratio (INR)) despite a stable dose. This should be considered when patients present with excessive anticoagulation.
2. For steroids remember the side effects (and thus more loosely the contraindications) by using the mnemonic STEROIDS: Stomach ulcers, Thin skin, oEdema, Right and left heart failure, Osteoporosis, Infection (including Candida), Diabetes (commonly causes hyperglycaemia and uncommonly progresses to diabetes), and Cushing’s Syndrome.
3. With NSAIDs the following cautions and contraindications may be remembered with the mnemonic NSAID: No urine (i.e. renal failure), Systolic dysfunction (i.e. heart failure), Asthma, Indigestion (any cause), and Dyscrasia (clotting abnormality).
4. For antihypertensives always think of the side effects in three categories:
a. Hypotension (including postural hypotension) that may result from all groups of antihypertensives.
b. Dividing the groups of antihypertensives into two mechanistic categories:
1. Bradycardia may occur with beta-blockers and some calcium-channel blockers.
2. Electrolyte disturbance can occur with angiotensin converting enzyme (ACE) inhibitors and diuretics (see Chapter 3).
Stay updated, free articles. Join our Telegram channel

Full access? Get Clinical Tree














