Mitoses > 20 in 10 HPF (based on count of at least 50 HPF; 1 HPF = 2 mm²), or
Ancillary Tests
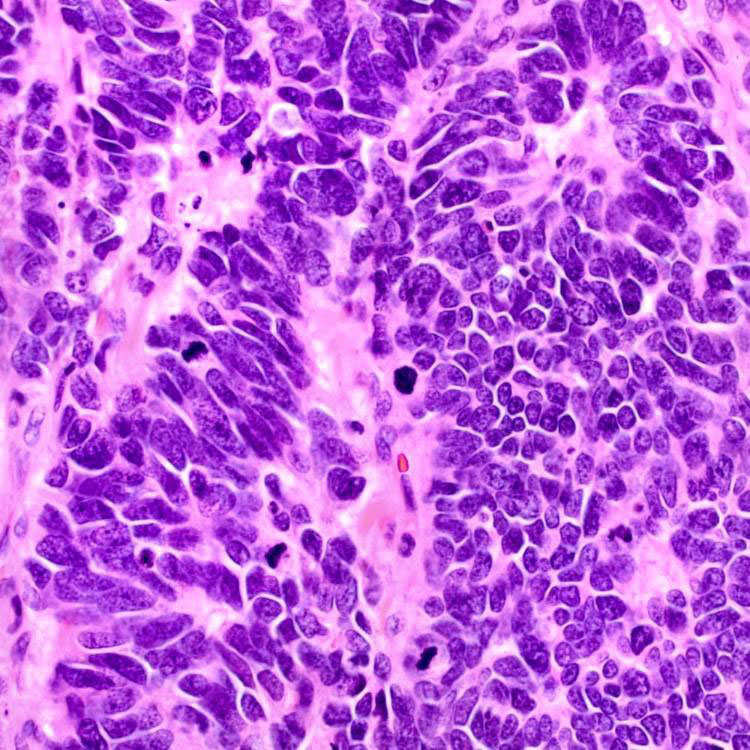
Small to medium-sized tumor cells with scant cytoplasm, indistinct nucleoli, molding, brisk mitoses and karyorrhectic debris are present.
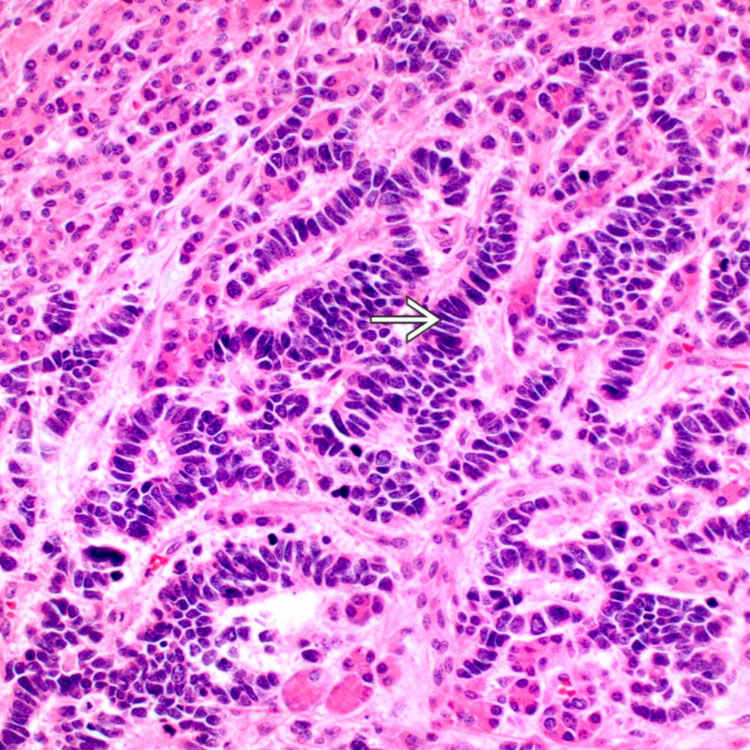
Pancreatic primary tumor metastatic to liver shows typical cytologic features of small cell neuroendocrine carcinoma, including prominent nuclear molding
 . Absence of significant cytoplasm or prominent nucleoli distinguishes it from large cell neuroendocrine carcinoma.
. Absence of significant cytoplasm or prominent nucleoli distinguishes it from large cell neuroendocrine carcinoma.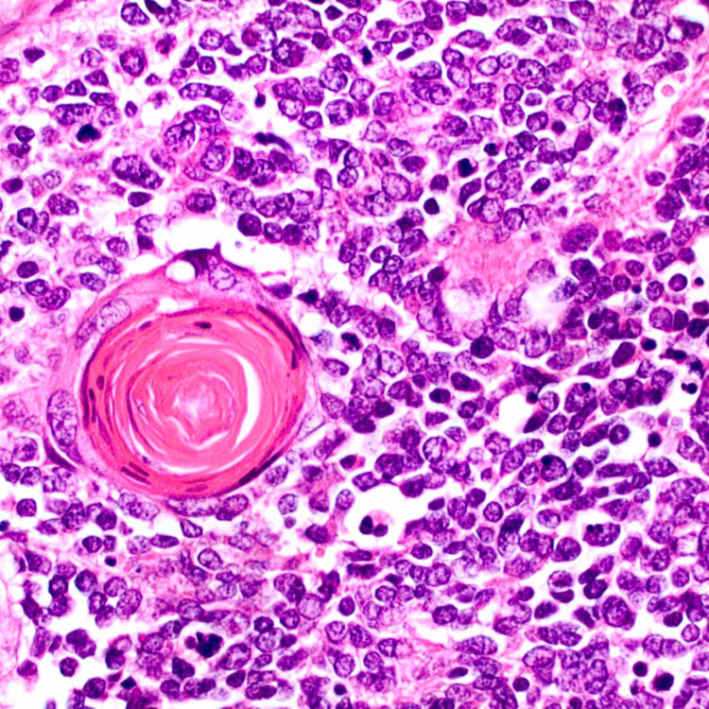
Squamous cells with keratin pearls indicating focal squamous differentiation in an otherwise typical small cell neuroendocrine carcinoma are shown.
ETIOLOGY/PATHOGENESIS
Unknown
• Do not arise from low-grade neuroendocrine tumors in most cases
 Immunohistochemical abnormalities in p53 (> 90%) and Rb (> 70%) common in small cell and large cell neuroendocrine carcinomas
Immunohistochemical abnormalities in p53 (> 90%) and Rb (> 70%) common in small cell and large cell neuroendocrine carcinomas
 Genes typically involved in well-differentiated neuroendocrine tumor like SMAD4 (DPC4), DAXX, and ATRX are normal
Genes typically involved in well-differentiated neuroendocrine tumor like SMAD4 (DPC4), DAXX, and ATRX are normal
• Genetic changes in small and large cell neuroendocrine carcinoma are similar, both are distinct from well-differentiated neuroendocrine tumor
 Immunohistochemical abnormalities in p53 (> 90%) and Rb (> 70%) common in small cell and large cell neuroendocrine carcinomas
Immunohistochemical abnormalities in p53 (> 90%) and Rb (> 70%) common in small cell and large cell neuroendocrine carcinomas Genes typically involved in well-differentiated neuroendocrine tumor like SMAD4 (DPC4), DAXX, and ATRX are normal
Genes typically involved in well-differentiated neuroendocrine tumor like SMAD4 (DPC4), DAXX, and ATRX are normalCLINICAL ISSUES
Epidemiology
Prognosis
• Aggressive neoplasms




Stay updated, free articles. Join our Telegram channel

Full access? Get Clinical Tree







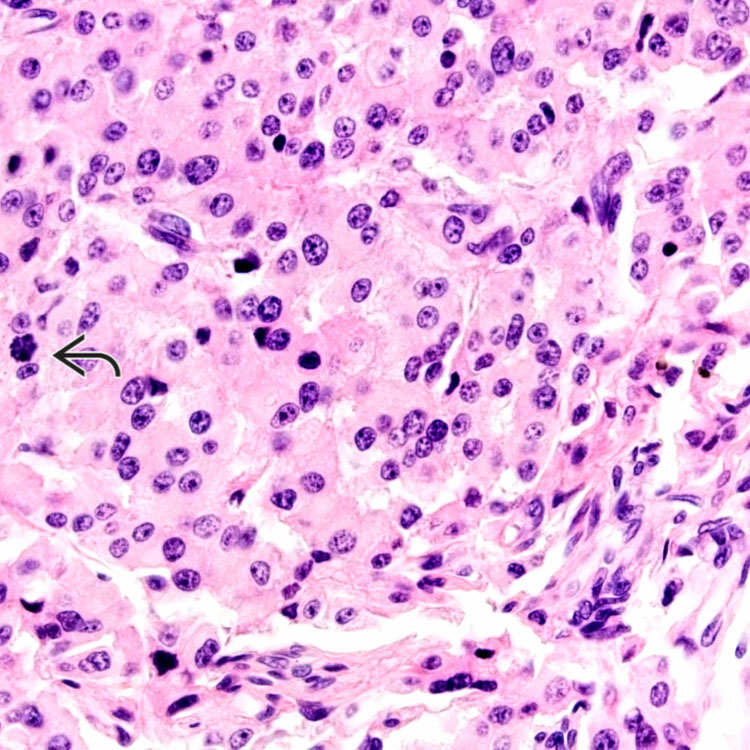
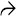 (30 mitoses/10 HPF) are typical features of large cell neuroendocrine carcinoma.
(30 mitoses/10 HPF) are typical features of large cell neuroendocrine carcinoma.









