Chapter 2 Pharmacodynamics
• A pharmacological antagonist that binds reversibly to a receptor so it can be overcome by increasing agonist concentration.
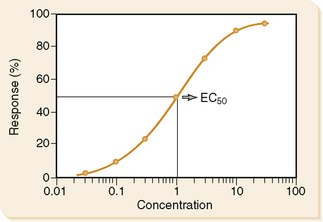
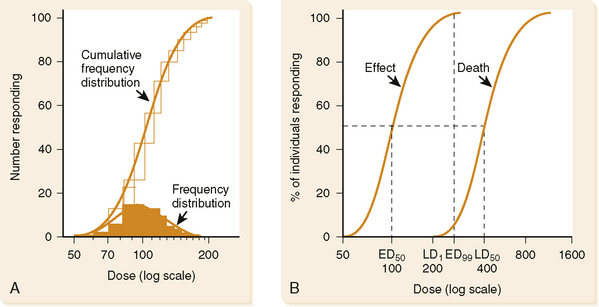
• A graph of the fraction of a population that gives a specified response at progressively increasing drug doses.
2. A steep slope in the midportion of the “S” indicates that a small increase in dosage will produce a large increase in response.
(a) TI (therapeutic index): ratio of the lethal dose in 50% of the population (LD50) divided by the effective dose for 50% of the population (ED50), or 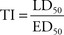
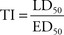
(b) MS (margin of safety): ratio of the lethal dose for 1% of the population (LD1) divided by the effective dose for 99% of the population (LD99), or 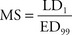
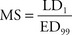
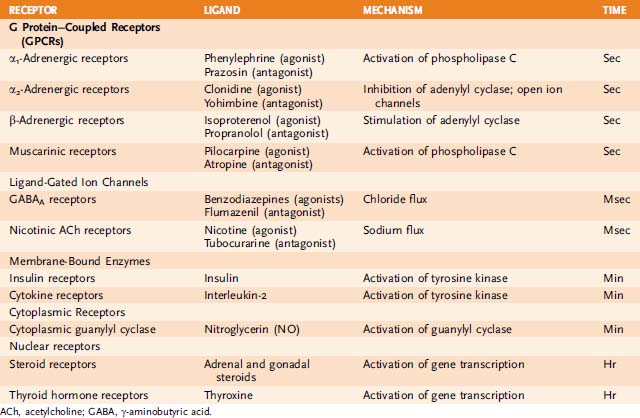
• Drug receptors are biologic components on the surface of or within cells that bind with drugs, resulting in molecular changes that produce a certain response.
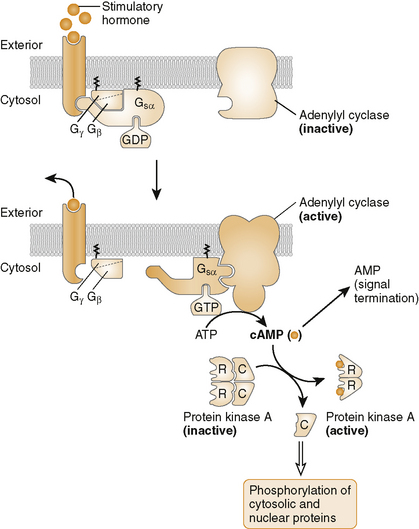
(1) These receptors are a superfamily of diverse guanosine triphosphate (GTP)-binding proteins that couple to “serpentine” (seven) transmembrane receptors.
TABLE 2-2 Major G Protein Signaling Pathways
| Gα Type | Function* | Coupled Receptors |
|---|---|---|
| Gs | Stimulates adenylyl cyclase (↑ cAMP) | Dopamine (D1), epinephrine (β1, β2), glucagon, histamine (H2), vasopressin (V2) |
| Gi | Inhibits adenylyl cyclase (↓ cAMP) | Dopamine (D2), epinephrine (α2) |
| Gq | Stimulates phospholipase C (↑ IP3, DAG) | Angiotensin II, epinephrine (α1), oxytocin, vasopressin (V1), Histamine (H1) |
cAMP, cyclic adenosine monophosphate; DAG, diacylglycerol; IP3, inositol triphosphate.
* In some signaling pathways, Gs and Gi are associated with ion channels, which open or close in response to hormone binding.
(Adapted from Pelley JW and Goljan EF: Rapid Review Biochemistry, 2nd ed. Philadelphia, Mosby, 2007, Table 3-3.)
TABLE 2-3 Effects of Elevated cyclic adenoside monphosphate (cAMP) in Various Tissues
| Tissue/Cell Type | Hormone Increasing cAMP | Major Cellular Response |
|---|---|---|
| Adipose tissue | Epinephrine | ↑ Hydrolysis of triglycerides |
| Adrenal cortex | Adrenocorticotropic hormone (ACTH) | Hormone secretion |
| Cardiac muscle | Epinephrine, norepinephrine | ↑ Contraction rate |
| Intestinal mucosa | Vasoactive intestinal peptide, epinephrine | Secretion of water and electrolytes |
| Kidney tubules | Vasopressin (V2 receptor) | Resorption of water |
| Liver | Glucagon, epinephrine | |
| Platelets | Prostacyclin (PGI2) | Inhibition of aggregation |
| Skeletal muscle | Epinephrine | ↑ Glycogen degradation |
| Smooth muscle (bronchial and vascular) | Epinephrine | |
| Thyroid gland | Thyroid-stimulating hormone | Synthesis and secretion of thyroxine |
(Adapted from Pelley JW and Goljan EF: Rapid Review Biochemistry, 2nd ed. Philadelphia, Mosby, 2007, Table 3-4.)
• IP3 (inositol 1,4,5-triphosphate), which can diffuse in the cytosol and release calcium from the endoplasmic reticulum
Stay updated, free articles. Join our Telegram channel

Full access? Get Clinical Tree