1. Describe the general characteristics of Pasteurella spp. and the additional organisms included in this chapter. 2. Describe the epidemiology associated with human infections caused by Pasteurella spp. and similar organisms, including the normal habitat and route of transmission. 3. Compare the Gram-stain appearance of the organisms included in this chapter. 4. Explain the limitations of antimicrobial susceptibility testing with respect to Pasteurella spp. and similar organisms. 5. Identify limitations associated with identification of Pasteurella spp. and similar organisms. Most of the organisms presented in this chapter constitute portions of both domestic and wild animal flora and are transmitted to humans during close animal contact, including bites. For most of these species, virulence factors are not recognized. As a result, the organisms may be considered opportunistic pathogens that require mechanical disruption of host anatomic barriers (i.e., bite-induced wounds; Table 30-1). Of the organisms listed in Table 30-2, P. multocida subsp. multocida is most commonly encountered in clinical specimens. Reported virulence factors for this subspecies include lipopolysaccharide, cytotoxin, six serotypes of the antiphagocytic capsule, surface adhesins, and iron-acquisition proteins. Other manifestations of infection by P. multocida subsp. multocida can include respiratory disease and systemic disease such as endocarditis and septicemia. Liver cirrhosis is viewed as a risk factor for systemic disease. Other Pasteurella spp. can be agents of systemic infection (P. pneumotropica) and genital tract-associated disease (P. bettyae). TABLE 30-1 Epidemiology of Selected Pasteurella spp. and Similar Organisms TABLE 30-2 Pathogenesis and Spectrum of Disease of Selected Pasteurella spp. and Similar Organisms An unusual feature of the organisms considered in this chapter is that most are susceptible to penicillin. Although most other clinically relevant Gram-negative bacilli are intrinsically resistant to penicillin, it is the drug of choice for infections involving P. multocida and several other species listed in Table 30-3. The general therapeutic effectiveness of penicillin and the lack of resistance to this agent among Pasteurella spp. suggest that in vitro susceptibility testing is typically not indicated. This is especially true with isolates emanating from bite wounds. Moreover, bite wounds can be complicated by polymicrobial infection. In this case, the empiric therapy directed toward multiple agents is generally also effective against Pasteurella spp. As a result, antimicrobial susceptibility testing for Pasteurella spp. may have greater utility for isolates recovered from sterile sources (blood, deep tissue) and from respiratory specimens obtained from immunocompromised patients. TABLE 30-3 Antimicrobial Therapy and Susceptibility Testing for Pasteurella spp. and Similar Organisms No special considerations are required for specimen collection and transport of the organisms discussed in this chapter. Refer to Table 5-1 for general information on specimen collection and transport. No special considerations are required for processing of the organisms discussed in this chapter. Refer to Table 5-1 for general information on specimen processing.
Pasteurella and Similar Organisms
Epidemiology, Spectrum of Disease, and Antimicrobial Therapy
Organism
Habitat (Reservoir)
Mode of Transmission
P. multocida, other Pasteurella spp.
Commensal found in nasopharynx and gastrointestinal tract of wild and domestic animals; potential upper respiratory commensal in humans having extensive occupational exposure to animals
Bite or scratch from variety of veterinary hosts (usually feline or canine); infections may be associated with non-bite exposure to animals; less commonly, infections may occur without history of animal exposure
S. indologenes
Unknown; rarely encountered in clinical specimens but may be part of human flora
Unknown
Organism
Virulence Factors
Spectrum of Disease and Infections
P. bettyae
Unknown
Genital tract infection; neonatal infection
P. multocida subsp. multocida
Endotoxin, cytotoxin, surface adhesins, capsule associated with P. multocida
Focal soft tissue infection; chronic respiratory infection, usually in patients with preexisting chronic lung disease and heavy exposure to animals; systemic disease (hematogenous dissemination) such as meningitis, endocarditis, osteomyelitis, dialysis-associated peritonitis, septicemia
P. multocida subsp. septica
Unknown
Focal soft tissue infection
P. pneumotropica
Unknown
Rare systemic infection
S. indologenes
Unknown
Rare ocular infection
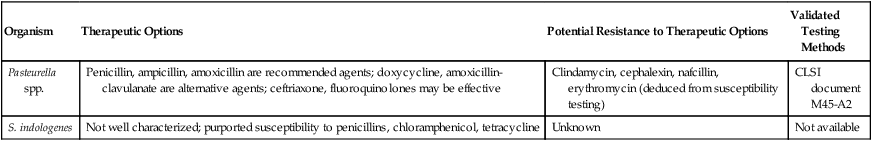
Organism
Therapeutic Options
Potential Resistance to Therapeutic Options
Validated Testing Methods
Pasteurella spp.
Penicillin, ampicillin, amoxicillin are recommended agents; doxycycline, amoxicillin-clavulanate are alternative agents; ceftriaxone, fluoroquinolones may be effective
Clindamycin, cephalexin, nafcillin, erythromycin (deduced from susceptibility testing)
CLSI document M45-A2
S. indologenes
Not well characterized; purported susceptibility to penicillins, chloramphenicol, tetracycline
Unknown
Not available
Laboratory Diagnosis
Specimen Collection and Transport
Specimen Processing
![]()
Stay updated, free articles. Join our Telegram channel

Full access? Get Clinical Tree


Basicmedical Key
Fastest Basicmedical Insight Engine
