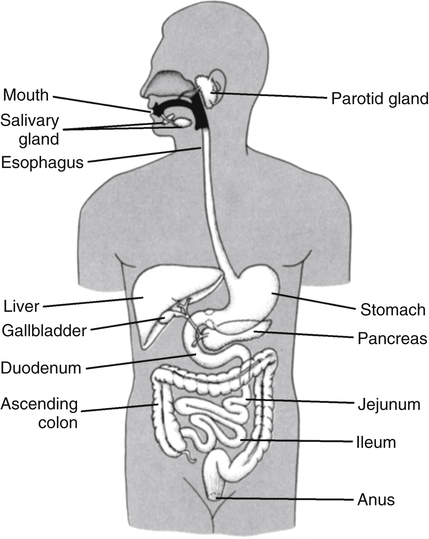
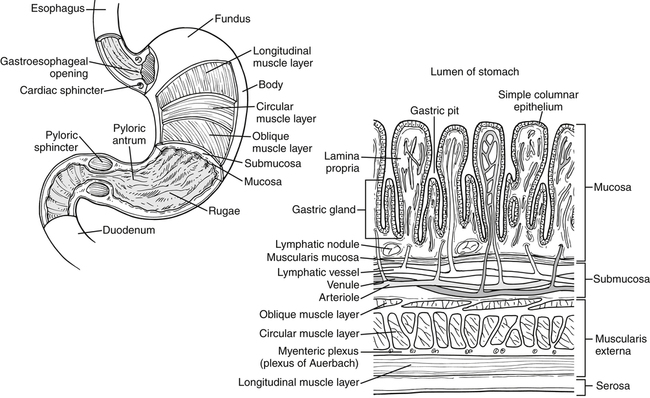
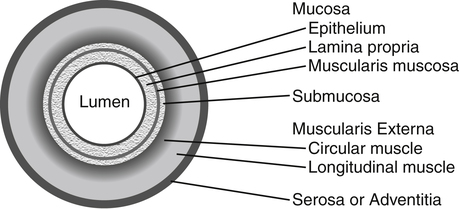
Alan B.R. Thomson, MD, PhD, and Patrick Tso, PhD The GI tract extends from the mouth to the anus and consists of a long muscular tube with a continuous lumen that opens to the exterior at both ends (Figure 7-1). It has openings for the entry of secretions from the salivary glands, the liver, and the pancreas. The GI system includes the oral cavity, pharynx, esophagus, stomach, small intestine, large intestine, and rectum, as well as accessory organs (salivary glands, pancreas, liver, and gallbladder) that provide essential secretions. Once past the oral cavity, most of the digestive tract has a distinct anatomical structure that is typical of tubular organs (Figure 7-2). Although there are variations along the GI tract, its wall generally comprises four basic tissue layers surrounding the lumen. The digestion and absorption of nutrients are both neurally and hormonally regulated. GI hormones are secreted by enteroendocrine cells located throughout the GI tract (Table 7-1). These enteroendocrine cells do not form endocrine glands but rather secrete GI hormones that exert local effects on the GI tract via paracrine and autocrine actions. They also affect other tissues via endocrine actions after entering the circulation. GI hormones play important roles in regulating GI functions, such as gut motility and the secretion of hydrochloric acid (HCl). The actions of these hormones on other tissues, such as brain, pancreas, liver, and gallbladder, also affect the regulation of the GI tract by these tissues. TABLE 7-1 The Endocrine Cells of the GI Tract GI, Gastrointestinal; HCI, hydrochloric acid. The process of digestion and absorption begins with the ingestion of food. A number of factors are involved in regulation of food intake, and the complex process of this regulation is discussed in Chapter 22. In the oral cavity, chewing involves the cutting and grinding of food by the teeth and the crushing of the food bolus into smaller particles. The process of chewing also mixes food with saliva. Secretion of saliva by the salivary glands is stimulated by the parasympathetic nervous system in response to the sight, smell, and taste of food and mechanical stimulation of the oral cavity. The stomach has four gross anatomical regions: cardia, fundus, body (or corpus), and pyloric antrum (Figure 7-3). The body, which is the largest part of the stomach, extends from the cardia to the pylorus, the sections that connect with the esophagus and the small intestine, respectively. The fundus is the upper end of the stomach that lies above the cardia and superior to the opening of the esophagus. The pylorus is sometimes described as having two sections: a pyloric antrum that narrows into the pyloric canal. The pyloric canal is surrounded by thickened, circular smooth muscle fibers to form a pyloric sphincter at the opening of the pyloric canal into the duodenum; this sphincter helps control the evacuation of food from the stomach. The lining of the stomach has folds or plaits called rugae, which are most pronounced toward the pyloric end of the stomach. They flatten and disappear as the stomach is filled and distends.
Overview of Digestion and Absorption
General Structure and Function of the Gi Tract
Basic Anatomical Structure of the Gi Tract
General Mechanisms for Regulation of Gi Tract Function
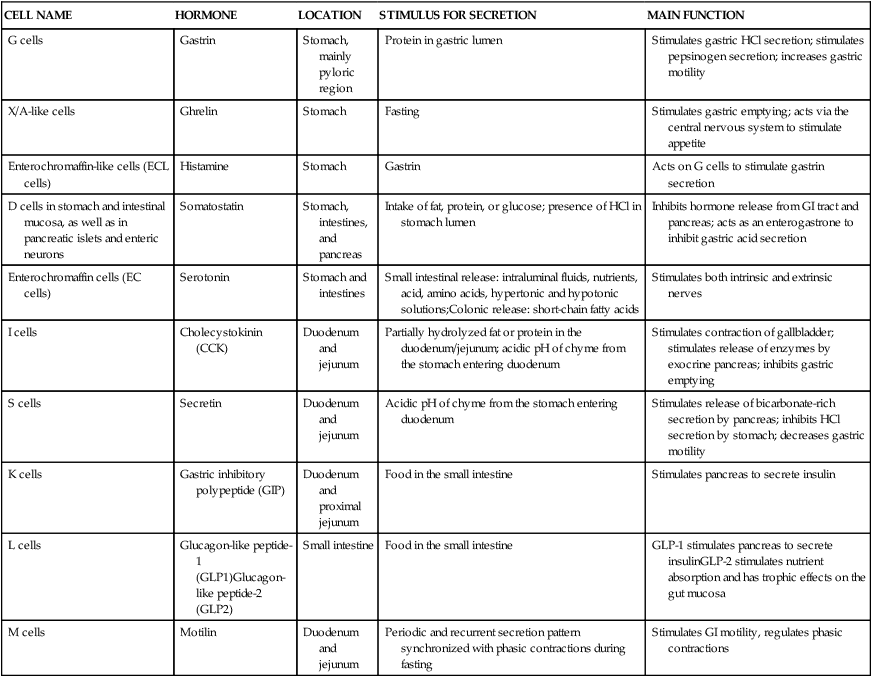
GI Hormones
CELL NAME
HORMONE
LOCATION
STIMULUS FOR SECRETION
MAIN FUNCTION
G cells
Gastrin
Stomach, mainly pyloric region
Protein in gastric lumen
Stimulates gastric HCl secretion; stimulates pepsinogen secretion; increases gastric motility
X/A-like cells
Ghrelin
Stomach
Fasting
Stimulates gastric emptying; acts via the central nervous system to stimulate appetite
Enterochromaffin-like cells (ECL cells)
Histamine
Stomach
Gastrin
Acts on G cells to stimulate gastrin secretion
D cells in stomach and intestinal mucosa, as well as in pancreatic islets and enteric neurons
Somatostatin
Stomach,
intestines, and
pancreas
Intake of fat, protein, or glucose; presence of HCl in stomach lumen
Inhibits hormone release from GI tract and pancreas; acts as an enterogastrone to inhibit gastric acid secretion
Enterochromaffin cells (EC cells)
Serotonin
Stomach and intestines
Small intestinal release: intraluminal fluids, nutrients, acid, amino acids, hypertonic and hypotonic solutions;Colonic release: short-chain fatty acids
Stimulates both intrinsic and extrinsic nerves
I cells
Cholecystokinin (CCK)
Duodenum and jejunum
Partially hydrolyzed fat or protein in the duodenum/jejunum; acidic pH of chyme from the stomach entering duodenum
Stimulates contraction of gallbladder; stimulates release of enzymes by exocrine pancreas; inhibits gastric emptying
S cells
Secretin
Duodenum and jejunum
Acidic pH of chyme from the stomach entering duodenum
Stimulates release of bicarbonate-rich secretion by pancreas; inhibits HCl secretion by stomach; decreases gastric motility
K cells
Gastric inhibitory polypeptide (GIP)
Duodenum and proximal jejunum
Food in the small intestine
Stimulates pancreas to secrete insulin
L cells
Glucagon-like peptide-1 (GLP1)Glucagon-like peptide-2 (GLP2)
Small intestine
Food in the small intestine
GLP-1 stimulates pancreas to secrete insulinGLP-2 stimulates nutrient absorption and has trophic effects on the gut mucosa
M cells
Motilin
Duodenum and jejunum
Periodic and recurrent secretion pattern synchronized with phasic contractions during fasting
Stimulates GI motility, regulates phasic contractions
The Upper Gi System
The Oral Cavity
The Stomach
Basic Anatomy of the Stomach
![]()
Stay updated, free articles. Join our Telegram channel

Full access? Get Clinical Tree


Overview of Digestion and Absorption