Chapter 28 Other Anti-Infective Drugs
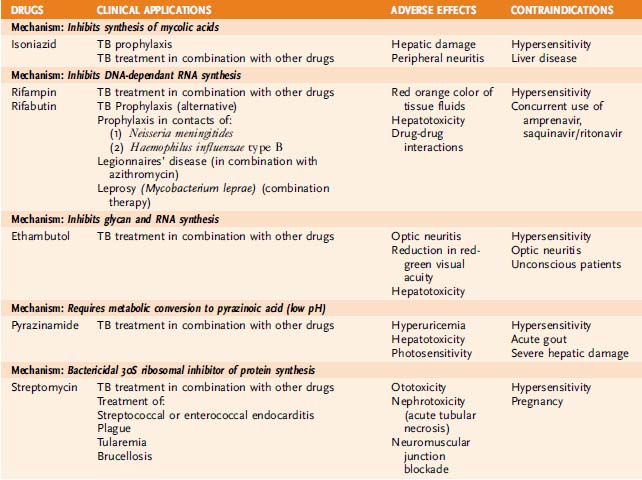
TABLE 28-1 Management of Tuberculosis
| Therapeutic Goal and Drug-Related Patient Features | Initial Drug Treatment | Subsequent Drug Treatment |
|---|---|---|
| Prevention of Tuberculosis | ||
| Not resistant to isoniazid | Isoniazid (6mo) | None |
| HIV-negative; resistant to isoniazid; >50 years of age | Rifampin (6mo) | None |
| HIV-positive | Rifampin⁎ or rifabutin (12 months) | None |
| Treatment of Tuberculosis | ||
| Not resistant to isoniazid | Combination of isoniazid, rifampin, ethambutol, and pyrazinamide for 2 months | Combination of isoniazid and rifampin (4 more months if HIV-negative or 7 more months if HIV-positive) |
| Possibly resistant to isoniazid | Combination of isoniazid, rifampin, pyrazinamide, and either ethambutol or streptomycin (6 months) | Individualized therapy based on microbial susceptibility testing |
| Resistant to multiple drugs† | Combination of at least four drugs believed to be active in patient population (6 months) | Individualized therapy based on microbial susceptibility testing |
HIV, human immunodeficiency virus.
⁎ In HIV-infected patients, substitution of rifabutin for rifampin minimizes drug interactions with protease inhibitors and nucleoside reverse transcriptase inhibitors.
† Patients suspected of having multidrug resistance include those from certain demographic populations, those who have failed to respond to previous treatment, and those who have experienced a relapse of tuberculosis.
BOX 28-2 Antiviral Drugs
Antiretroviral Drugs
Nucleoside Reverse Transcriptase Inhibitors (NRTIs)
Nucleotide Reverse Transcriptase Inhibitor
Nonnucleoside Reverse Transcriptase Inhibitors (NNRTIs)
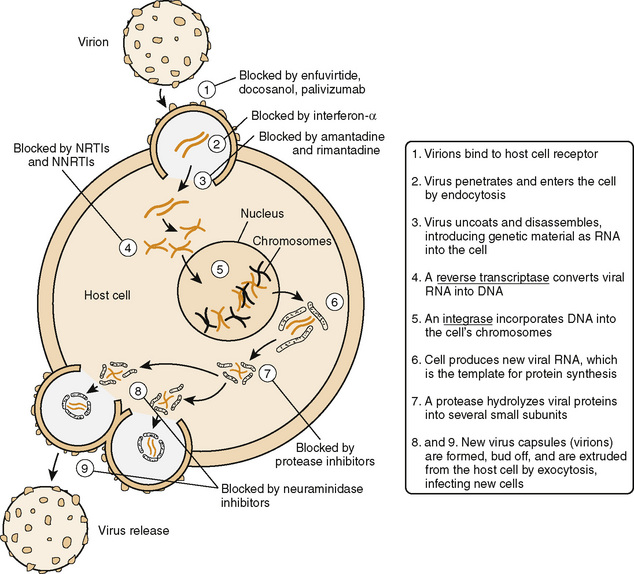
(From Wecker L, et al.: Brody’s Human Pharmacology, 5th ed. Philadelphia, Mosby, 2010, Figure 51-2.)
Stay updated, free articles. Join our Telegram channel

Full access? Get Clinical Tree