Solitary circumscribed neuroma (“palisaded encapsulated neuroma”) represents spontaneous proliferation of peripheral nerve fibers
 Multiple mucosal neuromas associated with multiple endocrine neoplasia syndrome (type 2B) represents rare autosomal dominant condition
Multiple mucosal neuromas associated with multiple endocrine neoplasia syndrome (type 2B) represents rare autosomal dominant condition Epithelial sheath neuroma represents proliferation of enlarged dermal nerves ensheathed by squamous epithelium
Epithelial sheath neuroma represents proliferation of enlarged dermal nerves ensheathed by squamous epithelium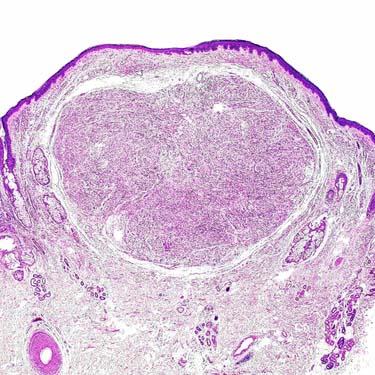
Solitary circumscribed neuroma [“palisaded encapsulated neuroma” (PEN)] represents a well-circumscribed, partially encapsulated, dermal-based neural neoplasm. Note the absence of overlying epidermal hyperplasia.
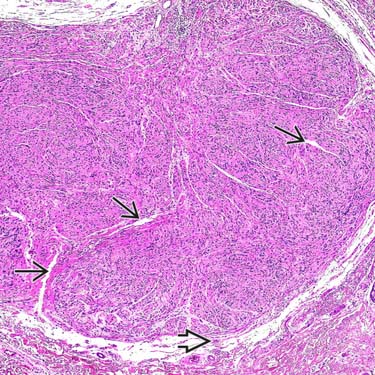
Solitary circumscribed neuroma is a circumscribed, sometimes partly encapsulated dermal lesion composed of Schwann cells and associated axons. Characteristic clefts
 and a small, preexisting nerve at the base of the lesion
and a small, preexisting nerve at the base of the lesion  can be seen.
can be seen.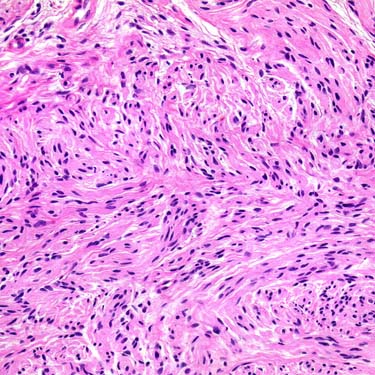
The neoplastic Schwann cells contain ill-defined, pale, eosinophilic cytoplasm and cytologically bland spindled nuclei with evenly distributed chromatin. No prominent cytologic atypia and no increased mitoses are present.
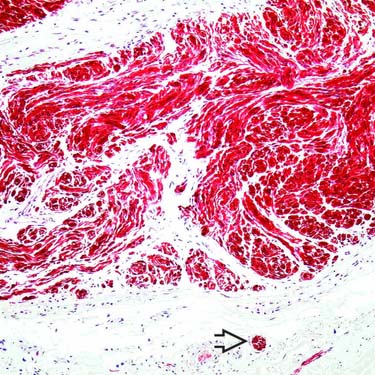
Solitary circumscribed neuroma is composed mainly of S100-positive Schwann cells. Preexisting peripheral nerves
 can often be seen at the base of these lesions.
can often be seen at the base of these lesions.TERMINOLOGY
Definitions
• Proliferation of peripheral nerve fibers in which ratio of axons to Schwann cell fascicles is in nearly equal proportions
 Solitary circumscribed neuroma [“palisaded encapsulated neuroma” (PEN)] is spontaneous proliferation of peripheral nerve fibers
Solitary circumscribed neuroma [“palisaded encapsulated neuroma” (PEN)] is spontaneous proliferation of peripheral nerve fibers
 Multiple mucosal neuromas associated with multiple endocrine neoplasia (MEN) syndrome (type 2B), rare autosomal dominant condition
Multiple mucosal neuromas associated with multiple endocrine neoplasia (MEN) syndrome (type 2B), rare autosomal dominant condition
 Solitary circumscribed neuroma [“palisaded encapsulated neuroma” (PEN)] is spontaneous proliferation of peripheral nerve fibers
Solitary circumscribed neuroma [“palisaded encapsulated neuroma” (PEN)] is spontaneous proliferation of peripheral nerve fibers Multiple mucosal neuromas associated with multiple endocrine neoplasia (MEN) syndrome (type 2B), rare autosomal dominant condition
Multiple mucosal neuromas associated with multiple endocrine neoplasia (MEN) syndrome (type 2B), rare autosomal dominant conditionCLINICAL ISSUES
Epidemiology
Site
• Epithelial sheath neuroma




Stay updated, free articles. Join our Telegram channel

Full access? Get Clinical Tree




























