Neuroma
Thomas Mentzel, MD
Key Facts
Terminology
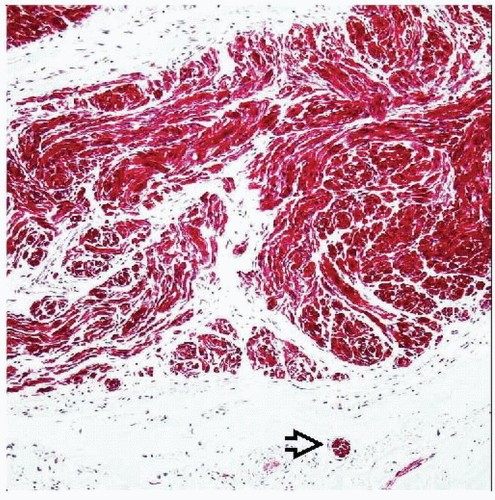
Neuroma represents proliferation of peripheral nerve fibers in which ratio of axons to Schwann cell fascicles approaches 1:1
Solitary circumscribed neuroma (“palisaded encapsulated neuroma”) represents spontaneous proliferation of peripheral nerve fibers
Multiple mucosal neuromas associated with multiple endocrine neoplasia syndrome (type 2B) represents rare autosomal dominant condition
Traumatic neuroma represents post-traumatic proliferation of peripheral nerve fibers
Morton neuroma represents degenerative neural change with reactive fibrosis on foot
Pacinian neuroma represents painful hyperplasia of Pacinian bodies on finger
Epithelial sheath neuroma represents proliferation of enlarged dermal nerves ensheathed by squamous epithelium
Clinical Issues
Solitary circumscribed neuroma occurs predominantly on face
Morton neuroma arises usually in distal parts of peripheral nerves of 3rd and 4th os metatarsale
Microscopic Pathology
Proliferation of peripheral nerve fibers
Proliferation of S100(+) Schwann cells
Proliferation of neurofilament(+) axons
No cytologic atypia
No increased proliferative activity
Perineural fibrosis in traumatic neuroma
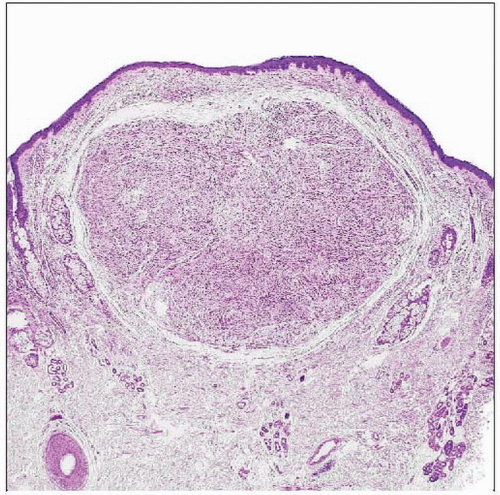 Solitary circumscribed neuroma (“palisaded encapsulated neuroma”) represents a well-circumscribed, partly encapsulated, dermal, neural neoplasm. |
TERMINOLOGY
Definitions
Represents proliferation of peripheral nerve fibers in which ratio of axons to Schwann cell fascicles approaches 1:1
Solitary circumscribed neuroma (“palisaded encapsulated neuroma”) represents spontaneous proliferation of peripheral nerve fibers
Multiple mucosal neuromas associated with multiple endocrine neoplasia syndrome (type 2B) represent rare autosomal dominant condition
Traumatic neuroma represents post-traumatic proliferation of peripheral nerve fibers
Morton neuroma represents degenerative neural change with reactive fibrosis on the foot
Pacinian neuroma represents painful hyperplasia of pacinian bodies on finger
Epithelial sheath neuroma represents proliferation of enlarged dermal nerves ensheathed by squamous epithelium
ETIOLOGY/PATHOGENESIS
Developmental Anomaly
Multiple mucosal neuromas in multiple endocrine neoplasia syndrome
Represents rare autosomal dominant condition
Also includes medullary carcinoma of thyroid, pheochromocytoma, and somatic abnormalities
Mucosal neuromas have been rarely reported without any other systemic features of the syndrome
Environmental Exposure
Traumatic neuroma
Amputation neuroma represents painful, reactive proliferation of nerve fibers after amputation
Supernumerary digit represents proliferation of nonencapsulated nerve fibers after intrauterine or perinatal amputation of supernumerary digits
Lesion on penis may occur after circumcision
Morton neuroma
Degenerative damage of peripheral nerves
CLINICAL ISSUES
Epidemiology
Age
Solitary circumscribed neuroma is most common in 5th and 7th decades
Gender
Solitary circumscribed neuroma occurs in equal ratio in both genders
Site
Solitary circumscribed neuroma
Majority (90%) located on face
Rare in other anatomic locations
Mucosal involvement has been reported rarely
Morton neuroma
Usually in distal parts of peripheral nerves of 3rd and 4th os metatarsale
Pacinian neuroma
Usually on fingers
Presentation
Painful or painless mass
Slow growing
Treatment
Surgical approaches
Simple excision is curative
Prognosis
Biologically benign lesions
MACROSCOPIC FEATURES
General Features
Raised dermal lesions
MICROSCOPIC PATHOLOGY
Stay updated, free articles. Join our Telegram channel

Full access? Get Clinical Tree