Nephrogenic Adenoma
Jesse K. McKenney, MD
Mahul B. Amin, MD
Key Facts
Etiology/Pathogenesis
Many are secondary to urothelial injury
Clinical Issues
Usually incidental microscopic findings
May have irritative symptoms from underlying inflammatory process
Macroscopic Features
May appear as papillary-polypoid mass or irregular flat velvety lesion
Microscopic Pathology
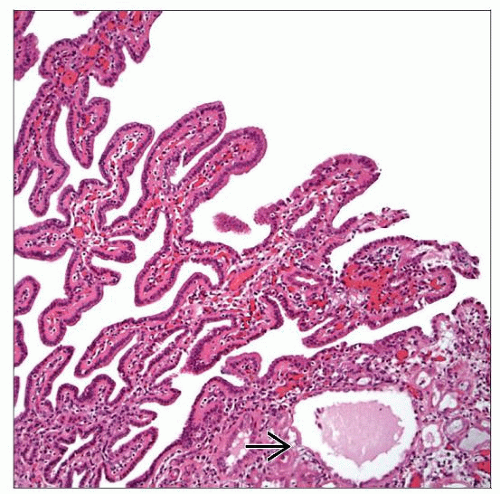
Papillary cores lined by single cuboidal epithelial layer
Tubular pattern with “hobnail” arrangement of epithelial cells
Rare cases have myxoid stroma and cording or spindling of cells (fibromyxoid pattern)
Rare cases have diffuse sheet-like growth
Thick basement membrane/hyalinized sheath may underlie epithelium
Degenerative-type atypia may be present
Ancillary Tests
Express cytokeratins, pax-2, and pax-8
May express PSA, PAP, and AMACR
Top Differential Diagnoses
Clear cell adenocarcinoma of bladder
Prostatic adenocarcinoma
Urothelial carcinoma with glandular differentiation
Nested or tubular variant of urothelial carcinoma
Papillary urothelial neoplasia
TERMINOLOGY
Abbreviations
Nephrogenic adenoma (NA)
Synonyms
Nephrogenic metaplasia
Definitions
Benign epithelial lesion of urinary tract characterized by tubular, glandular, &/or papillary growth pattern that commonly occurs secondary to injury of urothelium or renal transplant
ETIOLOGY/PATHOGENESIS
Injury of Urothelium
Many are secondary to urothelial injury
Infections, calculi, instrumentation, intravesical bacillus Calmette-Guérin (BCG) therapy, and surgery
Renal Transplant
Frequent in these patients; supports proposed renal tubular origin
CLINICAL ISSUES
Presentation
Usually incidental microscopic finding
Difficult to attribute irritative voiding symptoms to NA given other associated inflammatory findings
Treatment
Simple curetting for larger lesions
Prognosis
Completely benign, but recurrence is described
MACROSCOPIC FEATURES
General Features
May appear as papillary-polypoid mass or irregular, flat, velvety lesion
MICROSCOPIC PATHOLOGY
Histologic Features
Broad architectural spectrum
Tubular/glandular pattern most common
Low-power architecture may appear pseudoinfiltrative
Exophytic papillary cores lined by single cuboidal epithelial layer
Lining cells may have “hobnail” appearance
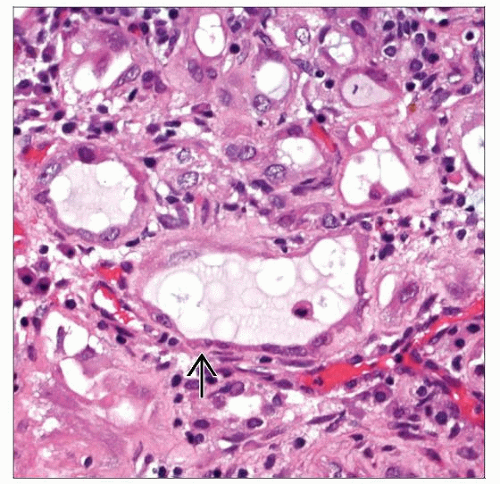
Cystic pattern with dilated tubules lined by variably atrophic epithelium
Single cells with minute lumen may closely mimic blood vessels or signet ring cells
Rare cases have myxoid stroma and cording or spindling of cells (fibromyxoid pattern)
Rare cases have diffuse sheet-like growth
Thick basement membrane/hyalinized sheath may underlie epithelium
Cytoplasm varies from eosinophilic to clear
Nucleoli may be present
Degenerative-type atypia may be present
Predominant Pattern/Injury Type
Glandular
Predominant Cell/Compartment Type
Epithelial
ANCILLARY TESTS
DIFFERENTIAL DIAGNOSIS
Stay updated, free articles. Join our Telegram channel

Full access? Get Clinical Tree