NASH
Matthew M. Yeh, MD, PhD
Key Facts
Etiology/Pathogenesis
Associated conditions
Diabetes
Obesity
Hyperlipidemia
Dyslipidemia
Drugs
Malabsorption, malnutrition
Clinical Issues
Patients often have metabolic syndrome
Transaminases usually elevated
Microscopic Pathology
NASH in pediatric population has different injury pattern
Inflammation, fibrosis accentuated in portal region
Ballooning degeneration and perisinusoidal fibrosis not obvious
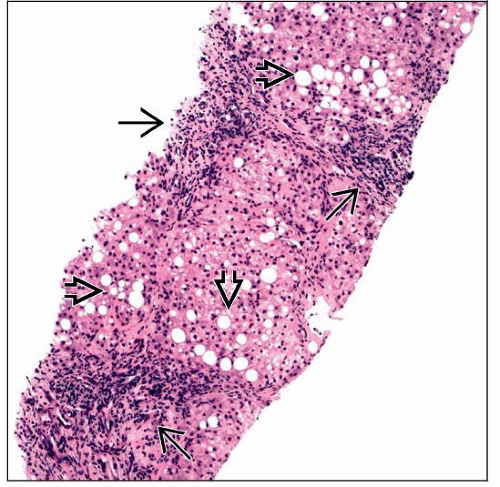
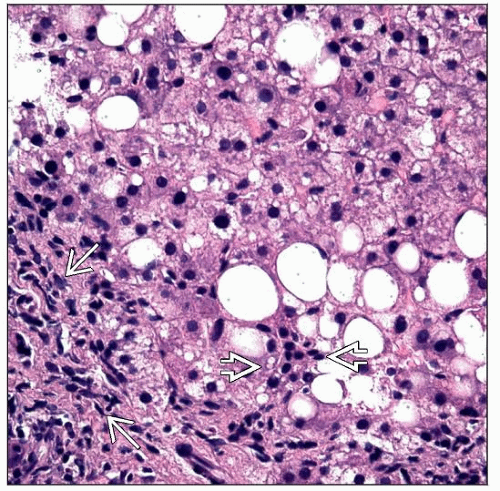
Steatosis (predominantly macrovesicular)
Ballooned hepatocytes
Mallory-Denk bodies
Megamitochondria
Glycogenated nuclei
Top Differential Diagnoses
Steatosis without specific liver injury
Chronic hepatitis B
Chronic hepatitis C
Autoimmune hepatitis
Glycogenic hepatopathy
Microvesicular steatosis
Wilson disease
Alcoholic hepatitis
TERMINOLOGY
Abbreviations
Nonalcoholic steatohepatitis (NASH)
Definitions
Steatosis, inflammation, and liver cell injury in absence of excessive alcohol use history
ETIOLOGY/PATHOGENESIS
Mechanism
Abnormal accumulation of lipids in hepatocytes provides source of oxidative stress
Leads to injury/inflammation
Subsequent activation of TGF-β and hepatic stellate cells results in liver fibrosis
Associated Conditions
Diabetes, obesity, hyperlipidemia, dyslipidemia, drugs, malabsorption, malnutrition
CLINICAL ISSUES
Presentation
Hepatomegaly
Metabolic syndrome
Central (visceral) obesity
Type 2 diabetes
Dyslipidemia (hypertriglyceridemia and low HDL)
Systemic hypertension
Laboratory Tests
Elevated transaminases
Treatment
Management of associated metabolic conditions (diabetes, hyperlipidemia, and dyslipidemia)
Exercise
Dietary control and weight reduction
Prognosis
May lead to liver fibrosis, cirrhosis, and hepatocellular carcinoma
MICROSCOPIC PATHOLOGY
Histologic Features
Steatosis (predominantly macrovesicular)
Portal inflammatory infiltrate
Lymphocytes, pigmented macrophages, Kupffer cells
Inflammation typically accentuated in portal region, unlike typical zone 3 injury pattern seen in adult nonalcoholic fatty liver disease (NAFLD)/NASH
Stay updated, free articles. Join our Telegram channel

Full access? Get Clinical Tree