Metastatic Kaposi Sarcoma
Carlos E. Bueso-Ramos, MD, PhD
Key Facts
Etiology/Pathogenesis
HHV8 infection plays critical role in most cases
Interacts with other factors
Clinical Issues
Multiple presentations of KS
Sporadic (Mediterranean countries)
Endemic (equatorial Africa)
Iatrogenic (e.g., post transplantation)
Epidemic (HIV-associated)
Common sites: Skin, lymph nodes, gastrointestinal tract
Often multifocal
Microscopic Pathology
Wide histologic spectrum
Lacework of thin-walled capillaries
Ectatic vessels without pericytes
Cleft-like vascular spaces, nonbranching
Well-formed bundles and whorls of spindle cells
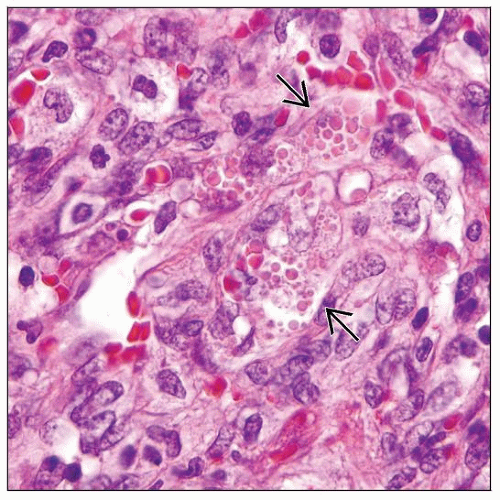
Extravasated erythrocytes
Intracytoplasmic eosinophilic hyaline globules
Plasma cells and small lymphocytes common
Hemosiderin-laden macrophages common
Ancillary Tests
Immunohistochemistry
HHV8(+), CD31(+), CD34(+)
FVIIIRAg(+) in well-differentiated tumors
Top Differential Diagnoses
Bacillary angiomatosis
Vascular transformation of lymph node sinuses
Angiosarcoma
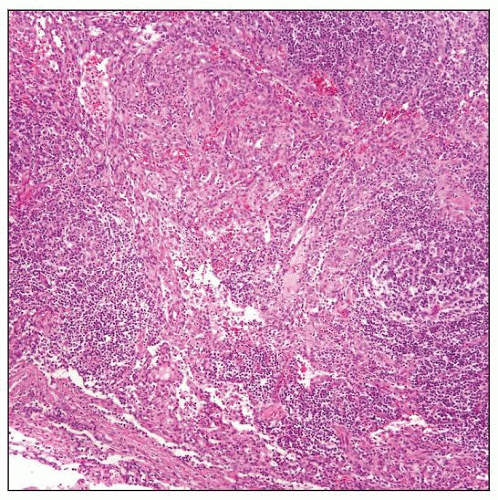 Kaposi sarcoma (KS) associated with multicentric Castleman disease. In the center of the field, focal KS is present among hyaline-vascular follicles. KS is predominantly sinusoidal. |
TERMINOLOGY
Abbreviations
Kaposi sarcoma (KS)
Human herpes virus type 8 (HHV8)
Definitions
Kaposi sarcoma (KS): Distinctive type of vascular neoplasm that can involve any body site
Almost always associated with HHV8 infection
Occurs sporadically at low frequency but is much more frequent in setting of immunosuppression
ETIOLOGY/PATHOGENESIS
Infectious Agents
HHV-8, a Gammaherpesviridae, is uniformly expressed in KS
a.k.a. Kaposi sarcoma-associated herpes virus (KSHV)
HHV8 establishes latent infection in most infected KS cells; lytic replication occurs in small subset of KS cells
Transmission via sexual and nonsexual routes
Saliva contains shed epithelial cells infected by HHV-8
Pathogenesis
KS may be multicentric neoplasm at time of conception
HHV8 interacts with other factors in pathogenesis
e.g., HIV TAT protein has mitogenic and modulating effects on KS cells
Angiogenic factors and cytokines are likely to be involved
Viral proteins expressed during both latent and lytic phases of viral life cycle contribute to KS pathogenesis
Cell of Origin
KS involves progenitor cell from either blood vessel or lymphatic endothelia
CD34(+) suggests progenitor endothelial cells
CLINICAL ISSUES
Epidemiology
Incidence
Varies greatly depending on presentation
Age
Varies depending on presentation
Gender
Male predominance in all types of KS
Ethnicity
Sporadic cases more common around Mediterranean sea
Site
Skin, mucosal surfaces, lymph nodes, and all internal organs
Skin most common site
Oral mucosa and gastrointestinal tract are frequent sites
Lymph node involvement usually associated with skin disease
Rare patients reported with only lymph node disease
Presentation
Presentation of KS can be divided into 4 clinical subsets
Sporadic (classic)
Involves distal extremities of elderly patients
Common in men of Mediterranean and Jewish Ashkenazi origin
Clinically indolent
Subset of cases can be clinically aggressive; associated with coexistent non-Hodgkin lymphoma
In USA, 0.2 per 100,000 tumors
African (endemic)
Sub-Saharan central Africa
9% of malignant neoplasms in Uganda
Children often have generalized lymphadenopathy and aggressive clinical course
Subset of aggressive cases likely related to HIV infection
Middle-aged adults have KS on extremities; more indolent
Iatrogenic immunosuppression
KS arises more frequently after organ transplantation or steroid therapy
128x increased incidence after kidney transplantation
Usually clinically indolent; can be aggressive
AIDS-associated (epidemic)
451x increased incidence in setting of AIDS infection
More common in homosexuals; less frequent in IV drug users and hemophiliacs
Natural History
In patients who die, KS can be widespread at autopsy
Organs: Virtually any organ can be involved
Lungs common
Treatment
Drugs
Highly active antiretroviral therapy (HAART)
Prognosis
Depends, in large part, on clinical presentation and associated illness
HAART therapy has reduced frequency and improved prognosis for epidemic KS
MACROSCOPIC FEATURES
Lymph Nodes
Enlarged and matted
Skin
Size range: 0.1 cm up to 3 cm
Pink-red or purple lesions
Patches, plaques, or nodules
Stay updated, free articles. Join our Telegram channel

Full access? Get Clinical Tree