• One of every four American adults and children has been diagnosed with a mental condition. • More than 30% of the 20 top-selling medications are for psychiatric disorders. • The fourth most common diagnostic category for inpatient admissions is substance-related mental disorders. • Approximately 40 million Americans are diagnosed with anxiety. • The number of discharges for patients with substance-related mental health disorders has sharply escalated, from 20,000 in 1998 to 110,000 in 2008. • Approximately 7.5 million Americans are classified as mentally retarded. • Given these statistics, the terminology related to mental and behavioral disorders is content that cannot be ignored. Similar to previous chapters, this chapter examines disorders that result when an individual has a maladaptive response to his or her environment (internal or external). (See Chapter 11 for an explanation of the anatomy and physiology of the brain and nervous system.) However, even though some mental illnesses have organic causes in which neurotransmitters and other known brain functions play a role, there is no mental “anatomy” per se. Instead, behavioral health is a complex interaction among an individual’s emotional, physical, mental, and behavioral processes in an environment that includes cultural and spiritual influences. Terms Related to Signs and Symptoms Involving Cognition, Perception, Emotional State, and Behavior and Speech and Voice (R4Ø-R49) • Blunted: moderately reduced range of affect. • Flat: the diminishment or loss of emotional expression sometimes observed in schizophrenia, mental retardation, and some depressive disorders. • Labile: multiple, abrupt changes in affect seen in certain types of schizophrenia and bipolar disorder. • Full/wide range of affect: generally appropriate emotional response. Terms Related to Mental Disorders Due to Known Physiological Conditions (FØ1-FØ9) Terms Related to Mental and Behavioral Disorders Due to Psychoactive Substance Use (F1Ø-F19) Terms Related to Schizophrenia, Schizotypal and Delusional, and Other Non-Mood Psychotic Disorders (F2Ø-F29) Terms Related to Mood (Affective) Disorders (F3Ø-F39) Terms Related to Anxiety, Dissociative, Stress-Related, Somatoform, and Other Nonpsychotic Mental Disorders (F4Ø-F48)
Mental and Behavioral Disorders
 Recognize and use terms related to the pathology of mental and behavioral health.
Recognize and use terms related to the pathology of mental and behavioral health.
 Recognize and use terms related to the procedures for mental and behavioral health.
Recognize and use terms related to the procedures for mental and behavioral health.
Introduction to Mental and Behavioral Health
Pathology

Affect is observable demonstration of emotion that can be described in terms of quality, range, and appropriateness. The following list defines the most significant types of affect encountered in behavioral health:
Term
Word Origin
Definition
amnesia
Inability to remember either isolated parts of the past or one’s entire past; may be caused by brain damage or severe emotional trauma.
anhedonia
an- no, not, without
hedon/o pleasure
-ia condition
Absence of the ability to experience either pleasure or joy, even in the face of causative events.
confabulation
Effort to conceal a gap in memory by fabricating detailed, often believable stories. Associated with alcohol abuse.
dyscalculia
dys- difficult
calcul/o stone
-ia condition
Difficulty with performing mathematical calculations.
dysphoria
dys- abnormal
phor/o to carry, to bear
-ia condition
Generalized negative mood characterized by depression.
echolalia
echo- reverberation
-lalia condition of babbling
Repetition of words or phrases spoken by others.
euphoria
eu- good, well
phor/o to carry, to bear
-ia condition
Exaggerated sense of physical and emotional well-being not based on reality, disproportionate to the cause, or inappropriate to the situation.
hallucination
Any unreal sensory perception that occurs with no external cause.
hyperkinesis
hyper- excessive
-kinesis movement
Excessive movement and activity.
stupor
From the Latin term for “numbness,” a stupor is a state of near unconsciousness.
Term
Word Origin
Definition
dementia
de- down, lack of
ment/o mind
-ia condition
Lack of normal mental functioning due to injury or disease. May include changes to personality as well as memory and reasoning.
Term
Word Origin
Definition
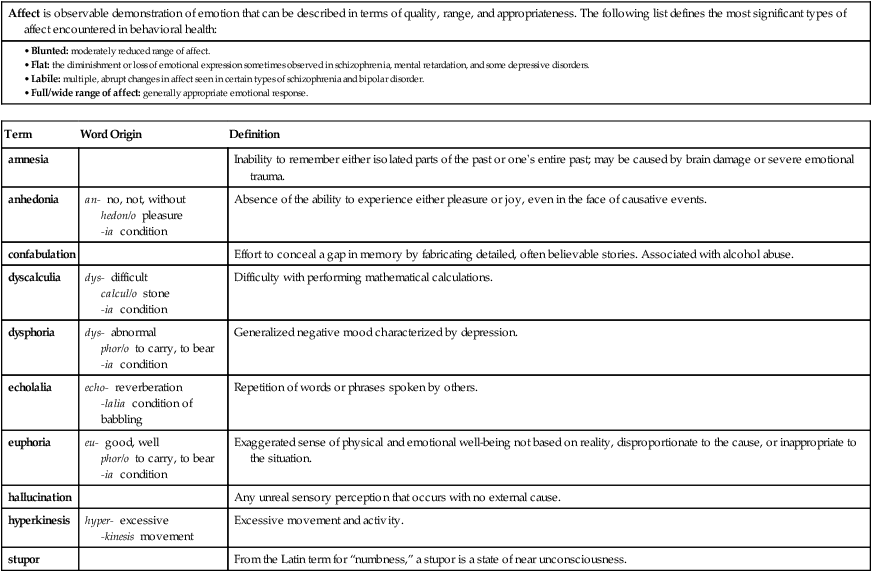
delirium tremens (DTs)
Acute and sometimes fatal delirium induced by the cessation of ingesting excessive amounts of alcohol over a long period.
dependence
Difficulty in controlling use of a drug.
intoxication
in- in
toxic/o poison
-ation process of
Episode of behavioral disturbance following ingestion of alcohol or psychotropic drugs. ICD-10-CM provides a code for blood alcohol level.
withdrawal state
Group of symptoms that occur during cessation of the use of a regularly taken drug.

Term
Word Origin
Definition
catatonia
cata- down
ton/o tension
-ia condition
Paralysis or immobility from psychological or emotional, rather than physical, causes.
catatonic schizophrenia
cata- down
ton/o tension
-ic pertaining to
schiz/o split
phren/o mind
-ia condition
Also called schizophrenic catalepsy. This form of schizophrenia is dominated by prominent psychomotor disturbances that may alternate between extremes, such as hyperkinesis and stupor, and may be accompanied by a dreamlike (oneiric) state and hallucinations.
delirium
Condition of confused, unfocused, irrational agitation. In mental disorders, agitation and confusion may also be accompanied by a more intense disorientation, incoherence, or fear, and illusions, hallucinations, and delusions.
hebephrenia
hebe goddess of youth
phren/o mind
-ia condition
Although more often referred to as disorganized schizophrenia, hebephrenia was named for its original association with initial occurrence at the time of puberty. It is characterized by prominent affective changes, fleeting and fragmentary delusions and hallucinations, and irresponsible and unpredictable behaviors. Shallow, inappropriate mood, flighty thoughts, social isolation, and incoherent speech are also present.
oneirism
oneir/o dream
-ism state
A state of a dreamlike hallucination.
paranoia
para- abnormal
-noia condition of the mind
A type of delusional disorder, paranoia includes the inaccurate perception of suspicious thinking. Also called delusional disorder, or late paraphrenia.
psychosis
psych/o mind
-osis abnormal condition
Disassociation with or impaired perception of reality; may be accompanied by hallucinations, delusions, incoherence, akathisia (the inability to sit still), and/or disorganized behavior.
schizophrenia
schiz/o split
phren/o mind
-ia condition
A group of disorders characterized by fundamental distortions of thinking and perception, coupled with affect that is inappropriate or blunted. The patient exhibits characteristic inability to recognize an appropriate perception of reality, although his/her intellectual capacity is usually intact (Fig. 12-1).
schizotypal disorder
Unlike the other forms of schizophrenia, patient exhibits anhedonia, eccentric behavior, cold affect, and social isolation. Also called borderline schizophrenia, latent schizophrenia and prodromal schizophrenia.
Term
Word Origin
Definition
bipolar disorder (BP, BD)
bi- two
pol/o pole
-ar pertaining to
Disorder characterized by swings between an elevation of mood, increased energy and activity (hypomania and mania), and a lowering of mood and decreased energy and activity (depression).
cyclothymia
cycl/o recurring
-thymia condition of the mind
Disorder characterized by recurring episodes of mild elation and depression that are not severe enough to warrant a diagnosis of bipolar disorder.
dysthymia
dys- difficult
-thymia condition of the mind
Mild, chronic depression of mood that lasts for years but is not severe enough to justify a diagnosis of depression. Euthymia is a normal range of moods and emotions.
major depressive disorder
Depression typically characterized by its degree (minimal, moderate, severe) or number of occurrences (single or recurrent, persistent). Patient exhibits dysphoria, reduction of energy, and decrease in activity. Symptoms include anhedonia, lack of ability to concentrate, and fatigue. Patient may experience parasomnias (abnormal sleep patterns), diminished appetite, and loss of self-esteem. SAD (seasonal affective disorder) is caused by decreased exposure to sunlight in autumn and winter.
mania
mania from the Greek term for “madness”
A state of an unstable, inappropriate mood.
Term
Word Origin
Definition
acrophobia
acro- heights, extremes
-phobia condition of fear, sensitivity
Fear of heights.
agoraphobia
agora- marketplace
-phobia condition of fear, sensitivity
Fear of leaving home and entering crowded spaces.
androphobia
andr/o man, men
-phobia condition of fear, sensitivity
Fear of men.
anthropophobia
anthrop/o man
-phobia condition of fear, sensitivity
Fear of scrutiny by other people; also called social phobia.
anxiety
Anticipation of impending danger and dread accompanied by restlessness, tension, tachycardia, and breathing difficulty not associated with an apparent stimulus.
claustrophobia
claustr/o a closing
-phobia condition of fear, sensitivity
Fear of enclosed spaces.
delusion
Persistent belief in a demonstrable untruth or a provable, inaccurate perception despite clear evidence to the contrary.
dissociative identity disorder
Maladaptive coping with severe stress by developing one or more separate personalities. A less severe form, dissociative disorder or dissociative reaction, results in identity confusion accompanied by amnesia, oneirism, and somnambulism. Formerly termed multiple personality disorder.
dyslexia
dys- difficult
lex/o word
-ia condition
Inability or difficulty with reading and/or writing.
generalized anxiety disorder (GAD)
Anxiety disorder characterized by excessive, uncontrollable, and often irrational worry about everyday things that is disproportionate to the actual source of worry.
gynephobia
gyn/e female, women
-phobia condition of fear, sensitivity
Fear of women.
illusion
Inaccurate sensory perception based on a real stimulus; examples include mirages and interpreting music or wind as voices.
obsessive-compulsive disorder (OCD)
Disorder characterized by recurrent, distressing, and unavoidable preoccupations or irresistible drives to perform specific rituals (e.g., constantly checking locks, excessive handwashing) that the patient feels will prevent some harmful event.
panic disorder (PD)
Anxiety disorder characterized by recurring, severe panic attacks. Common symptoms of an attack include rapid heartbeat, perspiration, dizziness, dyspnea, uncontrollable fear, and hyperventilation. ![]()
Stay updated, free articles. Join our Telegram channel

Full access? Get Clinical Tree

 Get Clinical Tree app for offline access
Get Clinical Tree app for offline access