Melanotic Neuroectodermal Tumor of Infancy
Jeremy Wallentine, MD
Cyril Fisher, MD, DSc, FRCPath
Key Facts
Terminology
Rare, fast-growing, pigmented neoplasm, likely of neural crest origin
Clinical Issues
Most present in 1st year of life
Commonly involve craniofacial sites
Maxilla (69%)
Rapidly enlarging expansile mass
Elevated urinary vanillylmandelic acid may be present
Microscopic Pathology
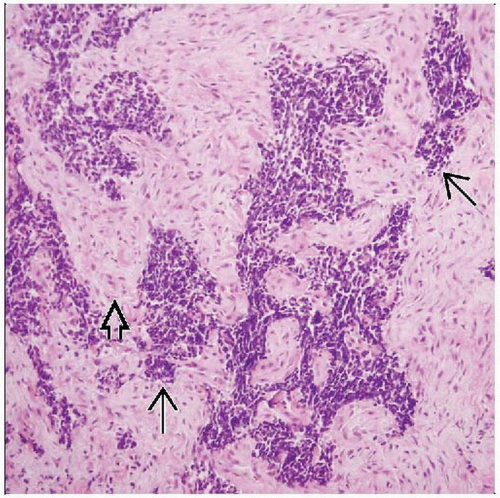
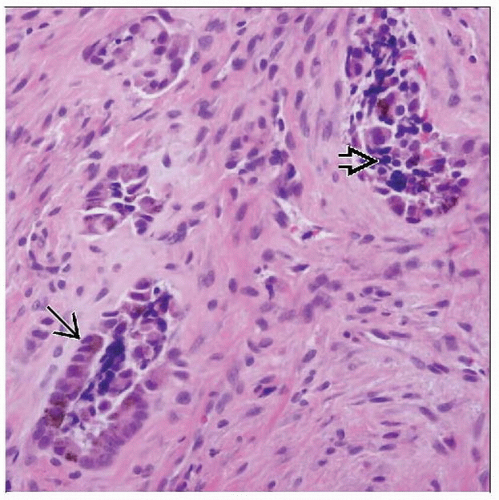
3 distinct components
Clusters of small round neuroblastic cells
Primitive gland-like structures
Fibrocollagenous stroma
Top Differential Diagnoses
Neuroblastoma
Sheets and lobules of small round hyperchromatic cells
Alveolar rhabdomyosarcoma
Aggregates and nests of poorly differentiated small hyperchromatic cells
Characteristic immunohistochemical and cytogenetic findings
Primitive neuroectodermal tumor
Sheets of small-medium round blue cells
Characteristic t(11;22)
Congenital epulis
Characteristic location in labial aspect of dental ridge
Protruding round or ovoid nodule
TERMINOLOGY
Abbreviations
Melanotic neuroectodermal tumor of infancy (MNTI)
Synonyms
Retinal anlage tumor
Melanotic progonoma
Melanotic ameloblastoma
Definitions
Rare, fast-growing, pigmented neoplasm, likely of neural crest origin
ETIOLOGY/PATHOGENESIS
Disputed Histogenesis
Current studies support neural crest (neuroectodermal) origin
CLINICAL ISSUES
Epidemiology
Age
Most present in 1st year of life (> 90%)
Site
Most involve craniofacial sites
Upper and lower jaw
Maxilla (69%)
Mandible (6%)
Skull (11%)
Unusual sites
Epididymis, mediastinum, brain, shoulder, and skin
Presentation
Rapidly enlarging, firm, expansile mass
Erosion into adjacent bone
Nontender
Intact overlying mucosa
Bluish discoloration
Laboratory Tests
Elevated urinary vanillylmandelic acid may be present
Treatment
Complete local excision
Local recurrence rate: 10-15%
Usually recurs in 1st postoperative year
Prognosis
Benign to intermediate clinical course
Recurrence rate: 10-15%
Metastatic spread in < 5%
IMAGE FINDINGS
General Features
Well-demarcated radiolucent lesion
Capacity for local destruction
MACROSCOPIC FEATURES
Gross Features
Firm
Well circumscribed
Gray to blue-black cut surface
MICROSCOPIC PATHOLOGY
Predominant Pattern/Injury Type
Stay updated, free articles. Join our Telegram channel

Full access? Get Clinical Tree