Chapter 42 First stage: Preclinical Alzheimer’s disease in which only mild symptoms are occasionally seen Second stage: Mild cognitive impairment (MCI): small changes in memory, behavior, and thinking may be observed. Some patients in this stage are already identified by their health care providers as “probable Alzheimer’s.” Third stage: Dementia because of Alzheimer’s. Drugs may not be very effective at this stage. • Qaseem A et al: Current pharmacologic treatment of dementia: a clinical practice guideline from the American College of Physicians and the American Academy of Family Physicians, Ann Intern Med 148(5):370-378, 2008. • Doody RS, Stemves JC, Beck C, et al: Practice parameter: management of dementia (an evidence-based review): report of the quality standards subcommittee of the American Academy of Neurology, Neurology 56:1154-1166, 2001. • American Psychiatric Association (APA): Practice guidelines for the treatment of patients with Alzheimer’s disease and other dementias, 2007, Washington, DC: US Prev Services Task Force. • U.S. Preventive Services Task Force: Screening for dementia: recommendation and rationale, Ann Intern Med 138:925-926, 2003. • The evidence is insufficient to compare the effectiveness of different pharmacologic agents for the treatment of dementia. • An overview of research suggests that donepezil improves cognitive function and global clinical state for up to 2 years in people with mild to severe AD. Quality of life was improved at 24 weeks. Donepezil given to patients with more severe dementia produced improvement in cognitive function at 24 weeks. Research suggests that donepezil delayed the median time to clinically evident functional decline by 5 months. • Additional studies suggest that galantamine improves cognitive function and global clinical state over 6 months in people with AD or vascular dementia. • One study in people with AD found no significant difference between donepezil and galantamine in cognitive function or adverse effects at 1 year. • Ginkgo biloba and memantine are likely to be beneficial. • Antidepressants given to Alzheimer’s patients with depression appear not to be effective and often cause adverse effects or introduce unwanted drug interactions.
Medications for Dementia
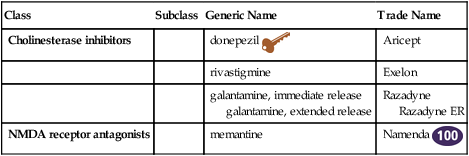
Class
Subclass
Generic Name
Trade Name
Cholinesterase inhibitors
donepezil ![]()
Aricept
rivastigmine
Exelon
galantamine, immediate release
galantamine, extended release
Razadyne
Razadyne ER
NMDA receptor antagonists
memantine
Namenda ![]()
Therapeutic Overview
Pathophysiology
Disease Process
Treatment Principles
Standardized Guidelines
Evidence-Based Recommendations
![]()
Stay updated, free articles. Join our Telegram channel

Full access? Get Clinical Tree


Medications for Dementia
Only gold members can continue reading. Log In or Register to continue
