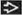Malignant Melanoma, Vulva
Maria Angelica Selim, MD
Key Facts
Clinical Issues
Predominantly postmenopausal
Mass, bleeding, discharge, pruritus, pain
˜ 30% amelanotic, especially mucosal surfaces
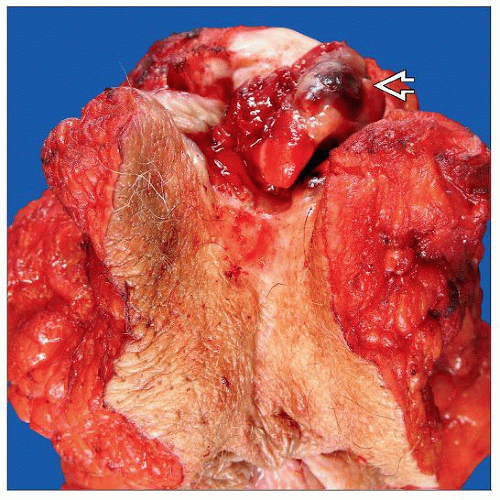
Macroscopic Features
Macule or plaque with irregular borders most common; polypoid in 1/3
Satellite lesions (in 1/5)
Frequently > 2 cm
Microscopic Pathology
Lentiginous/mucosal (up to 50%) > nodular > superficial spreading > unclassifiable
Dermal component: Sheets, nests, cords, single cells, rarely fascicles with no maturation phenomenon
Epithelioid > spindle > small cells
Severe cytologic atypia with prominent, typically eosinophilic nucleoli
Ancillary Tests
MART-1/Melan-A , HMB-45, S100 positive
MART-1/Melan-A, HMB-45 may be negative, especially if desmoplastic or spindled
p75, C-kit, SOX10 positive, especially if spindled morphology
Top Differential Diagnoses
Atypical nevus of the genital type
Malignant melanoma in situ
Extramammary Paget disease
Invasive squamous cell carcinoma (vs. amelanotic melanoma)
Leiomyosarcoma (vs. spindled melanoma)
TERMINOLOGY
Abbreviations
Malignant melanoma (MM)
Definitions
Malignant tumor composed of melanocytes
ETIOLOGY/PATHOGENESIS
Genetic Associations
KIT mutation most frequent genetic alteration
Melanocortin type I receptor germline mutation (rare)
Familial
CDKN2A and CDK4 mutations
Linked to cases of familial melanoma
Only account for a small percentage of familial melanoma cases
CLINICAL ISSUES
Epidemiology
Incidence
Annual incidence: 0.108 per 100,000
8-11% of all vulvar malignancies
2nd most common malignant vulvar neoplasm after squamous cell carcinoma
˜ 2-5% of all malignant melanomas in women
Vulva most common location in female genital tract
Age
Predominantly postmenopausal (6th to 8th decade)
Ethnicity
Caucasians > African Americans
Site
Labia majora (up to 50%) > labia minora (up to 35%) > periclitoral/clitoris (up to 30%) > labia majora and minora (up to 20%)
Presentation
Mass or swelling
Bleeding, discharge, pruritus, pain
Asymptomatic less common
Discoloration on clinical examination
˜ 30% amelanotic, especially mucosal surfaces
May be multifocal
1/3 lymph node metastasis at presentation
˜ 20% with history of atypical nevus outside vulva
“ABCD” rule
A = asymmetry
B = border irregularity
C = color variation (nonuniform)
D = diameter (malignant lesions usually > 6 mm)
Treatment
Complete resection with margins defined by Breslow thickness (distance from top of granular layer to deepest part of tumor)
Stay updated, free articles. Join our Telegram channel

Full access? Get Clinical Tree