Lesions restricted to cutis only rarely metastasize
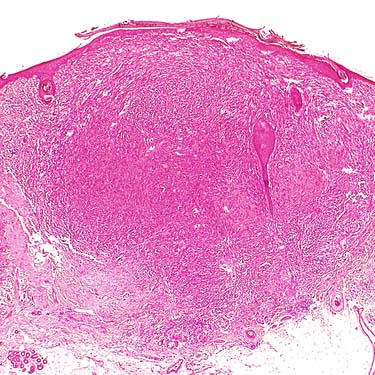
Based on the lack of involvement of the subcutaneous adipose tissue, a favorable prognosis would be anticipated for this lesion. In fact, some observers have suggested diagnosing such superficial cutaneous lesions as atypical smooth muscle tumors.
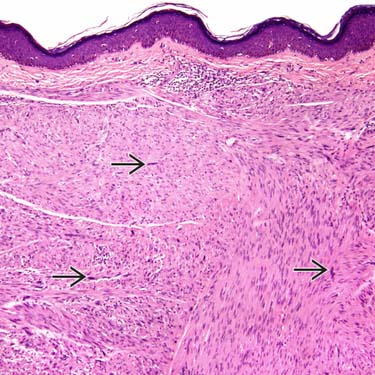
This leiomyosarcoma (LMS) extended into the subcutis. It is composed of perpendicularly oriented fascicles of brightly eosinophilic cells. Even at scanning magnification, atypical nuclei stand out
 .
.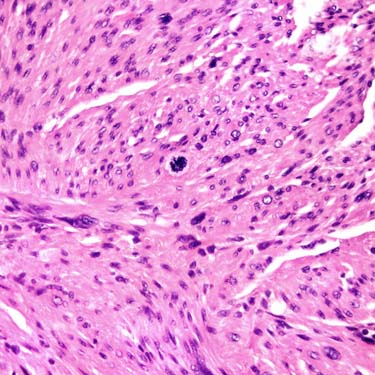
Mitotic figures are usually easily found in LMS. There is no need to search for numerous mitoses, although mitotic counts assist in assigning a sarcoma grade. Note the bright pink color of the tumor cells’ cytoplasm.
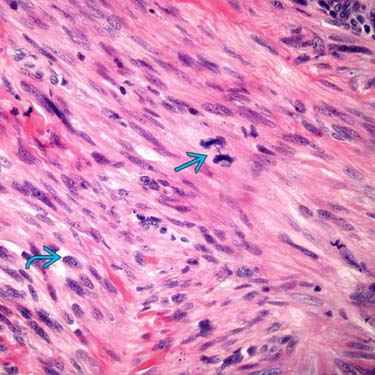
LMSs do not show a characteristic translocation and have chromosome instability, as indicated by the presence of anaphase bridges
 , long cords of chromatin that remain as cells separate in anaphase. Note the blunt-ended nuclei
, long cords of chromatin that remain as cells separate in anaphase. Note the blunt-ended nuclei  .
.MICROSCOPIC
Histologic Features
• Any number of mitoses sufficient in subcutis, scrotal lesions, or deep soft tissue if nuclear atypia is present
Variant and Special Forms
• Epithelioid leiomyosarcoma
 Literature confounded because many epithelioid gastrointestinal stromal tumors (GIST) were termed epithelioid LMS in past
Literature confounded because many epithelioid gastrointestinal stromal tumors (GIST) were termed epithelioid LMS in past
 Older studies reported smooth muscle actin (SMA) and muscle specific actin (MSA)-positive, desmin-negative immunophenotype, but desmin labels most lesions using modern methods
Older studies reported smooth muscle actin (SMA) and muscle specific actin (MSA)-positive, desmin-negative immunophenotype, but desmin labels most lesions using modern methods
 Literature confounded because many epithelioid gastrointestinal stromal tumors (GIST) were termed epithelioid LMS in past
Literature confounded because many epithelioid gastrointestinal stromal tumors (GIST) were termed epithelioid LMS in past Older studies reported smooth muscle actin (SMA) and muscle specific actin (MSA)-positive, desmin-negative immunophenotype, but desmin labels most lesions using modern methods
Older studies reported smooth muscle actin (SMA) and muscle specific actin (MSA)-positive, desmin-negative immunophenotype, but desmin labels most lesions using modern methods• Myxoid leiomyosarcoma
 Extensive myxoid change, but zones of typical leiomyosarcoma allow for diagnosis
Extensive myxoid change, but zones of typical leiomyosarcoma allow for diagnosis




 Extensive myxoid change, but zones of typical leiomyosarcoma allow for diagnosis
Extensive myxoid change, but zones of typical leiomyosarcoma allow for diagnosisStay updated, free articles. Join our Telegram channel

Full access? Get Clinical Tree





















