Chapter 2 Inflammation and Repair
ACUTE INFLAMMATION
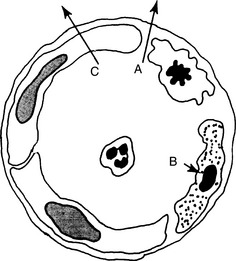
5 What are the three main sets of events taking place in tissues during acute inflammation?
Three main events in acute inflammation are:
6 What is the difference between an exudate and a transudate?
TABLE 2-1 Differences Between Transudate and Exudate
| Transudate | Exudate | |
|---|---|---|
| Appearance | Clear | Turbid |
| Specific gravity | <1.015 | >1.020 |
| Protein content | <3 g/dL | >3 g/dL |
| Cells | Scant | Numerous neutrophils |
8 Why does edema develop in acute inflammation?
Inflammatory edema has three main causes:
 Increased hydrostatic pressure in microcirculation: Arteriolar dilatation associated with an increased influx of blood promotes transudation of fluid in capillaries and venules.
Increased hydrostatic pressure in microcirculation: Arteriolar dilatation associated with an increased influx of blood promotes transudation of fluid in capillaries and venules. Increased permeability of blood vessels: The vessel walls of capillaries and venules become leaky under the influence of mediators of inflammation, allowing the passage of plasma proteins and fluid. The loss of fluid leads to hemoconcentration, which promotes stasis of blood cells. Stasis is associated with increased blood pressure in venules, which in turn prevents the return of the fluids from the interstitial spaces into the bloodstream.
Increased permeability of blood vessels: The vessel walls of capillaries and venules become leaky under the influence of mediators of inflammation, allowing the passage of plasma proteins and fluid. The loss of fluid leads to hemoconcentration, which promotes stasis of blood cells. Stasis is associated with increased blood pressure in venules, which in turn prevents the return of the fluids from the interstitial spaces into the bloodstream. Reduced oncotic pressure of the plasma: The loss of proteins as a result of increased transudation or exudation will gradually reduce the oncotic pressure of the plasma. Decreased oncotic pressure of the plasma facilitates the passage of fluid into the interstitial space. At the same time, the return of water from the interstitial space into the circulating blood at the venular end of microcirculation is reduced.
Reduced oncotic pressure of the plasma: The loss of proteins as a result of increased transudation or exudation will gradually reduce the oncotic pressure of the plasma. Decreased oncotic pressure of the plasma facilitates the passage of fluid into the interstitial space. At the same time, the return of water from the interstitial space into the circulating blood at the venular end of microcirculation is reduced.9 How does the permeability of small vessels increase during inflammation?
There are several mechanisms, the most important of which are the following:
 Formation of gaps between endothelial cells: This is the most common form of increased permeability. In early stages of inflammation, it occurs predominantly in venules under the influence of histamine or bradykinin. In later stages of inflammation, it is mediated by cytokines. These mediators of inflammation cause widening of intercellular gaps as a result of retraction of endothelial cells.
Formation of gaps between endothelial cells: This is the most common form of increased permeability. In early stages of inflammation, it occurs predominantly in venules under the influence of histamine or bradykinin. In later stages of inflammation, it is mediated by cytokines. These mediators of inflammation cause widening of intercellular gaps as a result of retraction of endothelial cells. Direct injury of endothelial cells: Usually a sign of severe injury caused by a variety of agents, it occurs in arterioles, as well as capillaries or venules. The defect in the vessel wall cannot be repaired easily, thus allowing indiscriminate leakage of cells and plasma components into the interstitial spaces.
Direct injury of endothelial cells: Usually a sign of severe injury caused by a variety of agents, it occurs in arterioles, as well as capillaries or venules. The defect in the vessel wall cannot be repaired easily, thus allowing indiscriminate leakage of cells and plasma components into the interstitial spaces. Leukocyte-mediated injury: Adherence of neutrophils to endothelial cells, especially in pulmonary venules or glomerular capillaries, increases their permeability.
Leukocyte-mediated injury: Adherence of neutrophils to endothelial cells, especially in pulmonary venules or glomerular capillaries, increases their permeability. Increased transcytosis: Vesicular transport of fluids across the cytoplasm of venules may occur under the influence of vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGF). VEGF is also a cause of increased leakiness of newly formed blood vessels in the granulation tissue and chronic inflammation.
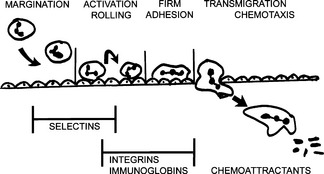
Increased transcytosis: Vesicular transport of fluids across the cytoplasm of venules may occur under the influence of vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGF). VEGF is also a cause of increased leakiness of newly formed blood vessels in the granulation tissue and chronic inflammation.10 What are the main events leading to transmigration of leukocytes across the vessel wall?
 Margination: The slowing of the blood flow allows the neutrophils to exit from the center of the bloodstream into the peripheral part and thus establish contact with endothelial cells.
Margination: The slowing of the blood flow allows the neutrophils to exit from the center of the bloodstream into the peripheral part and thus establish contact with endothelial cells. Rolling: The leukocytes, which are normally found in the bloodstream, continue rolling over the endothelial cells. During this process, leukocytes and endothelial cells become activated and establish loose contacts with one another. These contacts are mediated by surface adhesion molecules called selectins.
Rolling: The leukocytes, which are normally found in the bloodstream, continue rolling over the endothelial cells. During this process, leukocytes and endothelial cells become activated and establish loose contacts with one another. These contacts are mediated by surface adhesion molecules called selectins. Adhesion: Progressive activation of leukocytes and endothelial cells leads to expression of polypeptide adhesion molecules called integrins. Integrins on the surface of neutrophils attach to complementary integrins or endothelial cells, thus firmly binding these cells to each other.
Adhesion: Progressive activation of leukocytes and endothelial cells leads to expression of polypeptide adhesion molecules called integrins. Integrins on the surface of neutrophils attach to complementary integrins or endothelial cells, thus firmly binding these cells to each other. Transmigration: Neutrophils attached to endothelial cells by integrins assume an amoeboid shape and begin actively crawling over the inside surface of venules until they reach the intercellular gaps. Finally, leukocytes squeeze through the intercellular gaps and enter the intercellular spaces outside the vessels.
Transmigration: Neutrophils attached to endothelial cells by integrins assume an amoeboid shape and begin actively crawling over the inside surface of venules until they reach the intercellular gaps. Finally, leukocytes squeeze through the intercellular gaps and enter the intercellular spaces outside the vessels.13 What are the signs of leukocyte activation?
Activated leukocytes differ from inactive leukocytes in several respects:
 Expression of adhesion molecules: Selectins and integrins appear on the cell surface or are expressed in higher numbers and show higher affinity for liquids.
Expression of adhesion molecules: Selectins and integrins appear on the cell surface or are expressed in higher numbers and show higher affinity for liquids. Changes in the cytoskeleton: Owing to the polymerization and redistribution of microtubules and microfilaments, the cell shape changes from round to flattened or amoeboid. Leukocytes form pseudopods and start moving actively toward the stimuli. Cytoskeletal changes also contribute to the formation of phagocytic vacuoles.
Changes in the cytoskeleton: Owing to the polymerization and redistribution of microtubules and microfilaments, the cell shape changes from round to flattened or amoeboid. Leukocytes form pseudopods and start moving actively toward the stimuli. Cytoskeletal changes also contribute to the formation of phagocytic vacuoles. Degranulation: The contents of cytoplasmic granules are released into phagocytic vacuoles or the extracellular spaces. Inside the phagocytic vacuoles, these enzymes participate in the digestion of bacteria. Enzymes released from the granules into the outer spaces act on ECM molecules and basement membranes, allowing the leukocytes to penetrate the tissues.
Degranulation: The contents of cytoplasmic granules are released into phagocytic vacuoles or the extracellular spaces. Inside the phagocytic vacuoles, these enzymes participate in the digestion of bacteria. Enzymes released from the granules into the outer spaces act on ECM molecules and basement membranes, allowing the leukocytes to penetrate the tissues. Oxidative burst: Activated leukocytes generate free oxygen radicals, which are important for killing bacteria.
Oxidative burst: Activated leukocytes generate free oxygen radicals, which are important for killing bacteria.14 What is chemotaxis?
Chemotaxis is active movement of cells along a chemical gradient generated by a chemoattractant.
16 How do chemoattractants act on leukocytes?
 G protein–mediated activation of phospholipases, which leads to the production of secondary messengers, such as DAG and IP3
G protein–mediated activation of phospholipases, which leads to the production of secondary messengers, such as DAG and IP318 How do leukocytes kill bacteria?
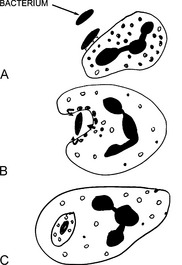
The killing of bacteria occurs in three stages and involves:
22 What are the main bactericidal substances used by neutrophils?
Bacteria can be killed through two mechanisms:
 Oxygen-dependent killing: This mechanism depends on the oxygen burst resulting from the activation of nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide phosphate (NADPH) oxidase. Oxidation of NADPH generates superoxide, which spontaneously transforms into hydrogen peroxide (H2O2). H2O2 is the substrate for myeloperoxidase, which links it to a chloride ion, generating hypochloric acid. Hypochloric acid, similar to household Clorox, is the most potent bactericidal chemical generated in the phagosomes.
Oxygen-dependent killing: This mechanism depends on the oxygen burst resulting from the activation of nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide phosphate (NADPH) oxidase. Oxidation of NADPH generates superoxide, which spontaneously transforms into hydrogen peroxide (H2O2). H2O2 is the substrate for myeloperoxidase, which links it to a chloride ion, generating hypochloric acid. Hypochloric acid, similar to household Clorox, is the most potent bactericidal chemical generated in the phagosomes. Oxygen-independent killing: Although less efficient than oxygen-dependent killing, this mechanism plays an important role in the fight against bacteria. It depends on the action of lysozyme, lactoferrin, and cationic proteins (e.g., defensin). The overall acidic environment inside the phagocytic vacuoles is toxic to some bacteria. Oxygen-independent killing of bacteria is especially important in people suffering from congenital deficiency of NADPH oxidase (chronic granulomatous disease) or myeloperoxidase deficiency.
Oxygen-independent killing: Although less efficient than oxygen-dependent killing, this mechanism plays an important role in the fight against bacteria. It depends on the action of lysozyme, lactoferrin, and cationic proteins (e.g., defensin). The overall acidic environment inside the phagocytic vacuoles is toxic to some bacteria. Oxygen-independent killing of bacteria is especially important in people suffering from congenital deficiency of NADPH oxidase (chronic granulomatous disease) or myeloperoxidase deficiency.24 What are the most important congenital defects of leukocyte function?
 Defects in leukocyte adhesion: This category encompasses deficiencies of various leukocyte adhesion molecules, integrins, and enzymes that synthesize the carbohydrate ligands for the selectins.
Defects in leukocyte adhesion: This category encompasses deficiencies of various leukocyte adhesion molecules, integrins, and enzymes that synthesize the carbohydrate ligands for the selectins. Defects of phagocytosis: Deficiency of C3 complement impairs opsonization. Chediak–Higashi syndrome, a defect in microtubule polymerization, is characterized by defective leukocyte migration and phagocytosis. Neutrophils typically have giant granules and are unable to degranulate upon stimulation.
Defects of phagocytosis: Deficiency of C3 complement impairs opsonization. Chediak–Higashi syndrome, a defect in microtubule polymerization, is characterized by defective leukocyte migration and phagocytosis. Neutrophils typically have giant granules and are unable to degranulate upon stimulation. Defective bactericidal activity: Deficiency of NADPH oxidase is the basic defect in children suffering from chronic granulomatous disease. In this disease, the leukocytes cannot generate superoxide, which impairs the oxygen-dependent killing of bacteria. These children are especially sensitive to infection with catalase-positive microbes such as Staphylococcus aureus. Catalase-negative streptococci are less dangerous. These bacteria produce peroxide that is used by the leukocytes to generate hypochloric acid and to kill the pathogens. Deficiency of myeloperoxidase is characterized by an inability of leukocytes to produce H2O2 and hypochloric acid. Affected children are prone to fungal infections.
Defective bactericidal activity: Deficiency of NADPH oxidase is the basic defect in children suffering from chronic granulomatous disease. In this disease, the leukocytes cannot generate superoxide, which impairs the oxygen-dependent killing of bacteria. These children are especially sensitive to infection with catalase-positive microbes such as Staphylococcus aureus. Catalase-negative streptococci are less dangerous. These bacteria produce peroxide that is used by the leukocytes to generate hypochloric acid and to kill the pathogens. Deficiency of myeloperoxidase is characterized by an inability of leukocytes to produce H2O2 and hypochloric acid. Affected children are prone to fungal infections.25 What are the most important plasma-derived mediators of inflammation?
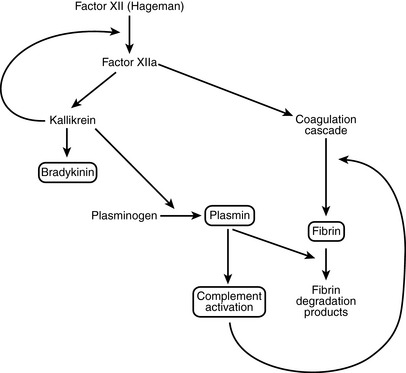
 Kinin system: This results in the formation of kallikrein and bradykinin. Kallikrein itself is capable of activating Hageman factor and could play a role in autocatalytic propagation of the entire enzymatic cascade.
Kinin system: This results in the formation of kallikrein and bradykinin. Kallikrein itself is capable of activating Hageman factor and could play a role in autocatalytic propagation of the entire enzymatic cascade. Fibrinolysis system: Activation of plasminogen into plasmin results in lysis of fibrin and also activation of the complement cascade.
Fibrinolysis system: Activation of plasminogen into plasmin results in lysis of fibrin and also activation of the complement cascade. Complement system: This involves sequential activation of complement proteins C1 to C9 and their activators and inhibitors.
Complement system: This involves sequential activation of complement proteins C1 to C9 and their activators and inhibitors.< div class='tao-gold-member'>
Only gold members can continue reading. Log In or Register to continue
Stay updated, free articles. Join our Telegram channel

Full access? Get Clinical Tree