Hibernoma
Khin Thway, BSc, MBBS, FRCPath
Key Facts
Terminology
Benign tumor with differentiation toward brown fat, most frequently seen in younger adults
Clinical Issues
Peak incidence in 3rd decade
Most tumors subcutaneous
Thigh is most common site
Can occur in abdomen and retroperitoneum
Microscopic Pathology
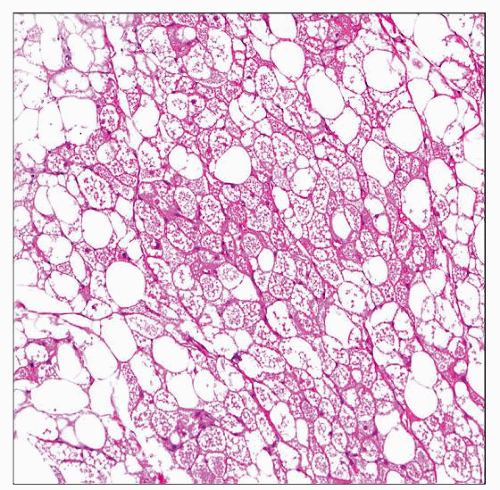
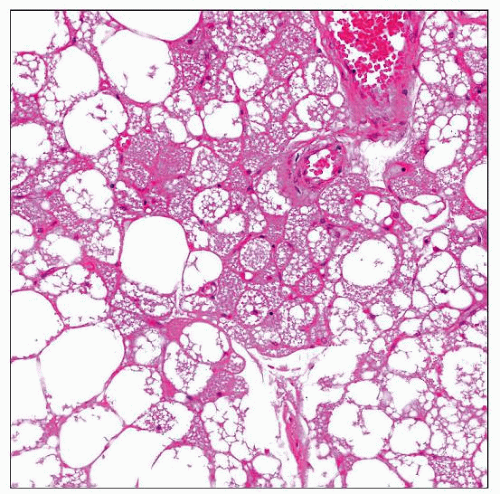
Variable differentiation toward brown fat
Cells are granular, multivacuolated, or univacuolated adipocytes
Myxoid, lipoma-like, and spindle cell variants
Cellular atypia unusual; mitoses exceptional
Ancillary Tests
Variable, sometimes strong positivity for S100
Rearrangements of 11q13-21 in several cases
TERMINOLOGY
Synonyms
Fetal lipoma, lipoma of embryonic fat
Definitions
Benign tumor most frequently occurring in younger adults, with differentiation toward brown fat
Tumor has characteristic cytogenetic aberrations, mainly involving 11q13-21
ETIOLOGY/PATHOGENESIS
Developmental Anomaly
Etiology unknown
Many occur at sites of normal brown fat in fetuses and newborns
Genetic changes in some
CLINICAL ISSUES
Epidemiology
Incidence
Rare; approximately 1% of all adipocytic tumors
Age
Peak incidence: 3rd decade
Rare in children
Gender
M = F