HER2
TERMINOLOGY
Abbreviations
HER2-positive breast cancer (HER2+BC)
Human epidermal growth factor receptor-2 (HER2)
Chromosome 17 centromere enumeration probe (CEP17)
Synonyms
HER2, HER2/neu, NEU, NGL, TKR1, c-erb, CD340, ERBB2
Definitions
HER2 is a proto-oncogene located on chromosome 17q12
Expressed normally in a number of glandular epithelia including breast
Translated into a 185 kDa transmembrane growth factor receptor protein
HER2 transmits signals regulating normal cell growth, development, and survival
In 15-20% of breast cancers, HER2 protein is overexpressed
In > 95% of HER2+BC, the mechanism of overexpression is due to increased numbers of HER2 gene (gene amplification)
Amplification of the gene drives mRNA production and protein expression
Clinical assays evaluate DNA, mRNA, or protein
In ˜ 5% of HER2+BC, there may be other mechanisms resulting in protein overexpression
These mechanisms have not been well studied
HER2 is a member of HER-family of growth factor receptors
This family also includes HER1 (EGFR), HER3, and HER4
Regulate intracellular signaling through MAP-kinase and PI3-kinase pathways
Regulate normal cell proliferation and cell survival
Overexpression results in increased HER2 receptors on the surface of tumor cells
ETIOLOGY/PATHOGENESIS
Histogenesis
HER2 alteration is thought to be early event in pathogenesis of HER2+BC
May play important role in carcinogenesis and tumor development
Higher proportions of DCIS overexpress HER2 compared to invasive carcinoma
HER2 alteration is stable genetic change in tumor cells
HER2 overexpression is seen in primary tumor as well as metastases from HER2+BC
However, in some cases HER2 overexpression is lost in residual carcinoma after treatment or in metastases
Most likely due to initial tumor heterogeneity and the selective effects of targeted therapy
Molecular Pathology
Binding of high affinity ligands to HER-receptors leads to conformational change in molecule
Conformational change promotes receptor activation through dimerization
HER-family members form homo-dimers and hetero-dimers
Receptor dimerization leads to activation of intracellular tyrosine kinase portion of molecule
Tyrosine kinase activation initiates receptor signaling through phosphorylation
Overexpression of HER2 increases likelihood of receptor activation and signaling
CLINICAL IMPLICATIONS
Prognostic Implications
HER2 gene amplification/overexpression plays a pivotal role in driving tumor biology
Contributes to more aggressive clinical course for HER2+BC
Significantly decreased disease-free and overall survival
Higher incidence of local recurrence compared to luminal A cancers (ER positive and HER2 negative)
Increased incidence of lymph node metastases
More frequent metastases to brain, liver, and lung compared to luminal A cancers
40-50% of patients with brain metastases have HER2+BC
HER2 overexpression significantly correlates with a number of unfavorable tumor characteristics
Higher proliferative index
Larger tumor size
Higher tumor grade
HER2 overexpression may predict response to certain adjuvant chemotherapy regimens and endocrine therapy
Treatment Implications
HER2 overexpression in breast cancer represents ideal target for therapy
Receptor located on surface of cell and is accessible
Receptor plays a pivotal role in driving clinical course of disease
Targeted therapy utilizes either a HER2 specific antibody or a HER2 small molecule inhibitor
Trastuzumab (Herceptin)
Humanized monoclonal antibody that targets the HER2 receptor
Combines mouse recognition sequence of monoclonal antibody (4D5) with human IgG1
Trastuzumab binds to extracellular epitope of HER2 receptor
Trastuzumab demonstrates high affinity and specificity for HER2 receptor
In preclinical studies, this drug inhibits growth of HER2 overexpressing breast cancer cells
Trastuzumab binding blocks receptor signaling
May stimulate immune-mediated tumor cell cytotoxicity
May act synergistically with chemotherapy to induce tumor cell apoptosis
In clinical trials, trastuzumab plus chemotherapy demonstrated remarkable efficacy against HER2+BC
Efficacy has been demonstrated for metastatic, adjuvant, and neoadjuvant therapy
Adjuvant trastuzumab plus chemotherapy can reduce relative risk of recurrence by 50% in early stage HER2+BC
Data suggest that only HER2+BC are likely to benefit from this therapy
Safety considerations
Cardiac dysfunction seen in 2-4% of patients treated with trastuzumab plus anthracycline-based chemotherapy
Data highlight the importance of accurate HER2 testing
Important to identify only those patients who will be most suitable candidates for treatment
Benefit from targeted therapy is not related to the degree of gene amplification
Cancers with low levels of gene amplification respond as well as cancers with large numbers of genes
Lapatinib (Tykerb)
Dual tyrosine kinase inhibitor that interrupts the kinase activity of both HER2 and EGFR (HER1)
Oral agent
Used for initial therapy in combination with chemotherapy or after carcinomas have progressed after treatment with trastuzumab
Clinical Assays for HER2 Status
Immunohistochemistry (IHC) detects HER2 protein overexpression
In situ hybridization (FISH or CISH) detects HER2 gene amplification
Both IHC and FISH have been clinically validated to help predict response to HER2-targeted therapy
Oncotype DX (Genomic Health; Redwood City, CA) assay detects HER2 mRNA overexpression using quantitative RT-PCR
Not currently used to make treatment decisions
Requires tissue microdissection if DCIS shows stronger HER2 positivity or if little carcinoma in relation to stroma is present
Will not detect heterogeneity of overexpression
HER2 testing has become an essential part of clinical evaluation for breast cancer patients
Treatment guidelines from ASCO and the NCCN recommend HER2 testing for all newly diagnosed breast cancer patients
Decisions about HER2-targeted therapy include concerns about cost and potential toxicities
HER2-targeted therapy should only be used in patients whose tumors have been evaluated by a validated HER2 assay
Specimen Handling
Breast specimens should be sectioned and placed in adequate volume of fixative within 1 hour from removal
If gross tumor is identified during initial specimen evaluation
Sample of tumor and fibrous normal tissue can be placed together into same cassette
Tissue is placed immediately into formalin; fixation start time should be recorded
Helpful to initiate good and rapid fixation
Helps ensure normal breast tissue is available as internal control for breast marker testing
Breast Tissue Fixation
Breast tissue samples must be fixed in 10% neutral buffered formalin
Formalin fixation is part of FDA approval for test kits that evaluate HER2 by IHC and FISH
Fixation time recommended to be no less than 6-8 hours and no more than 48 hours before processing
Underfixation can lead to technical problems with IHC assay
Only very long fixation times (weeks) have been demonstrated to alter results
Small biopsy samples require same amount of fixation time as larger resection samples
Acid decalcification can interfere with evaluation of specimens by FISH due to DNA degradation
Specimens treated with very careful EDTA decalcification and daily monitoring by specimen radiography can be used for FISH and IHC
Negative results using other methods of decalcification should be interpreted with caution
HER2 Assay Methodologies: IHC
Different antibodies have been used for evaluation of HER2 protein expression in formalin-fixed, paraffin-embedded samples
Antibody clones have varying sensitivities and specificities
3B5 (mouse, monoclonal), predominantly used in older studies: C-terminus, preferentially recognizes unphosphorylated form
AO85 (rabbit, polyclonal), part of FDA-approved kit: Cytoplasmic portion
CB11 (mouse, monoclonal), part of FDA-approved kit: Internal portion of receptor
4B5 (rabbit, monoclonal), part of FDA-approved kit
SP3 (rabbit, monoclonal): Extracellular domain
HER2 IHC Interpretation
Scoring of HER2 results by IHC needs to be semiquantitatively evaluated to be clinically relevant
Only areas of invasive carcinoma are scored
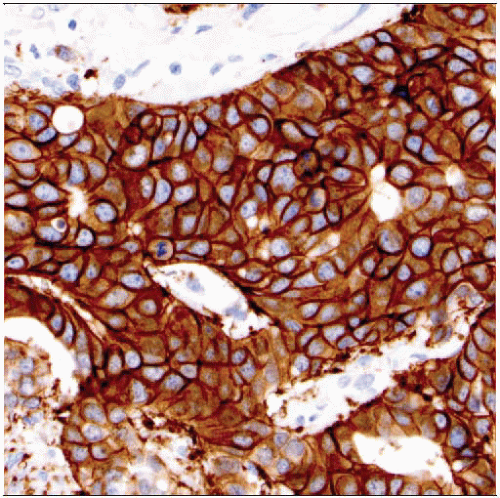
HER2+BC (IHC scored as 3+) ˜10-15% of cancers
Diffuse intense circumferential membrane “chicken wire” staining pattern in > 30% of invasive cancer
Score as HER2 IHC positive (3+)
In most cancers, the majority of the carcinoma is positive
If only focal positivity is present (e.g., strong positivity in 20% of the cancer), this should be described; these cases may correlate with genetic heterogeneity
Carcinomas with this staining pattern typically show good concordance with gene amplification by FISH (> 95%)
Patients with HER2 3+ carcinomas are candidates for treatment with HER2-targeted therapy
In rare cases, the associated DCIS overexpresses HER2 but the invasive carcinoma is HER2 negative
This finding should be documented to ensure this is taken into account during the evaluation of other assays
HER2-BC (IHC scored as 0 or 1+) ˜ 70-75% of cancers
Absent or weak incomplete membrane staining in invasive cancer
Score as HER2 IHC negative (0/1+)
Cancers with this staining pattern show a good concordance with absence of amplification by FISH (> 95%)
Breast cancer patients with HER2 IHC 0/1+ tumors are unlikely to benefit from targeted therapy
HER2 equivocal breast cancer (IHC scored as 2+) ˜ 15% of cancers
Weak, circumferential membrane staining &/or heterogeneity in staining distribution < 30% of invasive tumor
Score as HER2 IHC equivocal (2+)
In correlative studies, approximately 1/5-1/4 of 2+ cancers show HER2 gene amplification
Breast cancers with equivocal HER2 IHC result should be analyzed by FISH to assess for HER2 gene amplification
These cases are more likely to have low numbers of HER2 genes
If the studies are performed on a core needle biopsy, it is helpful to repeat on a larger area of carcinoma in the excision
Some cancers will have “equivocal” HER2 results by both IHC and FISH, reflecting that HER2 expression is continuous and not bimodal
HER2 IHC inadequate for interpretation (rejection); in some cases scoring is not possible
Needle core biopsies with crush artifact are inadequate for interpretation
Should not be overinterpreted as positive
Staining of adjacent normal breast tissue suggests that the assay is too sensitive
Results for the assay should be considered inadequate for interpretation
May lead to false-positive interpretation
Prolonged period of ischemia prior to initiation of formalin fixation
Time from tissue collection to fixation > than 1-2 hours
HER2 assay result may not be accurate
May lead to false-negative interpretation
Samples fixed for < 6-8 hours in neutral buffered formalin
Samples fixed for > 48 hours in neutral buffered formalin
Samples fixed in fixatives other than formalin
Alternative fixatives must be rigorously validated by laboratory
Samples with no residual invasive carcinoma on deeper levels
Samples on unstained slides stored for > 6 weeks prior to testing
Many laboratories utilize a HER2 testing algorithm in which tumor samples are initially screened by IHC
HER2 Assay Methodologies: In Situ Hybridization (ISH)
Morphology-based assay to evaluate gene copy number
Single probe methods evaluate the number of HER2 genes
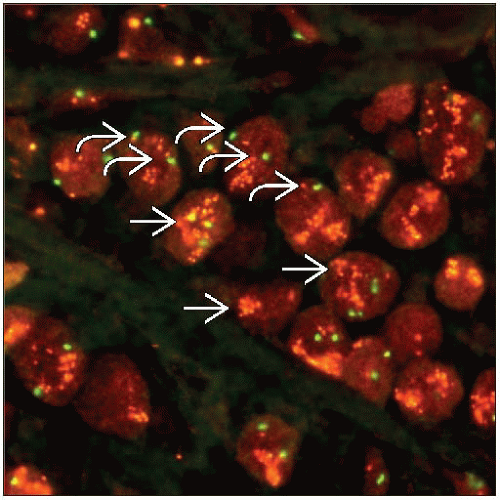
Dual probe methods evaluate the number of HER2 genes and chromosome 17 centromere sequences (CEP17)
Results are reported as the ratio HER2:CEP17
Multiple methods for ISH are available
FISH utilizes fluorescent labeled probes and fluorescence microscopy
Chromogenic/bright-field in situ hybridization (CISH, Duo-CISH) and silver-enhanced in situ hybridization (SISH) use light microscopy
Chromogen dye or silver deposition replaces fluorescent label for detection of gene copy number
Light microscopy facilitates correlation with histologic appearance
These methods correlate well with FISH
With FISH, quantitative interpretation of results more straightforward than with IHC
Concordance rates between observers are higher with FISH than with IHC in some studies
However, heterogeneity of expression is easier to detect with IHC
ISH and IHC assays are best viewed as complementary methodologies
Each assay examines a different aspect of HER2 biology
ISH assays can be used in conjunction with IHC or as primary methodology for HER2 testing
Chromosome 17 centromere sequences (CEP17)
Probe to the centromeric region of chromosome 17 is utilized in dual probe methods to determine the number of chromosomes present
10-50% of HER2+BC are reported to have increased CEP17 sequences
“Polysomy” is usually defined as ≥ 3 CEP17 signals per nucleus
However, true polysomy (duplication of the entire chromosome) is only present in 1-2% of cancers
In the majority of cancers, increased CEP17 is due to duplication of a segment of centromeric DNA
Carcinomas with 3-5 copies of the HER2 gene and increased CEP17 generally do not show increased protein expression
Carcinomas with > 6 gene copies are usually associated with HER2 overexpression
> 90% of these cases will also have HER2:CEP17 ratios > 2.2, and the carcinoma is classified as HER2 amplified
In rare cases, the ratio is < 2.2 due to the increased CEP17 numbers, and the 2 methods for determining HER2 amplification have different interpretations
If not previously performed, an IHC assay should be performed
Carcinomas with 3+ scores by IHC are classified as HER2+BC
It is not yet clear if carcinomas with 2+ scores by IHC, > 6 gene copies, but ratios < 2.2 will benefit from targeted therapy
Monosomy for chromosome 17 occurs in < 5% of cancers
It is not clear if ratios > 2.2 in the presence of monosomy will predict benefit from targeted therapy
HER2 FISH Interpretation
Guidelines for HER2 FISH interpretation were recommended by an ASCO/CAP task force
Different criteria for interpretation of CISH or SISH
H&E slide corresponding to the block used for FISH should be examined
Areas of invasive carcinoma are identified and marked
Areas of DCIS should be noted in order to exclude them from the evaluation
In rare cases, DCIS will show amplification but not the associated invasive carcinoma
Review of the HER2 IHC slide is helpful to identify areas of heterogeneous protein expression that should be correlated with FISH results
Stay updated, free articles. Join our Telegram channel

Full access? Get Clinical Tree