May regress after withdrawal of oral contraceptives
•
Associated with obesity or ethanol use
Clinical Issues
•
Typically in women of reproductive age

Noncirrhotic background liver
•
Symptoms

Abdominal pain; acute, intermittent, or chronic
•
Complications

Bleeding

Rupture; pregnancy is risk factor

Slight chance of malignant transformation
Microscopic
•
Cords or sheets of benign hepatocytes with uniform nuclei

Low nuclear:cytoplasmic ratio
•
Portal structures lacking
•
Numerous unpaired arteries
•
Intact reticulin framework
•
Hemorrhage &/or infarcts may be present with hemosiderin-laden macrophages or fibrotic regions
Top Differential Diagnoses
•
Well-differentiated hepatocellular carcinoma
•
Focal nodular hyperplasia
•
Nodular regenerative hyperplasia
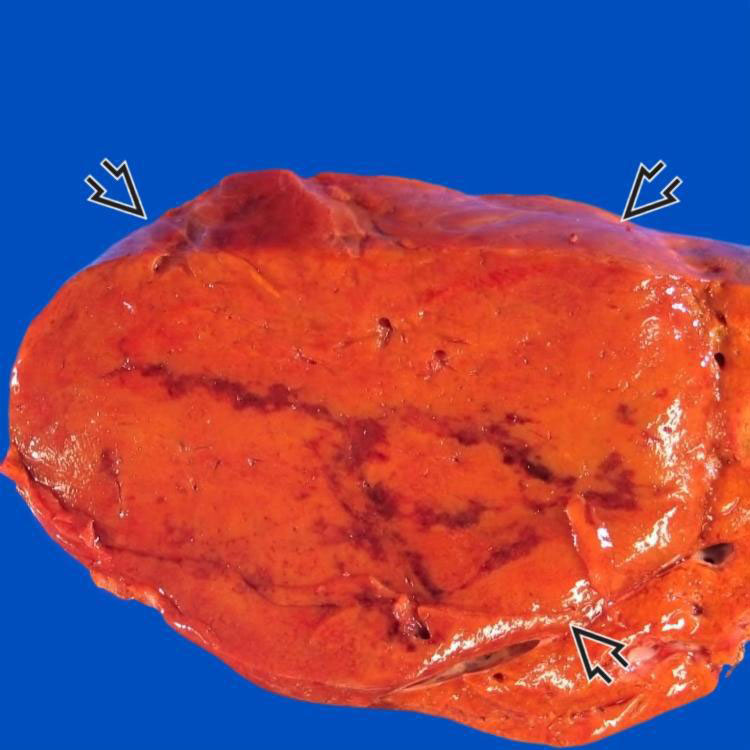

Gross Appearance
This large hepatic adenoma 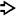 is well demarcated and tan-brown with streaks of hemorrhage.
is well demarcated and tan-brown with streaks of hemorrhage.
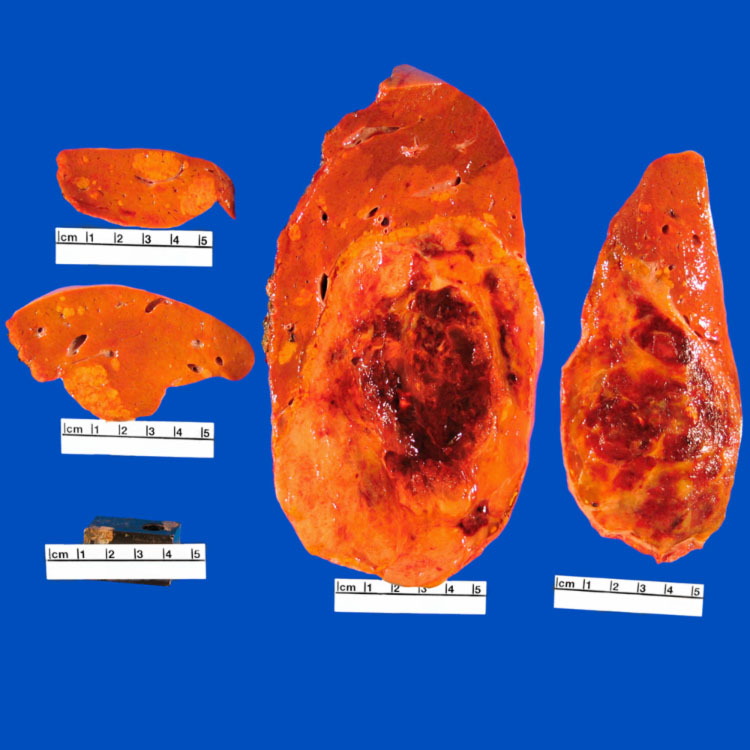
Hepatic Adenomatosis
This case of hepatic adenomatosis features multiple adenomas with hemorrhage and necrosis. 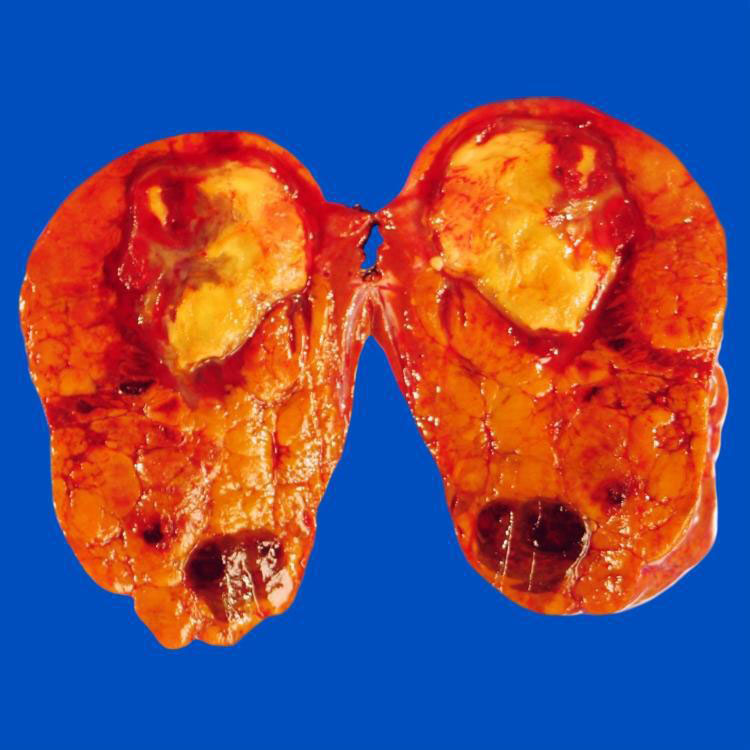
Gross Appearance
Areas of necrosis and hemorrhage are common in hepatic adenoma. 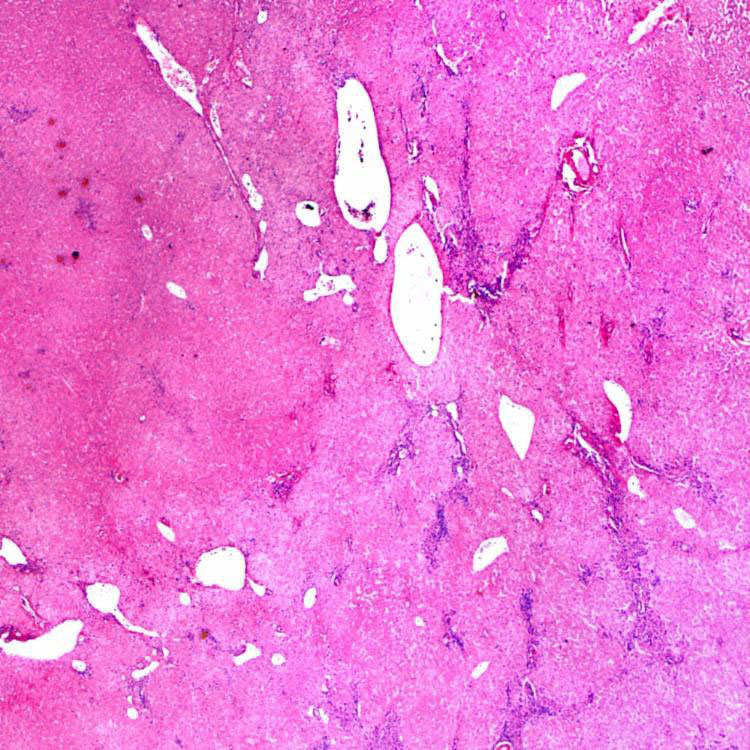
Sheets of Hepatocytes
Low-magnification view shows sheets of hepatocytes with numerous thin-walled vessels in hepatic adenoma.
TERMINOLOGY
Definitions
•
Benign liver neoplasm composed of cells of hepatocytic origin

> 10 individual adenomas in 1 liver

Associated with
–
Glycogenosis type Ia or III
ETIOLOGY/PATHOGENESIS
Definite Mechanism Unclear
•
Sex hormones appear to play role

Commonly associated with oral contraceptive or long-term steroid use
–
Newer generation contraceptive pills with lower estrogen content may be associated with lower risk
•
Also associated with obesity and ethanol use
•
Also associated with glycogen storage disease types I and III, galactosemia, tyrosinemia
CLINICAL ISSUES
Epidemiology
•
Age

Reproductive age in women
•
Sex

Typically women
Presentation
•
Liver mass

Arising in noncirrhotic liver without underlying liver disease

May be multiple
•
Symptoms

Abdominal pain
–
Acute, intermittent, or chronic
•
May be asymptomatic; found on imaging (20% of cases)
•
Associated clinical conditions

Oral contraceptive use
–
May regress after withdrawal of oral contraceptives

Obesity

Metabolic syndrome

Excessive alcohol use

Anabolic steroid use

Tobacco use

Glycogen storage disease

Maturity-onset diabetes of young (MODY) type 3
Laboratory Tests
•
Serum liver tests usually normal including α-fetoprotein
Treatment
•
Stop oral contraceptives

If tumors exceeds 5 cm

If growing in fear of
–
Malignant transformation
•
Liver transplantation in some cases (multiple, etc.)
Prognosis
•
Complete surgical resection should be curative
•
Rarely, malignant transformation (4-10%), bleeding, or rupture

Prevalence of malignancy 10x higher in affected men compared to female counterpart
Only gold members can continue reading.
Log In or
Register to continue
Like this:
Like Loading...
Related

Stay updated, free articles. Join our Telegram channel






