EXAMINATION
| TECHNIQUE | FINDINGS |
|---|---|
| HEART | |
| Inspect precordium | |
Have patient supine, and keep light source tangential. Apical impulse Apical impulse | EXPECTED:Visible about midclavicular line in fifth left intercostal space. Sometimes visible only with patient sitting. |
| UNEXPECTED:Visible in more than one intercostal space; exaggerated lifts or heaves. | |
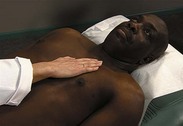
| Palpate precordium | |
 Apical impulse Apical impulseHave patient supine. With warm hands, gently feel precordium, using proximal halves of fingers held together or whole hand. As shown in figure on p. 114, methodically move from apex to left sternal border, base, right sternal border, epigastrium, axillae. | |
 | |
| Percuss precordium (optional) | |
| Begin by tapping at anterior axillary line, moving medially along intercostal spaces toward sternal borders until tone changes from resonance to dullness. Mark skin with marking pen. | EXPECTED:No change in tone before right sternal border; on left, loss of resonance generally close to point of maximal impulse at fifth intercostal space. Loss of resonance may outline left border of heart at second to fifth intercostal spaces. |
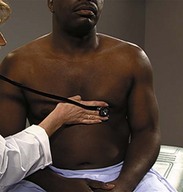
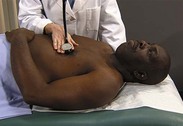
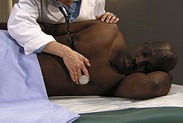
| Auscultate heart | |
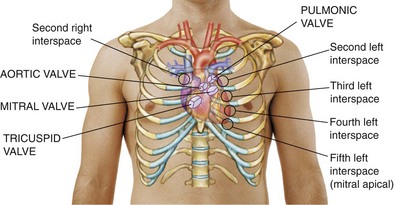
| Make certain patient is warm and relaxed. Isolate each sound and each pause in cycle, and then inch along with stethoscope. Approach each of the five precordial areas shown in figure on p. 115 systematically, base to apex or apex to base, using each position shown in figures at right and below. Use diaphragm of stethoscope first, with firm pressure, then bell, with light pressure. | |
 | |
 | |
 | |
 | |
EXPECTED:S1 usually heard as one sound and coincides with rise of carotid pulse. See table on p. 116. | |
| EXPECTED:S2 to become two components during inspiration. S2 to become an apparent single sound as breath is exhaled. See table on p. 116. | |
 Splitting Splitting | EXPECTED:S2 splitting—greatest at peak of inspiration—varying from easily heard to nondetectable. |
 S3 and S4 S3 and S4If needed, ask patient to raise a leg to increase venous return or to grip your hand vigorously and repeatedly to increase venous return.
Stay updated, free articles. Join our Telegram channel
Full access? Get Clinical Tree


| |