Chapter 11 Head and Neck
INFLAMMATORY LESIONS
4 What are the complications of caries?
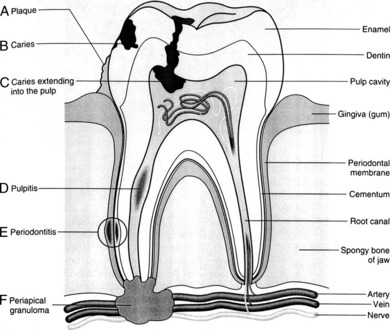
Destruction of enamel and dentin will allow the bacteria to enter the pulp and extend into the bone at the tip of the tooth (Fig. 11-1). Typical complications are as follows:
 Apical abscess: Bacteria extend from the pulp into the bone surrounding the root of the tooth. The pain is severe and usually throbbing. Pus may drain into the mouth along the lateral sides of the infected tooth.
Apical abscess: Bacteria extend from the pulp into the bone surrounding the root of the tooth. The pain is severe and usually throbbing. Pus may drain into the mouth along the lateral sides of the infected tooth. Periapical granuloma: This term, a misnomer, is used to describe the granulation tissue that develops inside the healing periapical abscess.
Periapical granuloma: This term, a misnomer, is used to describe the granulation tissue that develops inside the healing periapical abscess. Radicular cyst: If the pus from an abscess is resorbed, a cavity remains. This initial pseudocyst (no epithelial lining) may be partially covered by ingrowths of gingival epithelium.
Radicular cyst: If the pus from an abscess is resorbed, a cavity remains. This initial pseudocyst (no epithelial lining) may be partially covered by ingrowths of gingival epithelium.7 List the most common infectious diseases affecting the mouth and oropharynx
TABLE 11-1 Most Common Infectious Diseases Affecting the Mouth and Oropharynx
Exudative pharyngitis with swollen lymph nodes, hairy leukoplakia in acquired immune deficiency disease |
Stay updated, free articles. Join our Telegram channel

Full access? Get Clinical Tree