Immunosuppressed recipient cannot destroy donor cells
Microscopic
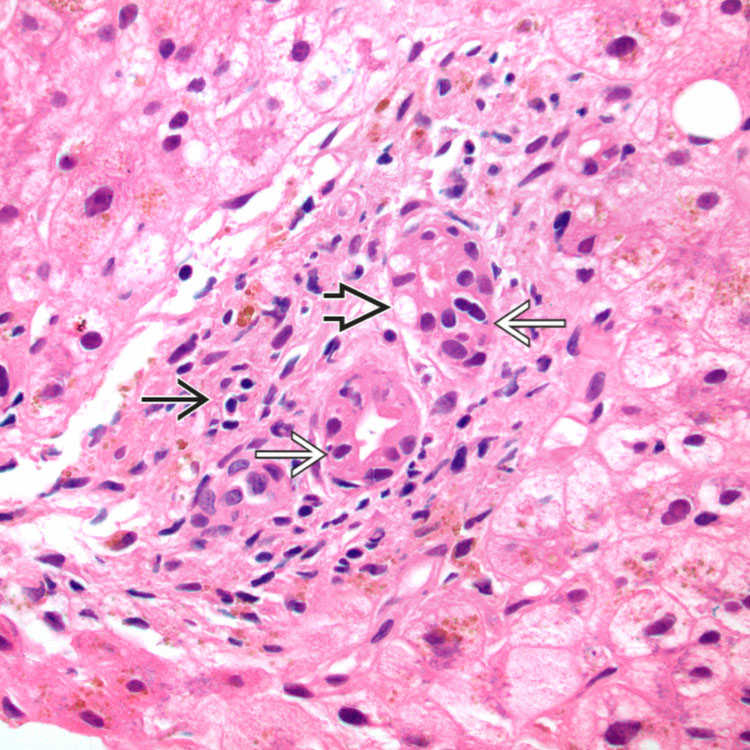
Mild portal inflammation
 and bile duct damage are seen in this case of hepatic graft-vs.-host disease (GVHD). The biliary epithelial cells are irregular and unevenly spaced
and bile duct damage are seen in this case of hepatic graft-vs.-host disease (GVHD). The biliary epithelial cells are irregular and unevenly spaced  and show cytoplasmic vacuolization
and show cytoplasmic vacuolization  . The duct lumen is irregular as well. These are all features of biliary epithelial damage.
. The duct lumen is irregular as well. These are all features of biliary epithelial damage.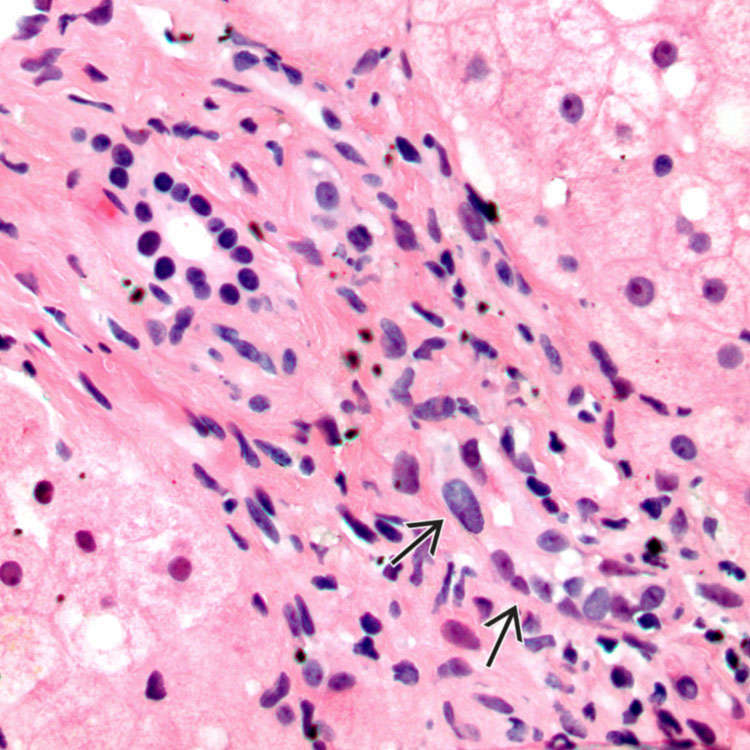
Bile duct epithelial cell nuclei are pleomorphic, varying in size and polarity, and unevenly spaced
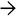 in this case of GVHD. There is cytoplasmic vacuolization. The portal inflammation is mild.
in this case of GVHD. There is cytoplasmic vacuolization. The portal inflammation is mild.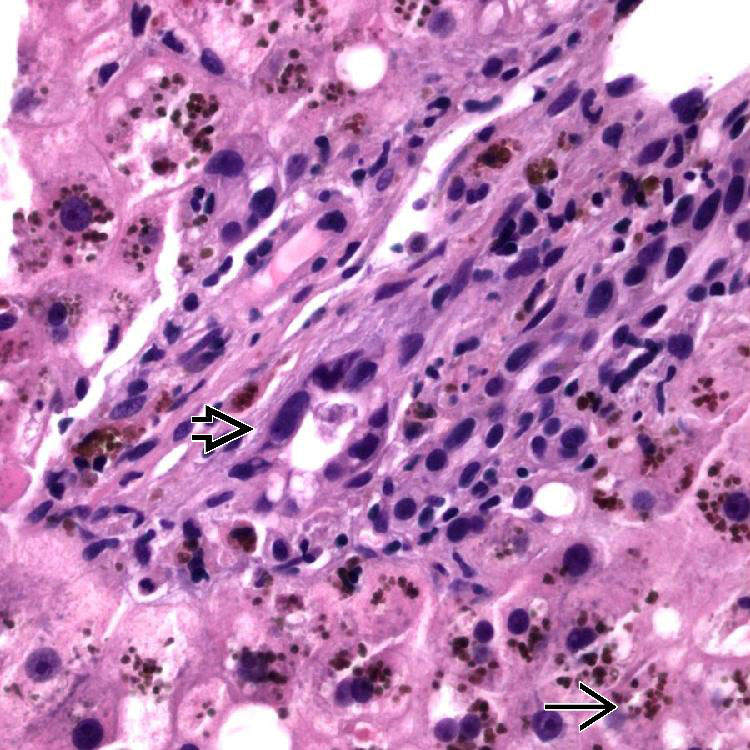
This case of GVHD shows mild portal inflammation and biliary epithelial cell injury
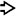 . The brown pigment indicates iron overload, which is often seen
. The brown pigment indicates iron overload, which is often seen 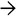 in stem cell transplant recipients. The portal inflammation is mild.
in stem cell transplant recipients. The portal inflammation is mild.TERMINOLOGY
Abbreviations
Definitions
• Attack of immunocompetent, donor-derived cells against recipient tissues




Stay updated, free articles. Join our Telegram channel

Full access? Get Clinical Tree







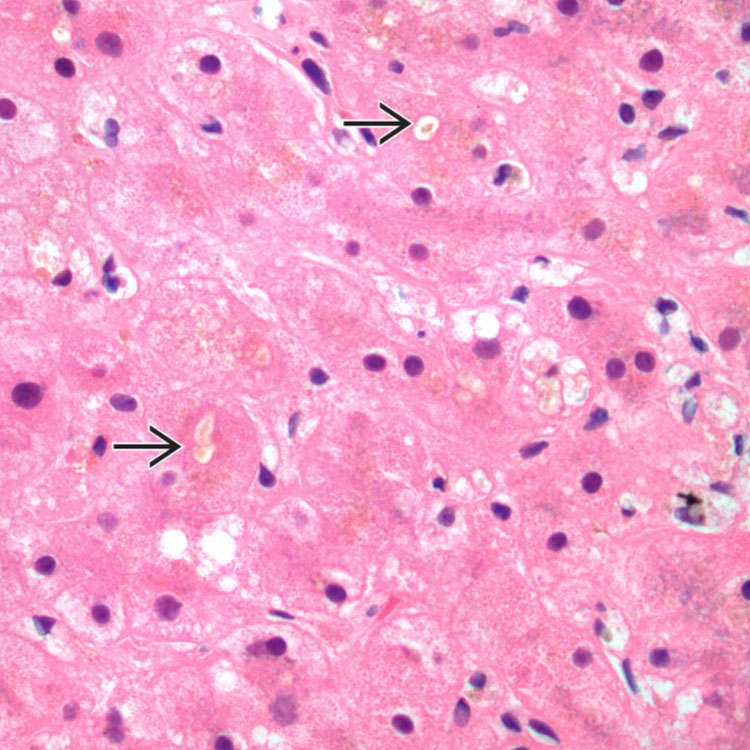
 , mild inflammation, and hepatocyte swelling.
, mild inflammation, and hepatocyte swelling.
