Results in different enzymatic defects in liver that are classified as glycogen storage disease (GSD) types 0, I, II, III, IV, VI, and IX

Types I, III, and IX account for 80% of hepatic GSD
•
Most forms autosomal recessive, except GSD IX, which is X-linked
Clinical Issues
•
Most patients present with hepatomegaly and hypoglycemia
•
Increased incidence of hepatic adenoma and hepatocellular carcinoma in GSD I and also GSD III
•
Liver transplantation corrects primary hepatic enzyme defect and is used primarily for GSD IV
•
Prognosis variable based on type of GSD
Microscopic
•
Histologic features not generally diagnostic of GSD
•
Assess liver for mosaic pattern of hepatocytes, glycogenated nuclei, fatty change, and fibrosis

Enlarged, pale-staining, swollen hepatocyte cytoplasm, and prominent cell membrane appearance

Compression of sinusoids by expanded hepatocytes

GSD 0 has decreased glycogen

GSD IV has characteristic cytoplasmic inclusions
•
Cirrhosis frequent in GSD IV and can occur in III and IX
Ancillary Tests
•
Electron microscopy

Lysosomal-bound glycogen for GSD II

Fibrillar glycogen for GSD IV
TERMINOLOGY
Abbreviations
•
Glycogen storage disease (GSD)
ETIOLOGY/PATHOGENESIS
Inborn Error of Carbohydrate Metabolism
•
Gene mutation causes deficiency of hepatic enzymes involved in glycogen synthesis, degradation, or regulation

GSD I, II, III, IV, VI, and IX display increased hepatic glycogen

GSD 0 is storage defect that results in decreased hepatic glycogen
•
Types I, III, and IX account for 80% of hepatic GSD
•
Most forms autosomal recessive, except GSD IX, which is X-linked
CLINICAL ISSUES
Presentation
•
Hepatomegaly: GSD I, III, IV, VI, IX, and rarely in GSD II

GSD VI also causes short stature and hyperlipidemia
•
Hypoglycemia

GSD Ia, Ib, III: Hypoglycemia in infancy due to inability to maintain steady blood glucose levels between feedings
–
Profound hypoglycemia can result in seizures

GSD 0: Hypoglycemia after short fasts, often in early childhood as feed intervals are extended

Hypoglycemia mild in GSD VI and IX, rare in GSD IV; not feature of GSD II
Laboratory Tests
•
Enzymatic activity assay in liver tissue

GSD Ia, III, IV, VI, and IX
•
DNA mutational analysis
Treatment
•
Dietary intervention to prevent hypoglycemia, particularly for GSD 0 and I, also in GSD III
•
Liver transplantation corrects primary hepatic enzyme defect

Best treatment option for GSD IV; also has been performed for GSD I, III, and IV
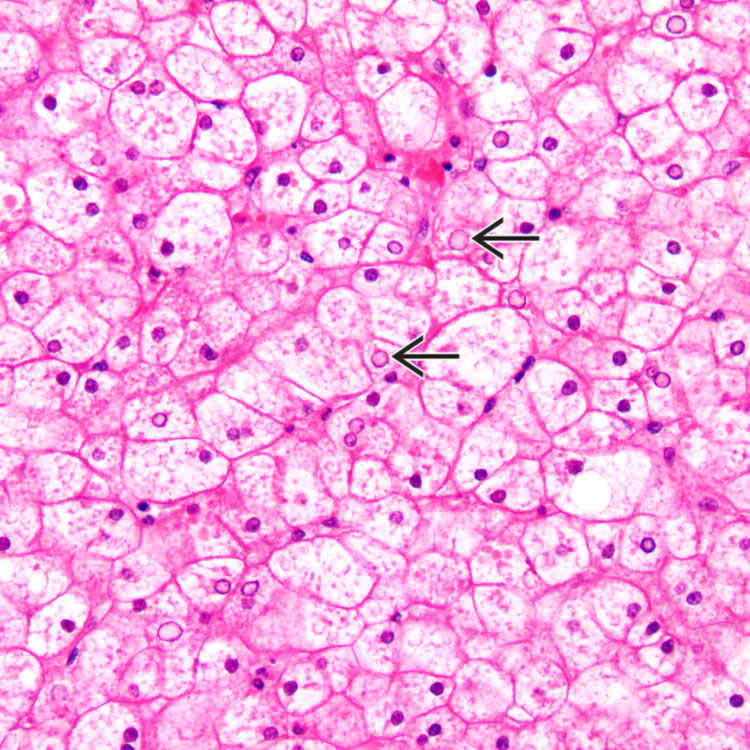
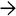 are seen.
are seen.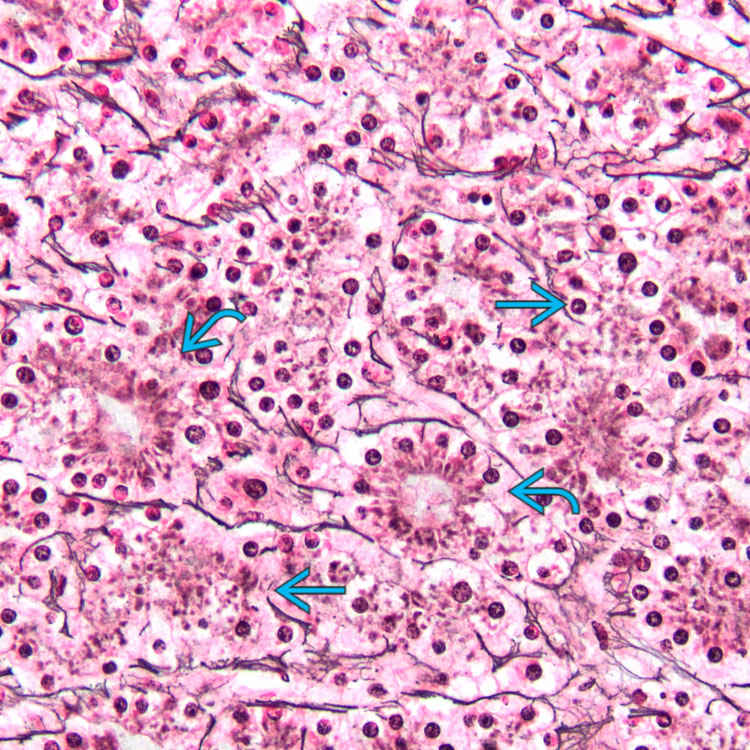
 , and pseudorosette formation
, and pseudorosette formation  in this hepatocellular carcinoma arising in a patient with glycogen storage disease (GSD) Ia.
in this hepatocellular carcinoma arising in a patient with glycogen storage disease (GSD) Ia.















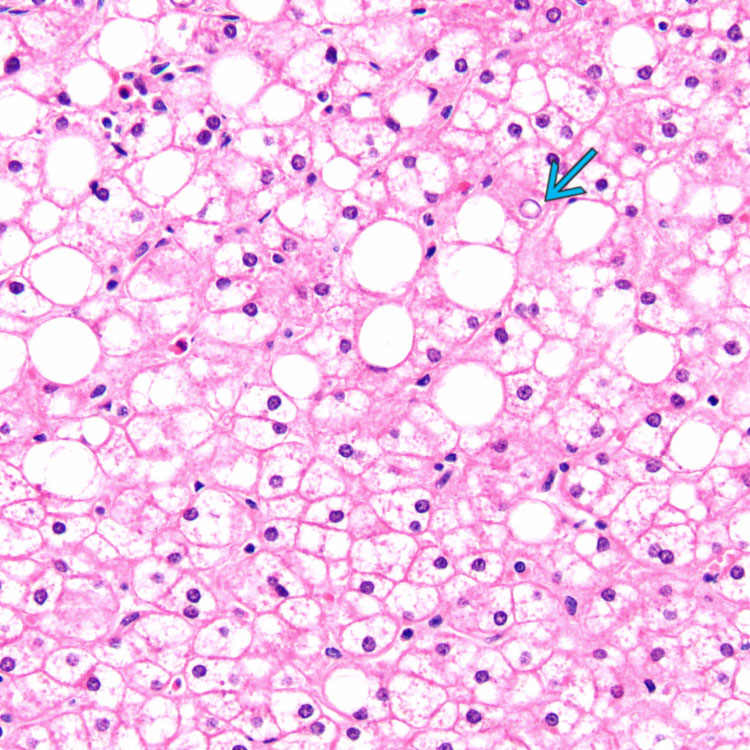
 . Fatty change is more apparent in this focus.
. Fatty change is more apparent in this focus.








