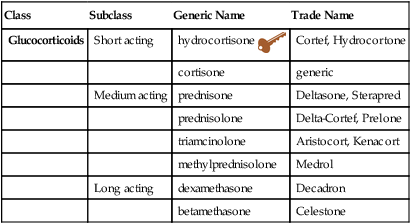
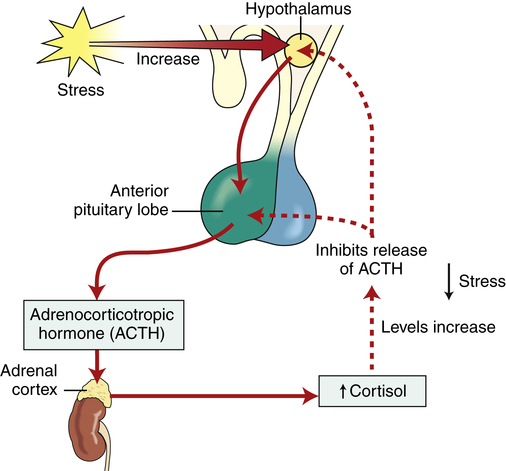
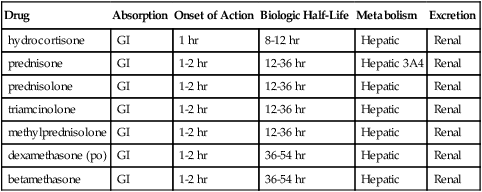
Chapter 51 The adrenal cortex synthesizes and secretes several hormones. Among them are the glucocorticoid cortisol, the mineralocorticoid aldosterone, and a small amount of the sex steroid androgen. Aldosterone, under the influence of the renin-angiotensin system and other metabolic pathways, regulates sodium, potassium, and water retention in the body. Cortisol has a powerful antiinflammatory effect, modifies the body’s immune response, and influences metabolic processes. The production of cortisol is controlled by a negative feedback loop involving the hypothalamus-anterior pituitary-adrenal cortex (HPA) axis (Figure 51-1). A low level of plasma cortisol stimulates the anterior pituitary to increase production of ACTH, which, in turn, stimulates the adrenal cortex to increase cortisol secretion. Similarly, a high level of circulating cortisol prompts downregulation of ACTH production and a resultant decrease in adrenal cortex production of cortisol. Glucocorticoids affect the metabolism of carbohydrates, proteins, and fats. They have direct and indirect effects on immune response, modulate inflammatory response, and play a role in the body’s response to stressful stimuli (i.e., fasting states). All drugs in this class are remarkably similar and may be discussed as a group; the most important differences between these drugs consist of duration of action and degree of inherent mineralocorticoid activity, which causes sodium and fluid retention (Table 51-2). Mineralocorticoid activity is needed in adrenal insufficiency but not in severe inflammation. Both cortisone and hydrocortisone have glucocorticoid and mineralocorticoid properties. Their synthetic analogs prednisone, prednisolone, and methylprednisolone have both effects as well, although glucocorticoid effects predominate. By contrast, triamcinolone, dexamethasone, and betamethasone have exclusively glucocorticoid antiinflammatory activity. TABLE 51-2 Pharmacokinetics of Selected Glucocorticoids Modified from Brunton LL, Chabner B, Knollman B, editors: Goodman & Gilman’s the pharmacological basis of therapeutics, ed 12, New York, 2010, McGraw-Hill.
Glucocorticoids
Class
Subclass
Generic Name
Trade Name
Glucocorticoids
Short acting
hydrocortisone ![]()
Cortef, Hydrocortone
cortisone
generic
Medium acting
prednisone
Deltasone, Sterapred
prednisolone
Delta-Cortef, Prelone
triamcinolone
Aristocort, Kenacort
methylprednisolone
Medrol
Long acting
dexamethasone
Decadron
betamethasone
Celestone
Therapeutic Overview
Anatomy and Physiology
Mechanism of Action
Drug
Absorption
Onset of Action
Biologic Half-Life
Metabolism
Excretion
hydrocortisone
GI
1 hr
8-12 hr
Hepatic
Renal
prednisone
GI
1-2 hr
12-36 hr
Hepatic 3A4
Renal
prednisolone
GI
1-2 hr
12-36 hr
Hepatic
Renal
triamcinolone
GI
1-2 hr
12-36 hr
Hepatic
Renal
methylprednisolone
GI
1-2 hr
12-36 hr
Hepatic
Renal
dexamethasone (po)
GI
1-2 hr
36-54 hr
Hepatic
Renal
betamethasone
GI
1-2 hr
36-54 hr
Hepatic
Renal
< div class='tao-gold-member'>
![]()
Stay updated, free articles. Join our Telegram channel

Full access? Get Clinical Tree


