Gestational Trophoblastic Disease
Overview of Early Placental Development
Molar Gestational Trophoblastic Disease
Early (First Trimester) Complete Hydatidiform Moles
Advanced (Second Trimester) Complete Hydatidiform Moles
Choriocarcinoma Associated with Full-term Pregnancy and Intraplacental Choriocarcinoma
Placental Site Trophoblastic Tumor
Non-Neoplastic Trophoblastic Lesions
Introduction
Gestational trophoblastic disease is a spectrum of disorders ranging from unusual presentations of normal implantation, through premalignant hydatidiform moles (complete, partial, and invasive mole) to malignant disorders including choriocarcinoma, placental site trophoblastic tumor, and epithelioid trophoblastic tumor (Table 34.1). Often, trophoblast remnants of normal gestations, including placental site nodules, and exaggerated placental site reaction may cause clinical symptoms, which can be clinically and histologically confused with trophoblastic tumors. Although each of these entities has its own clinical and pathologic characteristics, they may be grouped under the single umbrella of gestational trophoblastic disease because they are all related to pregnancy, and may progress from one to another.
Overview of Early Placental Development
Villous Trophoblast
At the end of the first week following conception, trophectoderm of the blastocyst implants in the endometrial surface and invades the endometrial stroma. The mononuclear trophoblastic shell, composed of previllous trophoblast, has not yet formed villous structures. This is responsible for erosion of maternal tissue by production of various hormones, cytokines, a number of extracellular matrix receptors, and matrix-degrading proteases and their inhibitors.1 The previllous trophoblast of the implanting embryonic pole differentiates into two components, the outer syncytiotrophoblast located at the maternal–fetal interface and the inner cytotrophoblast (Figure 34.1). The cytotrophoblast is an inner layer of ovoid, mononuclear cells with high proliferative activity that functions as the trophoblastic stem cell. Syncytiotrophoblast, the first differentiated trophoblast lineage, produces human chorionic gonadotropin (hCG) and proteolytic enzymes, and secretes factors that cause apoptosis of the endometrial epithelial cells and decidua. Penetration and erosion of the adjacent maternal capillaries results in the formation of lacunae within the syncytiotrophoblast,2 and these structures enlarge to form the intervillous space.
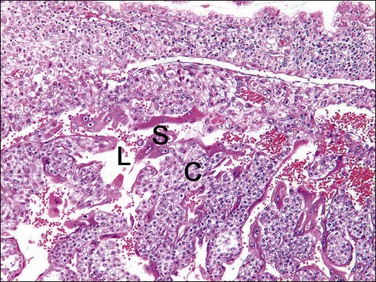
Figure 34.1 Lacunar stage in early placental development. As the trophoblastic cells invade the endometrium, they differentiate to form a double layer of cytotrophoblast (C) and syncytiotrophoblast (S) and intervening lacunar space (L).
Early in the third week, extraembryonic mesoderm grows into the solid primary villous trabeculae of cytotrophoblast and syncytiotrophoblast (Figure 34.2), forming secondary villi. These consist of an outer layer of syncytiotrophoblast, a middle layer of cytotrophoblast, and an inner connective tissue core. At this stage secondary chorionic villi cover the entire surface of the chorionic sac.2
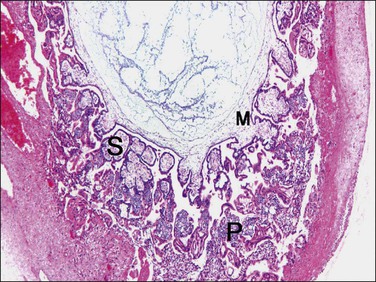
Figure 34.2 Villous stage in placental development. Mesenchymal cells derived from extraembryonic mesoderm (M) invade the villi, transforming the primary villi (P) into secondary villi (S).
Active vasculogenesis begins within the secondary villous stroma, transforming them into tertiary villi (Figure 34.3A–D). Early primitive capillaries in the villous core are formed by in situ differentiation of pluripotent mesodermal tissue into hemangioblastic stem cells that give rise to committed endothelial progenitors (angioblast) and hematopoietic stem cells. Angioblasts form angiogenic cell cords (Figure 34.3A), which develop slit-like vascular lumens during the third to fourth week (Figure 34.3B). Subsequently, distinct vascular lumens with variable numbers of immature hematopoietic cells begin to appear (Figure 34.3C). Frequent mitotic figures and occasional karyorrhexis are identified among the angiogenic cell cords and the stromal cells at this stage. After that, new blood vessels in the villous stroma are derived by sprouting, elongation, and remodeling of already existing blood vessels. Villous stroma is basophilic and myxomatous until the end of the fourth week when the ground substance gradually assumes an edematous and reticular appearance (Figure 34.3D).
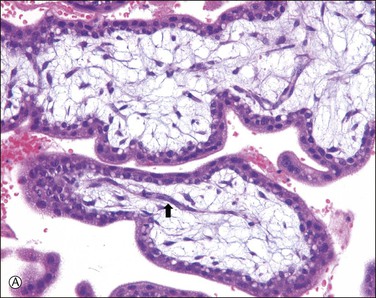
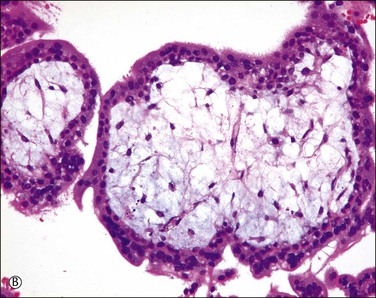
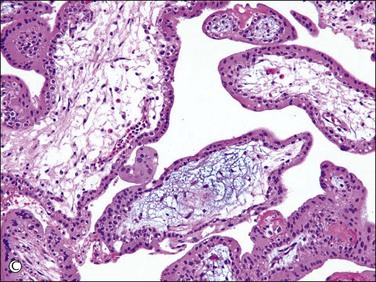
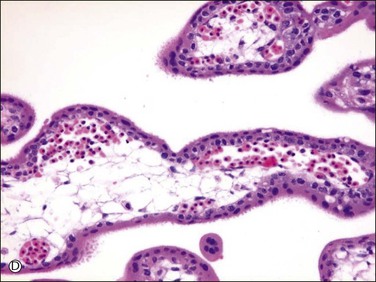
Figure 34.3 Vasculogenetic steps in chorionic villi during early pregnancy (A–D). Stromal vessels are differentiated from (A) immature angiogenic cell cords (arrow) within basophilic stroma to (B) immature blood vessels containing primitive slit-like vascular lumens and immature hematopoietic components to (C, D) mature blood vessels containing distinct vascular lumens and hematopoietic components. Note stromal changes from basophilic to edematous stroma.
As active vasculogenesis is occurring, the villi branch, trophoblast proliferates at the implanting embryonic pole, and forms a confluent shell along the external circumference of the chorionic villi (Figure 34.4). This cytotrophoblastic shell of early pregnancy mimics the trophoblastic hyperplasia of hydatidiform moles, with which it should not be confused.
Extravillous (Intermediate) Trophoblast
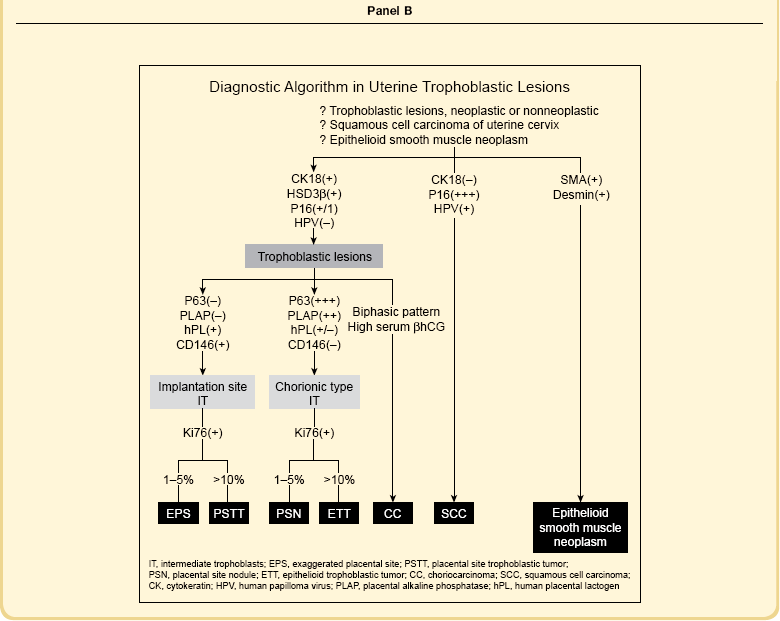
While one group of cytotrophoblast fuses to form multinucleated syncytiotrophoblast, which encases the free villi of the placenta, another differentiates into extravillous trophoblast and develops invasive properties.3 At the basal end of anchoring villi, cytotrophoblast proliferates to form columns of ‘villous intermediate trophoblast,’ a cohesive mass of cells with high proliferative activity (Figure 34.5A). As the cells in the trophoblastic column come into contact with decidua, these cells exit the cell cycle, thereby losing their proliferative activity, detach from the cell column, and acquire migratory and invasive properties. Subsequently, the cells move into the decidua and superficial myometrium (interstitial trophoblast) (Figure 34.5B) and penetrate the decidual spiral arteries (endovascular trophoblast) (Figure 34.5C). These are collectively referred to as ‘implantation site intermediate trophoblast.’4
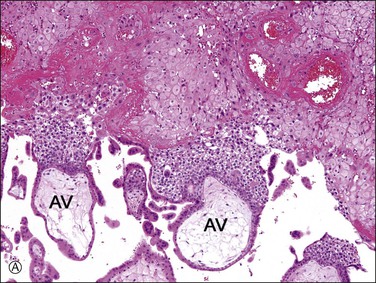
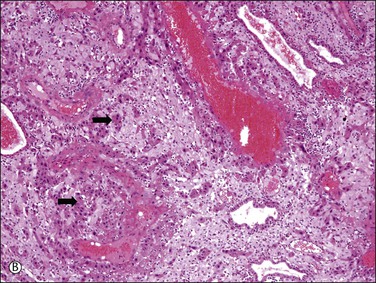
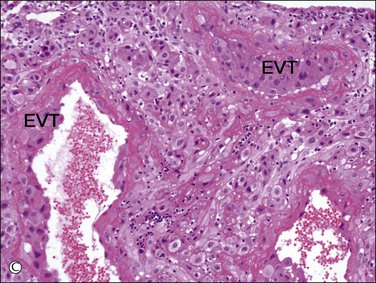
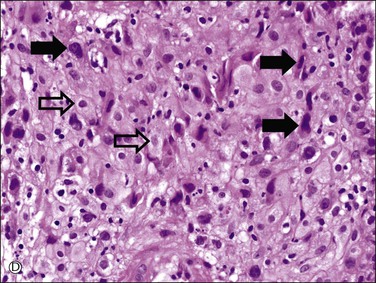
Figure 34.5 Villous and extravillous trophoblast at the implantation site. (A) Anchoring villi (AV) are attached to the decidua of the implantation site. (B) Extravillous (interstitial) trophoblast (closed arrows) infiltrating into the decidua have densely eosinophilic or amphophilic cytoplasm. (C) Extravillous (endovascular) trophoblast (EVT) infiltrating into the blood vessels. (D) Close-up view of extravillous trophoblast (closed arrows) shows slightly larger, irregular, and hyperchromatic nuclei with more eosinophilic or amphophilic cytoplasm than the admixed decidual cells with paler cytoplasm (open arrows).
Interstitial (intermediate) trophoblast cytology is similar to that of surrounding decidualized stromal cells (Figure 34.5A–D), but the trophoblast nuclei are slightly larger, irregular, and hyperchromatic. Trophoblastic spindle cells often have angular dark nuclei as they dissect individually or in small clusters between decidual cells (Figure 34.5D).
Chorionic villi cover the entire chorionic sac until the beginning of the eighth week but become asymmetrical as those associated with the decidua capsularis begin to degenerate. A variable thickness of trophoblastic cells persists in the chorion laeve until term, but this extravillous trophoblast is not invasive. Therefore, the fetal membrane is composed of amniotic epithelium sitting on thin connective tissue layers of amnion and chorion, maternal decidua parietalis with interposed extravillous trophoblast, and occasional ghost villi (Figure 34.6A). Microscopically, intermediate trophoblast in the chorion laeve of term placentas are composed of two populations with differing cytology and immunophenotypes (Figure 34.6A–F).4,5 These two types of intermediate trophoblast are not strictly separated into different compartments, but rather are admixed to some extent.
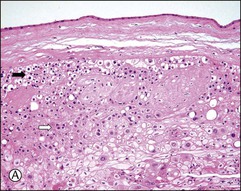
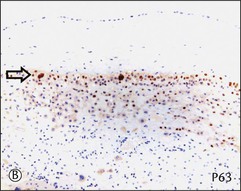
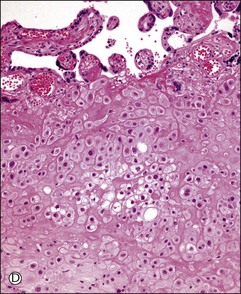
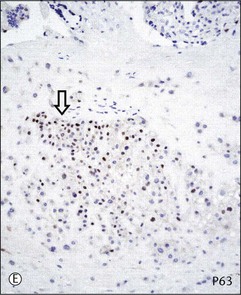
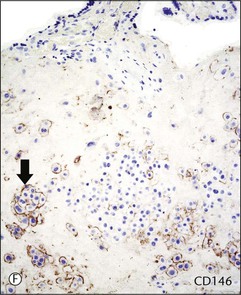
Figure 34.6 Cytomorphologic features and immunophenotypes of extravillous trophoblast. Trophoblast contacting chorionic stroma are relatively smaller and uniform with clear cytoplasm (A, closed arrow), while those directly contacting decidua have slightly larger nuclei and amphophilic cytoplasm (A, open arrow). P63 is only expressed in the former (B, open arrow), whereas CD146 (Mel-CAM) is mostly expressed in the latter (C, open arrow). Extravillous trophoblast in the implantation site (basal plate) is also composed of two populations (D). P63 is expressed in the smaller trophoblasts with clear cytoplasm (E, open arrow) and CD146 (Mel-CAM) is expressed in the larger trophoblasts with amphophilic cytoplasm (F, closed arrow).
Trophoblast Immunohistochemical Markers
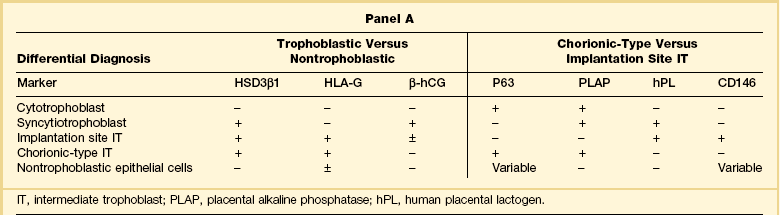
All trophoblastic cells, including cytotrophoblast, syncytiotrophoblast, and intermediate trophoblast, possess epithelial antigens detected by antibodies for cytokeratin (AE1 and AE3), epithelial membrane antigen, and low molecular weight cytokeratins (CAM 5.2 and Ber-P4). Although not specific to the trophoblast, these common antibodies are useful to distinguish trophoblastic from nonepithelial tumors, such as epithelioid smooth muscle neoplasia. Some antibodies, including HSD3β1, HLA-G, and β-hCG, are used in the differential diagnosis between trophoblastic and nontrophoblastic lesions. Others, including P63, placental alkaline phosphatase, human placental lactogen, and CD146 (Mel-CAM), are useful to infer ‘chorionic-type’ or ‘implantation site’ differentiation among intermediate trophoblast. Expressions of various trophoblastic markers in subpopulations of trophoblast are summarized in Panel A of Table 34.2, and their use in resolving various differential diagnoses is shown in Panel B.
Molar Gestational Trophoblastic Disease
Complete Hydatidiform Mole
Incidence
Epidemiologic studies have reported wide regional variation in the incidence of hydatidiform mole, of 0.57–1.6 per 1000 pregnancies6,7 in North America and Europe, rising to 2.0–8.5 in Asia, Africa, and Latin America.8,9 Although trophoblastic diseases occur more frequently in Asia than in North America or Europe, considerable difficulty exists in determining true incidence rates. Since these diseases are directly related to pregnancy, incidence ratios have been expressed per total number of pregnancies, number of deliveries, or live births in population-based or hospital-based studies. However, it is hard to obtain data regarding clinically unrecognized pregnancies, spontaneous and induced abortions, ectopic pregnancies, and uncomplicated live births and pregnancies that did not receive hospital-based care. Moreover, histopathologic examination of evacuated tissue is infrequent in some parts of the world and the diagnosis of hydatidiform mole can be missed, especially early in gestation.
Even in the high-incidence areas, overall incidence rates have significantly decreased over the last few decades with improved socioeconomic status of women, suggesting that environmental factors including dietary or nutritional factors are as important as ethnic or genetic factors.10–12 In the Netherlands, the incidence of trophoblastic disease increased significantly in recent years, partially explained by increased maternal age, increased proportion of live births of Asian descent, and improved diagnostic techniques.7
Risk Factors
Extremes of maternal age and prior molar pregnancy are established risk factors.7,13 Conceptions occurring at extreme reproductive age, women over 45 and girls under 15, have higher risks of molar pregnancy than those for women aged 16–40.6,14
Pathogenetic Mechanism
The genetic origin of hydatidiform moles was first suggested by the observation that about 90% have sex chromatin.15 Cytogenetic studies confirmed that about 90% of hydatidiform moles had a 46,XX karyotype16 and others triploid karyotypes.17 Based on the correlation of the histologic findings of hydatidiform moles and their karyotypes, existence of the two genetically distinct entities of complete and partial mole were suggested.18,19
Most complete hydatidiform moles are a diploid androgenetic pregnancy in which all 46 chromosomes are paternally derived. Usually these arise following endoreduplication of a haploid sperm (Figure 34.7), but a minor proportion result from fertilization of an anucleate egg by two sperms (dispermy)20 (Figure 34.7). The fate of the missing maternal chromosomes is unclear, but may be caused by extrusion of both maternal sets of chromosomes into one of the polar bodies during meiosis, giving rise to an anucleate egg. Alternatively, retained maternal chromosomes may degenerate and thus fail to participate in postfertilization cell division. Triploid and tetraploid complete moles have been reported; however, these are still generally androgenetic in origin, having three or four paternal sets of chromosomes.
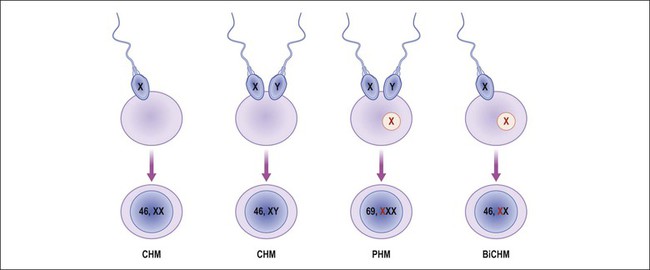
Figure 34.7 Genetic origins of hydatidiform moles. Endoreduplication of a haploid sperm or fertilization of two sperm in a functionally ‘empty’ ovum results in androgenetic complete hydatidiform mole (CHM). Fertilization of a normal ovum by two sperm results in triploid partial hydatidiform mole (PHM). Presence of biparental genome, but with mutation, results in biparental complete hydatidiform mole (BiCHM).
Rarely, complete moles are biparental diploid with both a maternal and paternal chromosome complement.21,22 This corroborates the suggestion that fertilization of an empty egg is not mandatory for the creation of a hydatidiform mole. Studies have shown that these biparental moles are frequently associated with patients with recurrent or familial molar disease.22 Biparental complete hydatidiform moles are now recognized as a clinically important subgroup, caused by maternal autosomal recessive mutation of NLRP7, located in a 1.1 Mb region on chromosome 19q13.4. Mutation in this gene may result in dysregulation of imprinting in the female germ line with abnormal development of both embryonic and extraembryonic tissue.
Clinical Features
Molar pregnancies are now diagnosed at an earlier gestational age due to routine use of first trimester ultrasonography. Formerly, the majority of patients presented by 20 weeks of gestation with vaginal bleeding, symptomatic anemia, passage of molar tissue, excessive uterine size, hyperemesis, and markedly elevated hCG levels. Pre-eclampsia was observed in approximately 27%, and clinically evident hyperthyroidism in about 7% of the cases. Abdominal pain and pelvic pain resulting from enlarged theca lutein cysts of the ovary were commonly associated, and pelvic ultrasound examination revealed a characteristic ‘snowstorm appearance.’ Recently, however, the gestational age at the time of ultrasound diagnosis ranges from 5.0 to 12.5 weeks (median 8–9 weeks). Accordingly, the clinical presentation has changed considerably; excessive uterine size, anemia, hyperemesis, and metastatic disease are less common, and earlier stage molar tissues are submitted for examination. Today 40% of women are asymptomatic, and most symptomatic patients present with vaginal bleeding or suspected miscarriage in early pregnancy. In the first trimester, a significant proportion of complete moles demonstrate minimal ultrasound findings and are missed by this modality.23 Overall sensitivity for the ultrasound diagnosis of molar gestations is 40–60%.23
Early (First Trimester) Complete Hydatidiform Moles
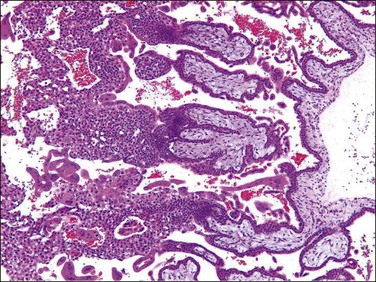
Early moles in which trophoblastic proliferation and hydropic change is minimal (Figure 34.8) are easily confused with non-molar hydropic abortions. At this early phase, molar chorionic villi have bulbous outlines resembling blunt finger-like projections, and the villous stroma may not have appreciable hydropic change. Villous trophoblastic proliferation is minimal or is frequently proliferated in a polar fashion (Figure 34.9), resembling polar proliferation of normal anchoring villi in early developing placentas. Trophoblastic pseudoinclusions, although often present, are not diagnostic, as they also may be seen in partial moles and aneuploid gestations. It is a combination of hypercellular basophilic stroma, immature blood vessels, and abnormal villous profiles that characterizes early complete moles, as these individual features may be seen separately and to a lesser extent in normal early developing placentas.
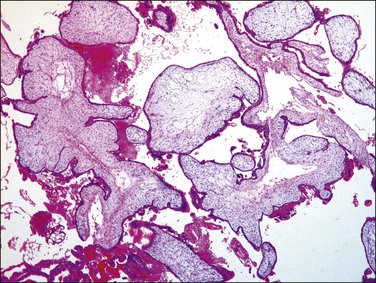
Figure 34.8 Early (first trimester) complete hydatidiform mole during the first trimester. Trophoblastic proliferation or hydropic change is nearly absent, which may cause underdiagnosis as non-molar hydropic abortion.
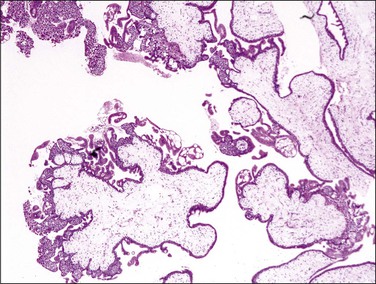
Figure 34.9 Early complete hydatidiform mole during the first trimester. Note the bulbous outlines of the chorionic villi and polar proliferation of villous trophoblast, resembling those of normal anchoring villi.
Poorly formed immature blood vessels in the villous stroma are characteristic of early moles. Vascular structures, when present (Figure 34.10), are linear cords in basophilic stroma, similar to the angiogenic cell cords of normal placentas (Figure 34.3A). Rarely, there are cleft-like spaces within the vascular structures, but unlike normal placentas they almost never contain hematopoietic components or red blood cells. There is characteristic karyorrhexis and apoptosis of stromal cells and immature vascular structures, scattering karyorrhectic nuclear debris throughout the villous stroma (Figure 34.11). Karyorrhexis and apoptosis within the villous stroma of non-molar hydropic abortuses and normal placentas are limited to a few cells within small terminal villi.
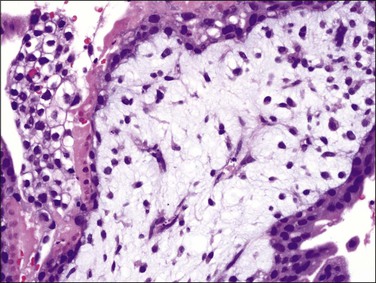
Figure 34.10 Early complete hydatidiform mole during the first trimester. Immature vascular structure with apoptotic nuclear debris in basophilic stroma is a characteristic feature of early moles.
Advanced (Second Trimester) Complete Hydatidiform Moles
The cellular and mildly edematous basophilic stroma of early moles progressively changes to form hydropic villi with central acellular cisternae, and eventually, diffusely hydropic hypocellular villi (Figure 34.12A–C). Stroma is progressively displaced from the central part of the villi by accumulated fluid. These hydropic vesicles have grossly visible ‘bunch of grapes’ appearance filling the entire uterine cavity (Figure 34.13). Circumferential proliferation of cytotrophoblast, intermediate trophoblast, and syncytiotrophoblast is prominent (Figures 34.14 and 34.15), sometimes forming large sheets of trophoblast around the edematous villi. The trophoblast of complete moles has variable degrees of cytologic atypia, which may include nuclear pleomorphism and heterochromasia, often accompanied by cytoplasmic vacuoles (Figure 34.16). The vacuoles are relatively more prominent than seen in normal trophoblast at the same gestational age. The degree of trophoblastic proliferation and hydropic change appears to be a time-dependent phenomenon that varies by gestational age, and is not related to the risk of subsequent persistent trophoblastic neoplasia.
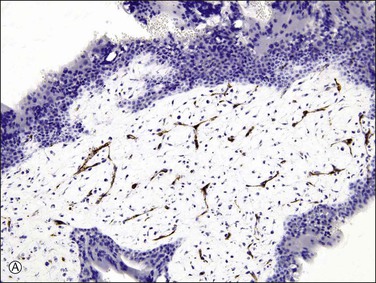
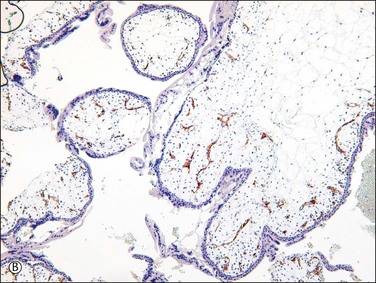
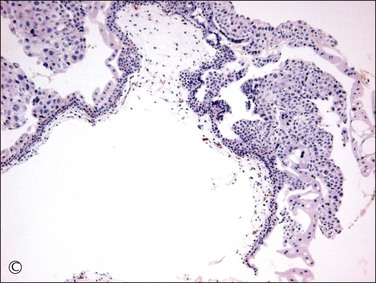
Figure 34.12 Progressive hydropic changes in the villous stroma of complete hydatidiform mole shown by blood vessel (CD31) immunostain. Numerous brown staining immature blood vessels are present in the cellular nonhydropic stroma during the first trimester (A), soon to be displaced. A cisterna is formed by accumulation of fluid in the center of the cellular nonhydropic stroma (B). In the second trimester, avascular hydropic villi are formed by extensive accumulation of vesicular fluid in vesicular cisternae (C).
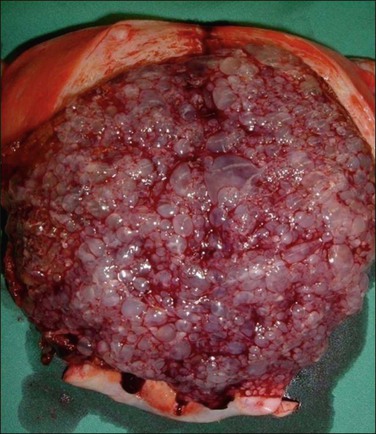
Figure 34.13 Complete hydatidiform mole in the second trimester of pregnancy. Molar tissue has a grossly visible ‘bunch of grapes’ appearance filling the entire uterine cavity
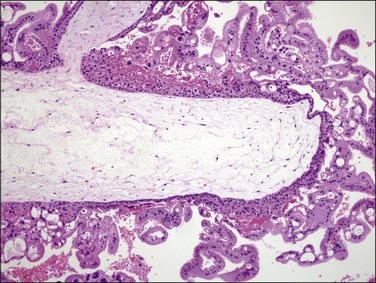
Figure 34.14 Complete hydatidiform mole in the second trimester of pregnancy. Circumferential trophoblastic proliferation and hydropic change of villous stroma are evident.
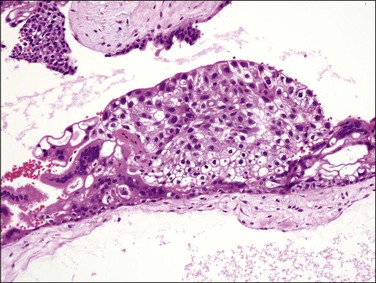
Figure 34.15 Complete hydatidiform mole in the second trimester of pregnancy. Proliferating trophoblast are composed of cytotrophoblast, intermediate trophoblast, and syncytiotrophoblast.
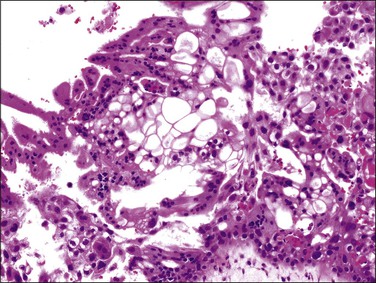
Figure 34.16 Complete hydatidiform mole in the second trimester of pregnancy. The trophoblast has variable degrees of cytologic atypia and frequent cytoplasmic vacuoles, although vacuoles themselves are not a diagnostic feature.
Molar implantation sites are almost always exaggerated, in that intermediate trophoblastic cells are more atypical and the Ki-67 labeling index is higher than for a normal pregnancy.24 Biparental, triploid, or tetraploid complete moles and 46,XX and 46,XY complete moles are histologically and immunohistochemically indistinguishable from the more common androgenetic diploid mole.25
Differential Diagnosis and Special Studies
Introduction of immunostaining for p57kip2 (CDKN1C), a paternally imprinted biomarker expressed only from the maternal genome of villous trophoblast, permits distinction between androgenetic (complete mole) and biparental (normal placenta, hydropic abortion, partial mole) tissues. Lack of p57kip2 immunohistochemical staining is thus a clinically useful feature of complete moles, contrasting with positive expression in all biparental gestations. Interpretation should be based solely on scoring of the villous cytotrophoblast as extravillous trophoblast relax the imprint and thus may demonstrate variable expression even in androgenetic cells (Figure 34.17A–C).
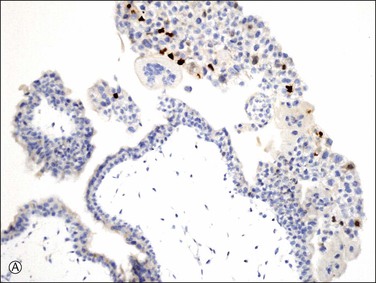
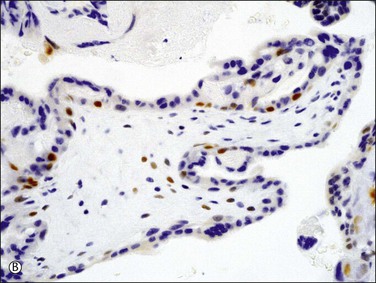
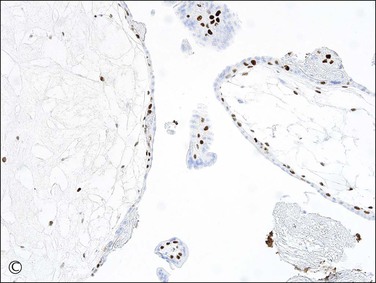
Figure 34.17 p57kip2 immunostaining patterns in complete and partial hydatidiform moles, and hydropic abortion (A–C). Immunonegativity for p57kip2 in the villous stromal cells and villous cytotrophoblastic cells of complete hydatidiform mole (A) is contrasted with the immunopositivities in those cell components in partial hydatidiform mole (B) and non-molar abortion (C). Diagnostic intrepretation should be based on villous surface trophoblast only, as solid columns of extravillous trophoblast emerging from the villous tips maintain p57 staining even in complete moles (A).
If both histologic features and the p57kip2 result are equivocal, DNA ploidy analysis by flow cytometry or image analysis and chromosomal enumeration by fluorescent or chromogenic in situ hybridization (Figure 34.18A and B) are of great value in making the distinction between a diploid complete (Figure 34.18A) and triploid partial hydatidiform mole (Figure 34.18B). Even with those ancillary studies, diagnosis of hydatidiform mole can sometimes be difficult. Recently, DNA genotyping has been used to confirm their unique parental chromosomal compositions of complete and partial hydatidiform moles except for rare biparental complete moles and complete moles arising from a twin gestation.26 However, decidual tissue should be carefully removed during the preparation.
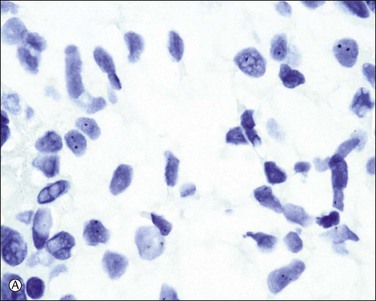
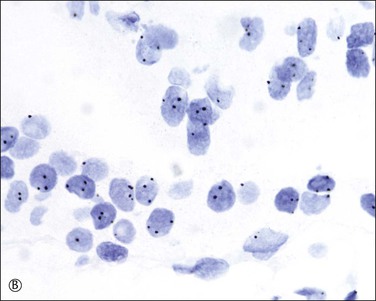
Figure 34.18 Chromogenic in situ hybridization using a centromere probe. Complete hydatidiform mole shows less than two signals in most of the cells (A), whereas a significant number of cytotrophoblast and villous stromal cells demonstrate three signals in partial hydatidiform mole (B). Although trisomy and triploid status cannot be distinguished, it is a simple and useful method to confirm the diagnosis of partial mole in conjunction with histologic features.
Hydropic non-molar abortion is often histologically difficult to differentiate from early complete mole because of hydropic stroma. Mature blood vessels containing hematopoietic components, if present, are a helpful feature for the exclusion of mole. However, hydropic abortuses in early pregnancy may lack mature vascular structures. In hydropic abortuses, trophoblastic cells lining the chorionic villi are frequently stretched and thin, and the villous outline is usually smooth and rounded (Figure 34.19). Although significant hydropic change is observed in hydropic abortion, central cisterna formation is less frequent, and extensive stromal karyorrhexis is rare. If the tissue is well preserved the diagnosis can easily be resolved with p57kip2 immunostaining.
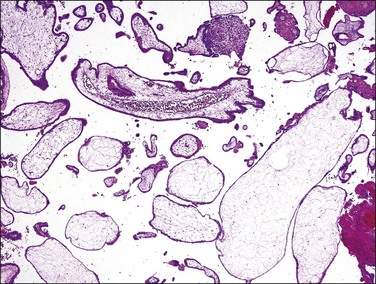
Figure 34.19 Non-molar hydropic abortion. The villous stroma has an edematous and myxoid appearance, but stromal blood vessels are well formed. The trophoblastic layer is thin, and the villous outline is usually smooth and rounded.
Nonhydropic normal early gestations may also be confused with complete moles because of prominent and confluent trophoblast along the external circumference of the chorionic villi (Figure 34.4). Mature stromal blood vessels containing distinct lumens and hematopoietic components, if present, and immunopositivity for p57kip2 antibody are helpful features for the exclusion of complete moles.
Although hydatidiform moles, either complete or partial, do occur in ectopic sites, molar pregnancies in ectopic locations should be diagnosed using strict histologic criteria. Non-molar ectopic gestations typically present early, when sheets of particularly prominent extravillous trophoblast and degenerative hydropic changes can easily be mistaken for molar disease (Figure 34.20).27,28 When the diagnosis is equivocal, positive immunohistochemical staining for p57kip2 will exclude complete mole.
Partial Hydatidiform Mole
Pathogenetic Mechanism
Partial moles differ from complete moles in that they are almost always triploid, having a 69,XXX, 69,XXY, or 69,XYY karyotype.31 In almost all cases, the additional chromosome set is paternally derived, or diandric.32 The most common mechanism is fertilization of an ovum by a diploid sperm or by two haploid sperm (Figure 34.7). However, only a portion of paternally derived triploid (diandric triploidy) placentas develop partial molar phenotype, indicating that the mere presence of two paternal haploid genomes is insufficient for molar development.33,34 Additionally, non-molar maternally derived triploidy (digynic triploids) may be accompanied by degenerative hydropic change but lack other histologic features of partial moles.32,35 Sometimes, a triploid placenta is associated with a grossly visible fetus,36 but most are digynic and thus not a partial mole32 or confined placental mosaicism with a diploid fetus. Thus, in the absence of pathognomonic histologic features, triploidy alone is not diagnostic of partial mole. This is especially the case with first trimester spontaneous abortions having degenerative hydropic change, as non-molar digynic triploidy is the most common form of triploidy in this subset of conceptuses.32 Occasionally, trisomies 2, 7, 15, 16, and 22 may share some features with partial mole, such as villous hydrops and trophoblastic proliferation.37 Tetraploid partial moles have also been reported and they usually have an excess of paternal genomes.38
Stay updated, free articles. Join our Telegram channel

Full access? Get Clinical Tree